The GWN7711(P) Series are Layer 2 lite managed network switches that enable small to medium-sized businesses to build scalable, secure, high-performance, intelligent business networks that are easy to use and manage. It supports VLAN for flexible and sophisticated traffic segmentation, QoS for prioritizing network traffic, IGMP snooping for optimizing network performance, and comprehensive security features against potential attacks. The PoE model provides intelligent dynamic PoE output to power IP phones, IP cameras, Wi-Fi access points, and other PoE endpoints, and the PoE model can support 24V DC passive PoE output mode. The GWN7711(P) Series is easy to manage and deploy, including the local web interface of the GWN7711(P) Series switch and GWN.Cloud. The desktop and wall-mount installation method is suitable for hotels, home offices, small-to-medium businesses, and other similar industries, making the GWN7711(P) Series the ideal managed network switch for small-to-medium businesses.
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Technical Specifications
GWN7711 | GWN7711P | |
Network Protocol | Network Protocol IPv4, IEEE 802.3i, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.3x, IEEE 802.1p, IEEE 802.3af, IEEE 802.3at | |
Gigabit Ethernet Ports | 8 | |
PoE Out Ports | / | 4 |
Power Supply | External 5VDC/0.6A | External 48-53.5VDC/1.22A |
PoE Output | / | Port 1-4 compliance with the 802.3af/at standard:
Port 1-4 can also switch to 24VDC Passive PoE-Out
|
Max Total PoE Output Power | / | 60W |
Maximum Output Power per | / | 30W |
Auxiliary Ports | 1x Reset Pinhole | |
Forwarding Mode | Store-and-forward | |
Total non-blocking throughput | 8Gbps | |
Switching Capability | 16Gbps | |
Jumbo Frame | 2K/3K/4K/5K/6K/7K/8//9K/12K/15K | |
Forwarding Rate | 11.9Mpps | |
MAC | 8K MAC address capacity | |
VLAN |
| |
LAG | 4 | |
Multicast | IGMP Snooping, Report Message Suppression | |
QoS |
| |
DHCP | DHCP client | |
Maintenance | Backup and restore, system reboot, factory reset, firmware upgrade, monitoring including port statistics, port mirroring, cable test and loop prevention, Ping watchdog | |
Security |
| |
Mounting | Desktop/Wall-mount | |
LED Indicators |
| |
Environmental |
| |
Dimensions (LxWxH) |
|
|
Enclosure | Plastic | Metal |
Weight | Unit: 0.17kg | Unit: 0.44kg |
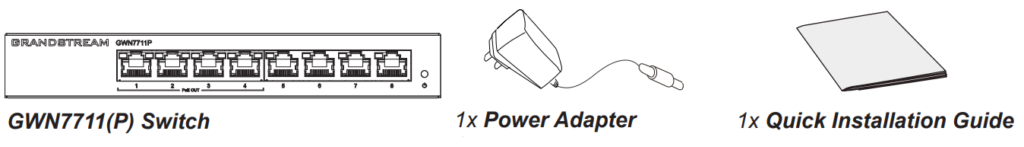
Package Content | 1x Switch, 1x QIG, 1x Power Adapter | |
Compliance | FCC, CE, RCM, IC | |
GWN7711(P) Technical Specifications
INSTALLATION
Before deploying and configuring the GWN7711(P) switch, the device needs to be properly powered up and connected to the network. This section describes detailed information on the installation, connection, and warranty policy of the GWN7711(P) switch.
Package Contents
GWN7711 Ports
GWN7711 | GWN7711P | |
Gigabit Ethernet Ports | 8 | |
PoE Out Ports | / | 4 |
PoE Output | / | Port 1-4 compliance with the 802.3af/at standard:
Port 1-4 can also switch to 24VDC Passive PoE-Out mode via WebUI:
|
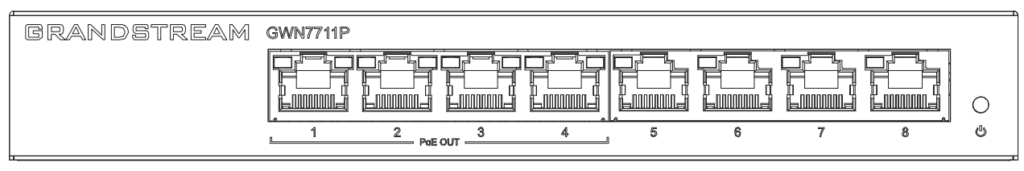
GWN7711(P) Ports
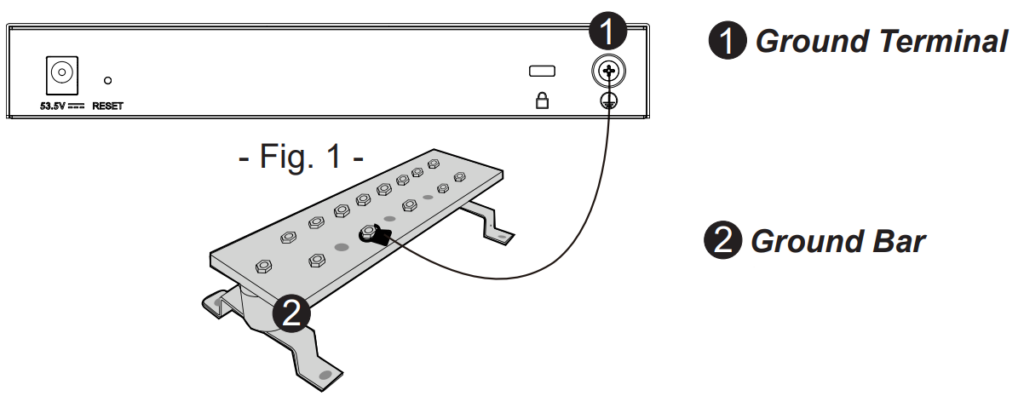
Grounding and Accessing GWN7711(P)
Grounding the GWN7711P Switch
- Remove the ground screw from the back of the switch, and connect one end of the ground cable to the wiring terminal of the switch.
- Put the ground screw back into the screw hole, and tighten it with a screwdriver.
- Connect the other end of the ground cable to the other device that has been grounded or directly to the terminal of the ground bar in the equipment room.
GETTING STARTED
LED Indicators
The front panel of the GWN7711(P) has LED indicators for power and interface activities, the table below describes the LED indicators’ status.
LED Indicator | Status | Description |
Power | Off | Power off. |
Solid green | Power on. | |
Link/Act | Off | No device is connected. |
Solid green | Port is connected and there is no activity. | |
Flashing green | Port is connected and data is transferring. | |
PoE LED (GWN7711P) | Off | Not providing PoE power. |
Solid yellow | Standard PoE normal power supply (connect PD to negotiate power | |
Flashing yellow | PoE power supply anomaly (Port Overload / 24V Throttling / PSE |
GWN7711(P) LED Indicators
Access and configure
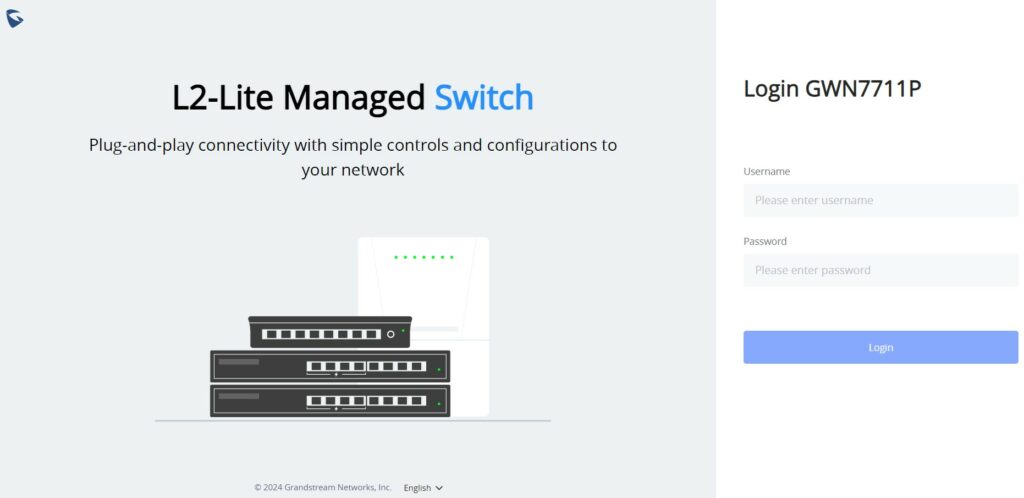
Login using the Web UI
- A PC uses a network cable to correctly connect any RJ45 port of the switch.
- Set the Ethernet (or local connection) IP address of the PC to 192.168.0.x (“x” is any value between 1-253), and the subnet mask to 255.255.255.0, so that it is in the same network segment with the switch IP address. If DHCP is used, this step could be skipped.
- Type the switch’s management IP address http:// in the browser, and enter username and password to log in. (The default administrator username is “admin” and the default random password can be found at the sticker on the GWN7711(P) switch).
Configure using GWN.Cloud/GWN Manager
Type https://www.gwn.cloud (https://<gwn_manager_IP> for GWN Manager) in the browser, and enter the account and password to log in to the cloud platform. If you don’t have an account, please register first or ask the administrator to assign one for you. To add GWN switch to GWN.Cloud/GWN manager refer to online documentation: https://documentation.grandstream.com.
WebUI Configuration
GWN7711(P) WebUI includes 9 main sections to configure and manage the switch and check the connection status.
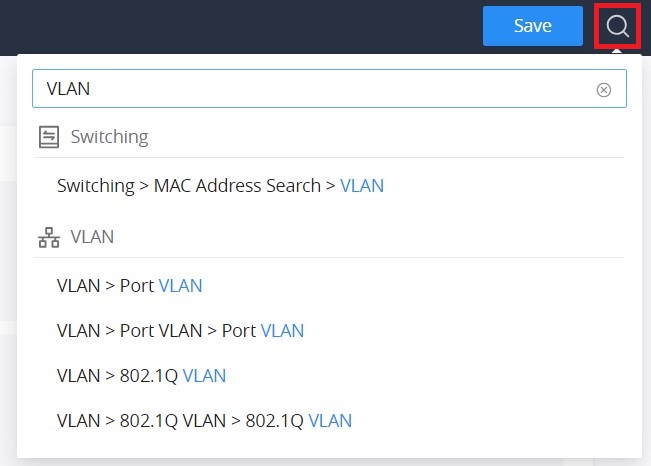
Search
GWN7711(P) Switches have search functionality to help the user find the right configuration, settings, parameters, etc.
On the top of the page, there is a search icon, the user can click on it and then enter the keyword relevant to his search, and then he will get all the possible locations of that keyword.
OVERVIEW
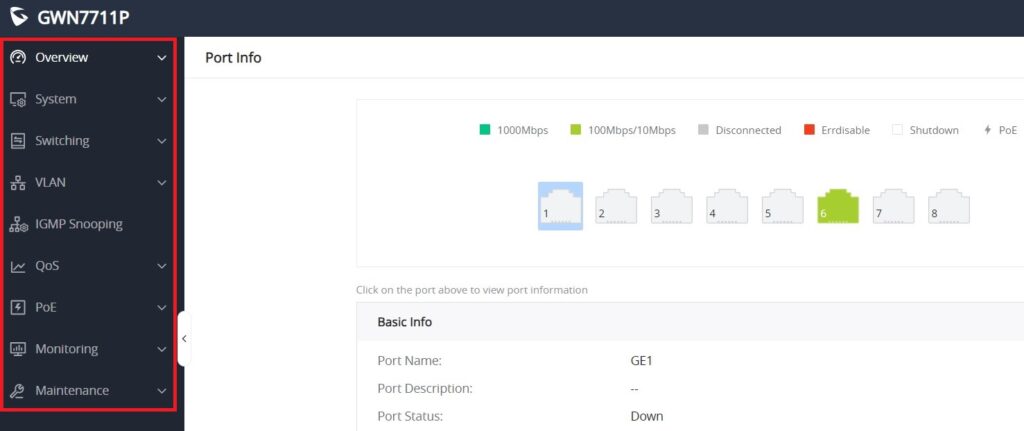
The overview is the first section that displays System information on the first page “System Info” and Port status on the second page “Port Info”. This section provides the user with a general and global view of the GWN7711(P) system and port status for easy monitoring.
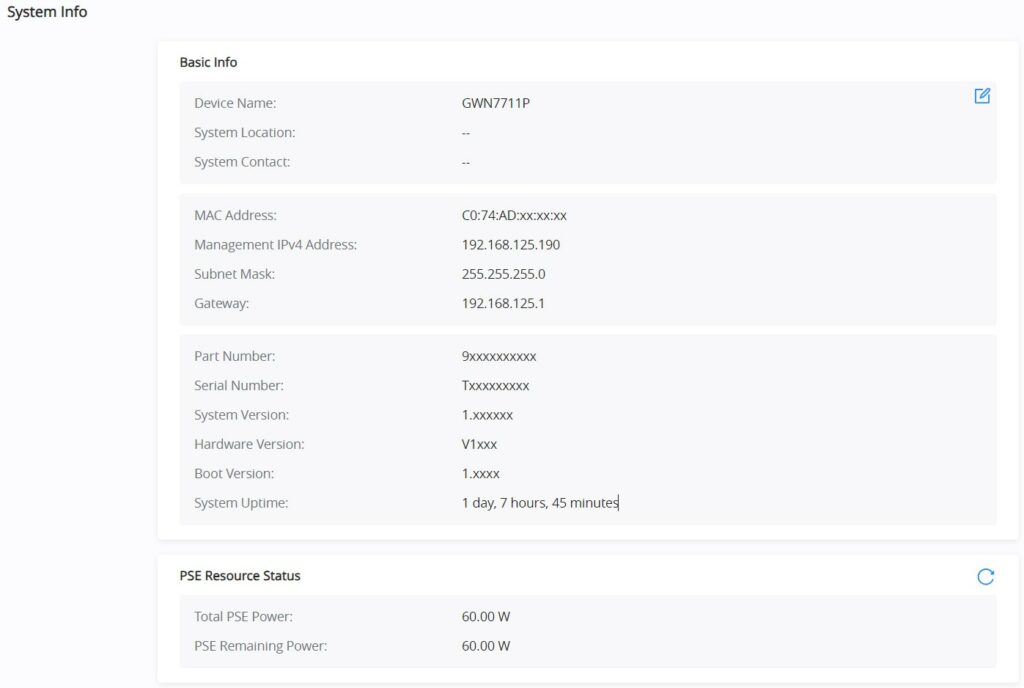
System Info
System Info is the first page after successfully logging into the GWN7711(P) Web Interface. It provides an overall view of the GWN7711(P) Switch information like, Device name, MAC Address, System Version, etc.
To name the device please click on
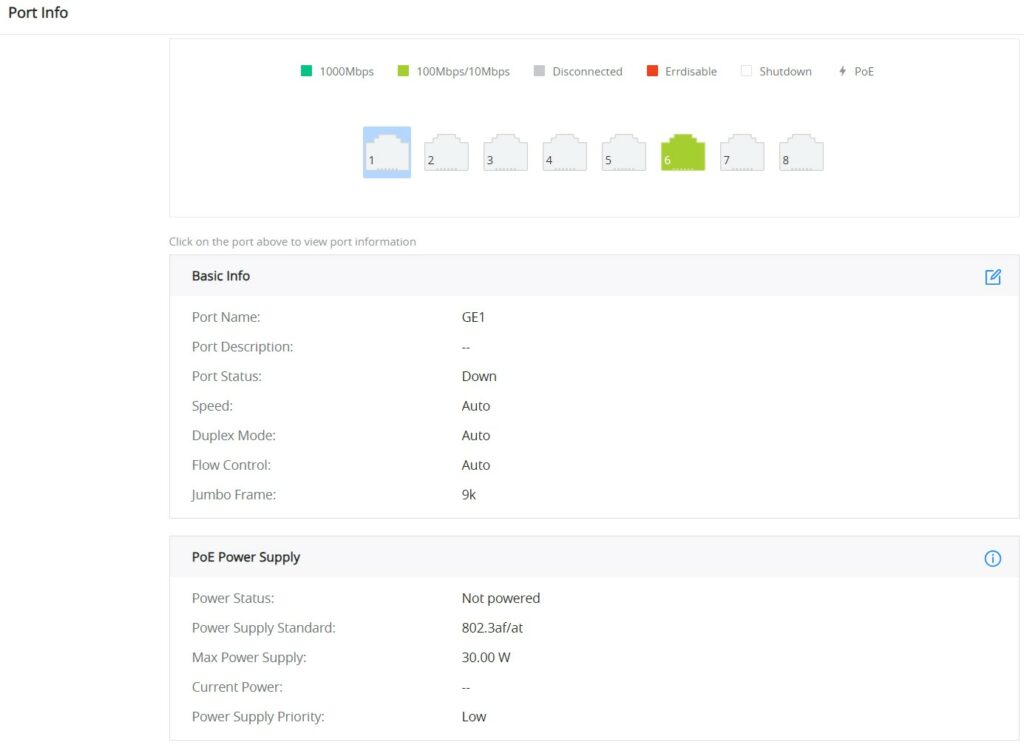
Port Info
This page displays the status for each port on the GWN7711(P) switches indicated by color code (green, red, grey, white, etc) and PoE symbol. Please refer to the figure below:
The following table explains the color code and the symbols used:
Ports Labels and Color code
Note: a PoE symbol and color code combination is also possible. Ex: 
There are 3 main sections for each port:
- Basic Info: displays info about the port name, speed, status etc.
Note: Click onto modify the port settings like Description, Speed, Duplex Mode, and Flow Control or to enable or disable the port.
- PoE Power Supply: displays PoE Current Power and priority, Status etc.
Note: Click on to change PoE settings.
SYSTEM
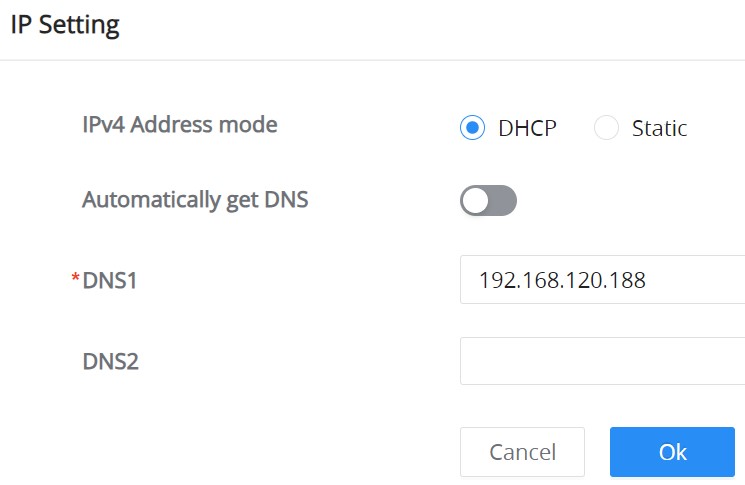
IP Setting
On this page, the user can either set a static IP for the switch or DHCP, If the DHCP is selected then the user can enter the preferred DNS or toggle the “Automatically get DNS” option ON for the DNS to be automatically set by the DHCP Server.
SWITCHING
The switching section covers Ports and LAG (Link Aggregation Group) configurations.
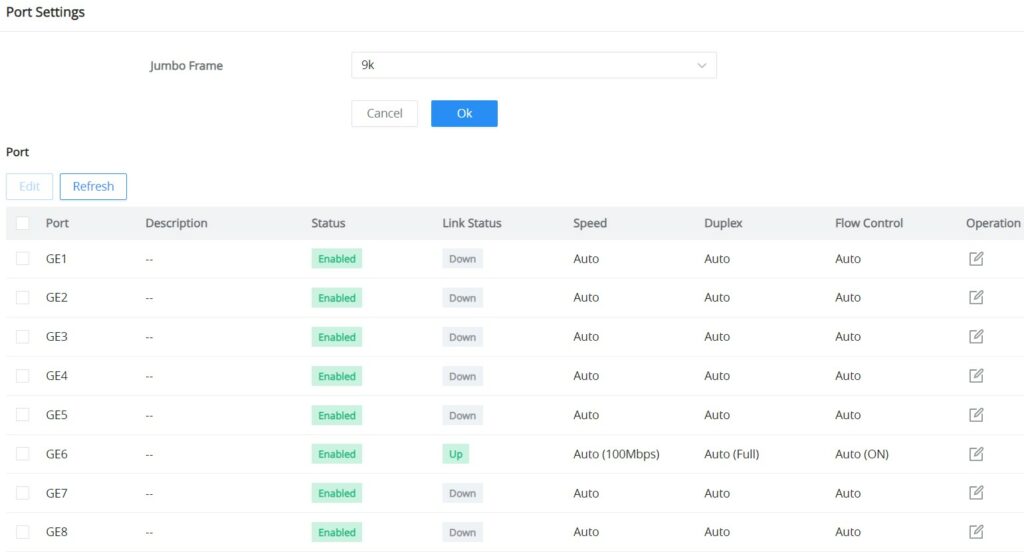
Port Settings
On this page, you can configure the basic parameters for GWN7711(P) Switch ports, like disabling or enabling the port, adding a Description, specifying the speed, Duplex mode, and Flow Control.
To configure a port, please navigate to Switching → Port Settings.
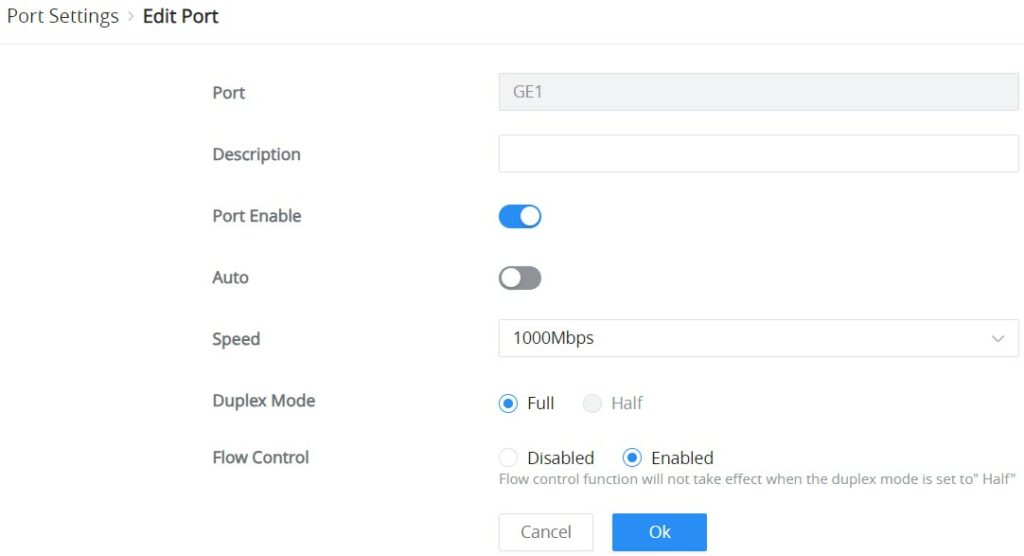
To configure a port, click on the “Edit” icon under the operation column.
Port | The selected Port to be configured. |
Description | It is used to configure the information description of this interface , which can be a description of usage, etc., with a maximum of 32 characters, and the characters limited to input are numbers 0-9 , letters az / AZ and special characters. |
Port Enable | Set whether to enable the interface. it is enabled by default. |
Auto | toggle ON or OFF Auto Detect, if it's ON the speed, Duplex Mode and Flow Control will be selected automatically, and if it's OFF the user can select speed, Duplex Mode and Flow Control manually. |
Speed | Set the rate of the interface:
|
Duplex Mode | Set the duplex mode of the interface. The options are {full-duplex, half-duplex}. The default is Duplex.
|
Flow Control | Set the flow control on the interface, the options are {Disabled, Enabled}. The default is Enabled. After enabling it, if the local device is congested, it will send a message to the peer device to notify the peer device to temporarily stop sending packets, after receiving the message, the peer device will temporarily stop sending packets to the local and vice versa. Thus, the occurrence of packet loss is avoided. |
Port Settings – Edit port
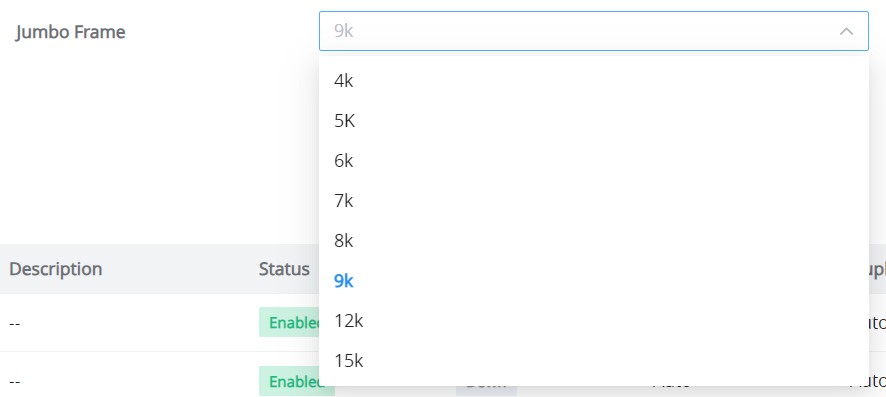
Jumbo Frame
The maximum Transmission Payload or MTU is typically 1500 bytes, in case the user requires even a bigger MTU length for a specific scenario, there is an option on the GWN7711(P) Switch to enable Jumbo Frame, the maximum Ethernet frame size ranges from 2K up to 15K. The default parameter is 9K.
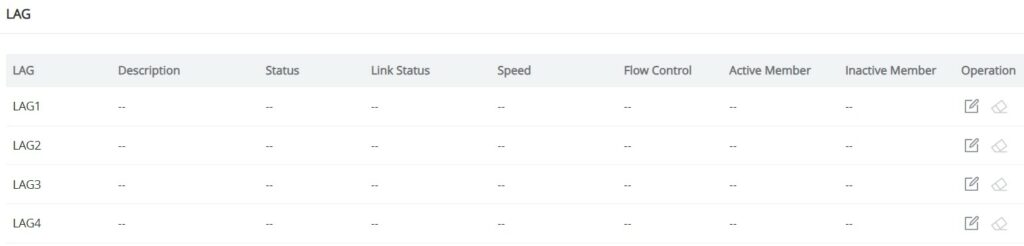
LAG
LAG means Link Aggregation Group which groups some physical ports to make a single high-bandwidth data path. Thus it can implement traffic load sharing among the member ports in a group to enhance the connection reliability.
To configure LAG, please navigate to Switching → LAG.
GWN7711(P) switches support up to 4 link aggregation groups as shown in the figure below:
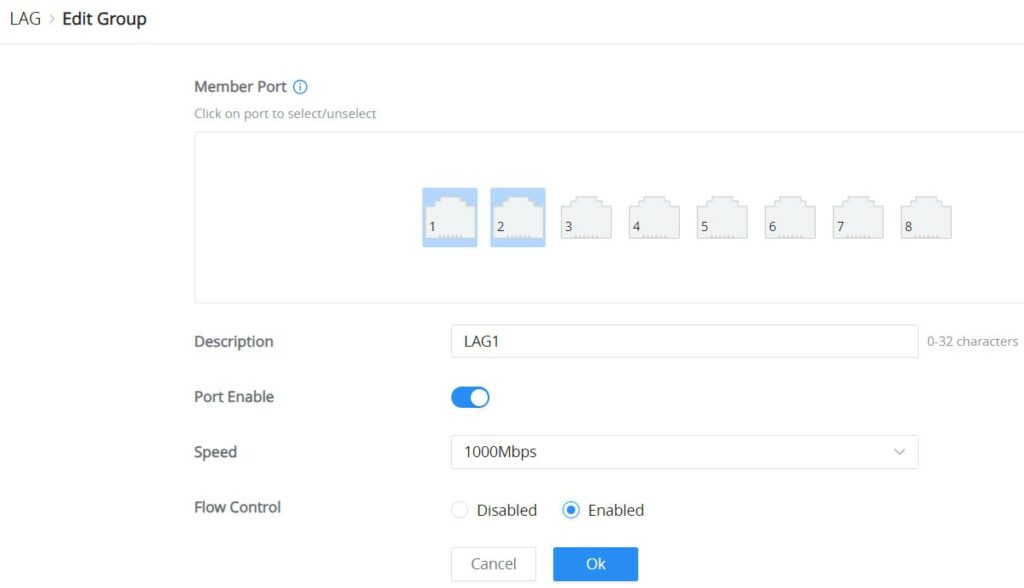
To edit/configure a LAG, click on the “Edit” icon under the operation column.
Member Port | Click on ports to be part of this LAG group. |
Description | It is used to configure the information description for this LAG , which can be a description of usage, etc., with a maximum of 32 characters, and the characters limited to input are numbers 0-9 , letters az / AZ and special characters. |
Port Enable | Set whether to enable the interface. it is enabled by default. |
Speed | Set the rate of the interface, the options are {10Mbps, 100Mbps, 1000Mbps}. The default is 1000Mbps. |
Flow Control | Set the flow control on the interface, the options are { Disabled, Enabled}. The default is Enabled. After enabling it, if the local device is congested, it will send a message to the peer device to notify the peer device to temporarily stop sending packets, after receiving the message, the peer device will temporarily stop sending packets to the local and vice versa. Thus, the occurrence of packet loss is avoided. |
Edit LAG
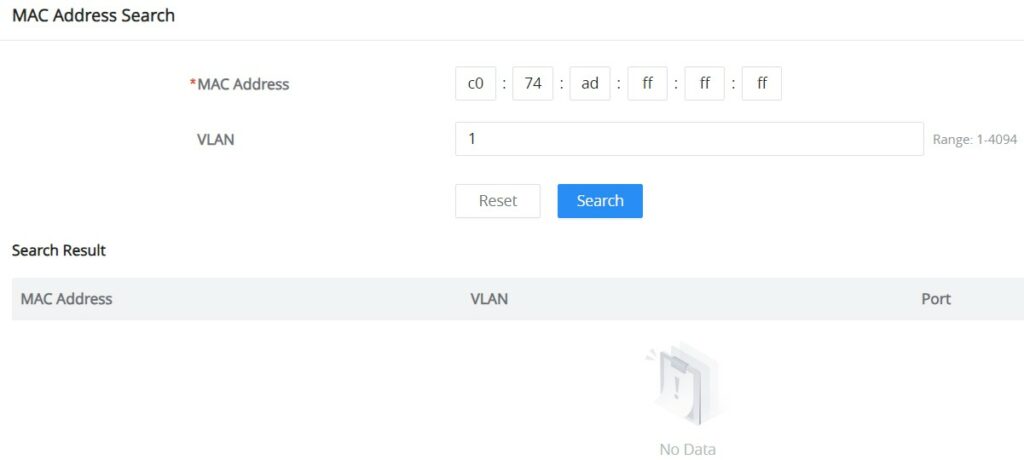
MAC Address Search
The MAC address table records the correspondence between the MAC addresses of other devices learned by the switch and the interfaces, as well as information such as the VLANs to which the interfaces belong. When forwarding a packet, the device queries the MAC address table according to the destination MAC address of the packet. If the MAC address table contains an entry corresponding to the destination MAC address of the packet, it directly forwards the packet through the outbound interface in the entry. If the MAC address table does not contain an entry corresponding to the destination MAC address of the packet, the device will use broadcast mode to forward the packet on all interfaces in the VLAN to which it belongs except the receiving interface.
On this page, the user can search using the MAC address and the VLAN, if the device MAC address is found, it will be displayed on the Search Result section.
VLAN
A virtual local area network, virtual LAN or VLAN, is a group of hosts with a common set of requirements that communicate as if they were attached to the same broadcast domain, regardless of their physical location. A VLAN has the same attributes as a physical local area network (LAN), but it allows for end stations to be grouped even if they are not located on the same network switch. VLAN membership can be configured through software instead of physically relocating devices or connections.
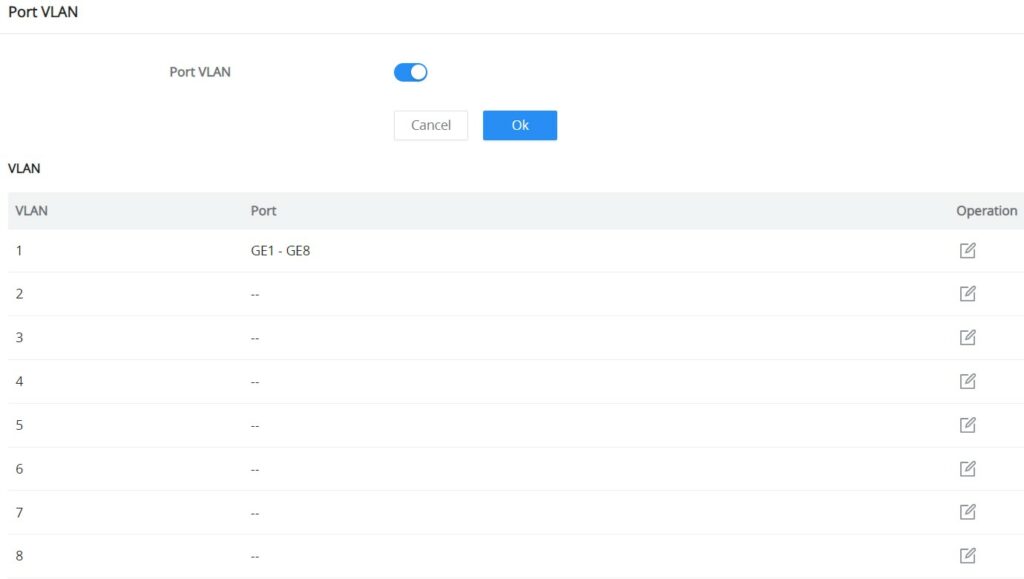
Port VLAN
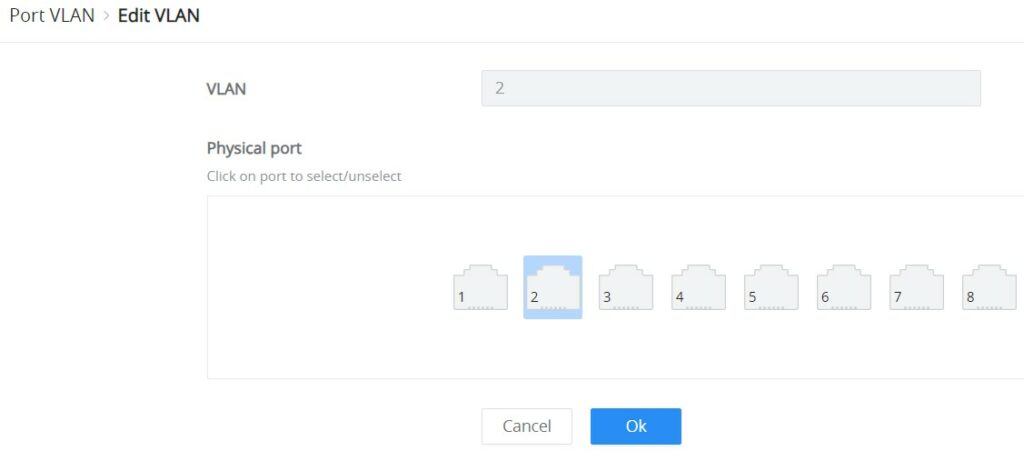
On this page, the user can select which VLANs (a preset from 1 to 8) can be allowed on GWN7711(P) ports. This is a simplified way to manage VLAN from 1 to 8. To have more flexibility and control, please enable 802.1Q VLAN and Port VLAN will be disabled automatically.
First Enable Port VLAN as shown below:
Click the “Edit” icon under the Operation column to edit a VLAN, then select which ports this VLAN will be allowed on.
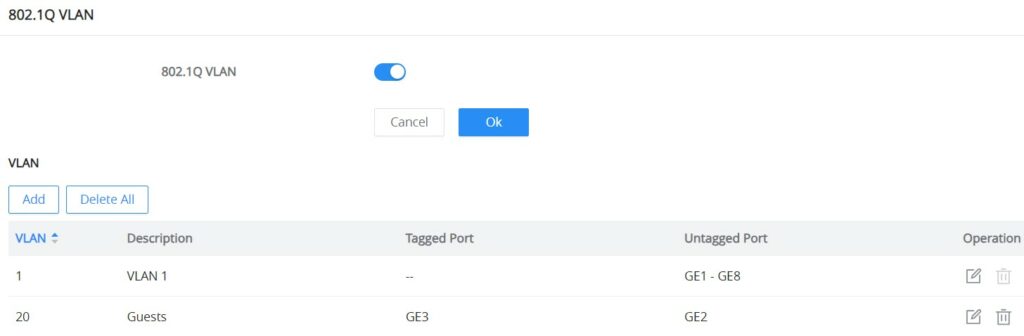
802.1Q VLAN
For more flexibility and control over VLAN configuration, the user can enable 802.1Q VLAN, and this case the user is not only restricted to VLANs from 1 to 8.
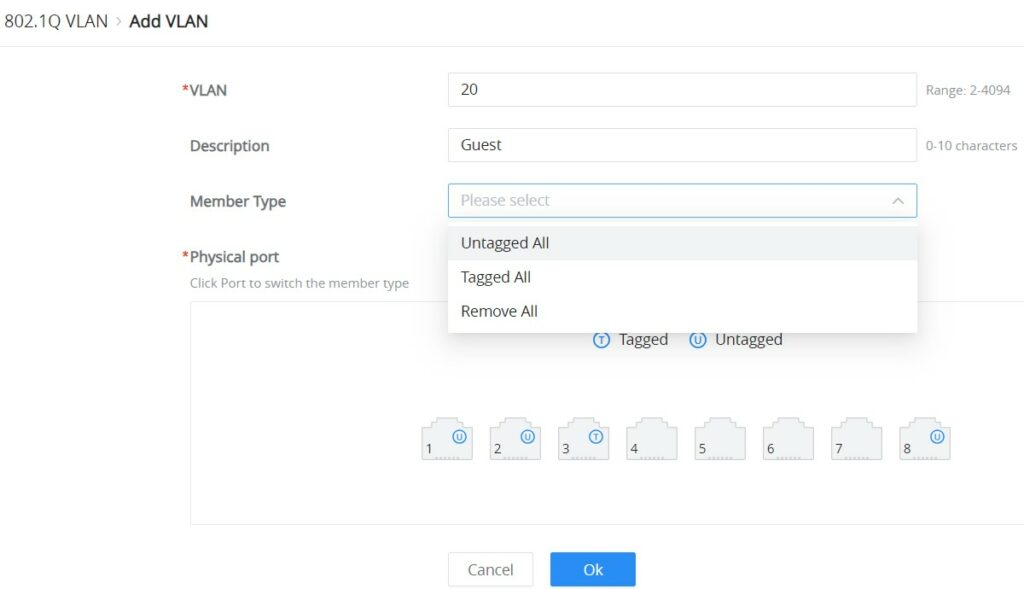
Click on the “Add” button to add a VLAN, as shown below:
On this screen, the user can configure the VLAN:
- VLAN: specify the VLAN ID (Range 2-4094).
- Description: enter a description for the VLAN.
- Member Type: a shortcut to untag/tag or remove all members.
- Physical port: select the tagged/untagged ports accordingly.
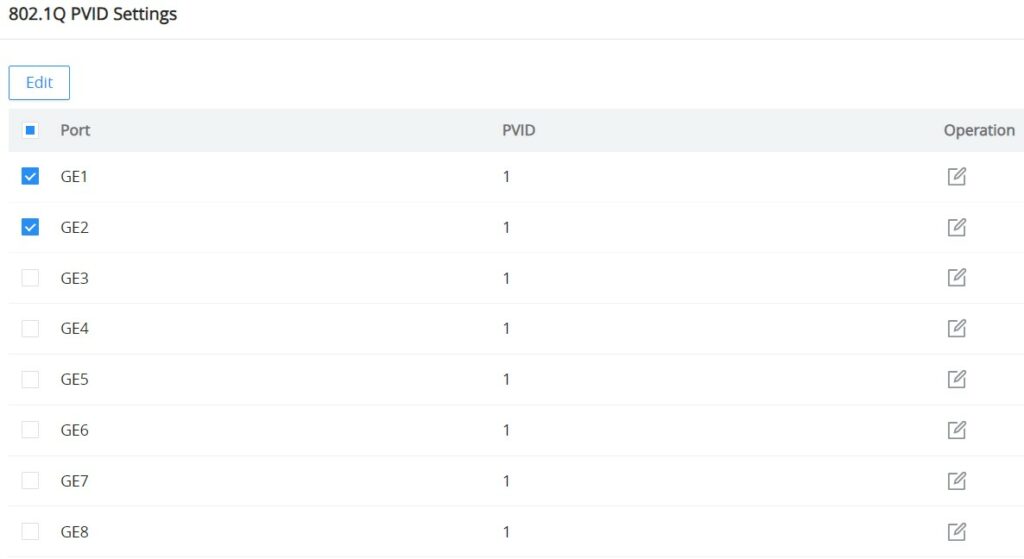
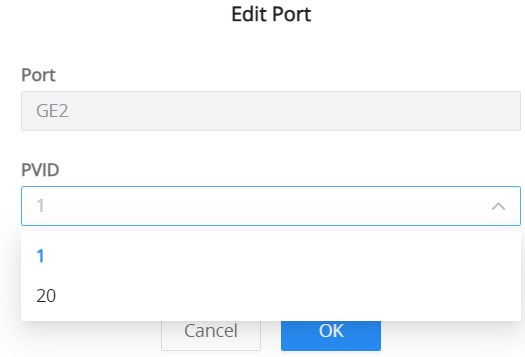
802.1Q PVID Settings
If the 802.1Q VLAN is enabled, the user can select the PVID (Port VLAN ID) or native VLAN when there is more than one VLAN on a port. Click on the “Edit” icon under operation to modify the PVID on a specific port.
Under PVID, select the VLAN from the drop-down list as shown below:
IGMP SNOOPING
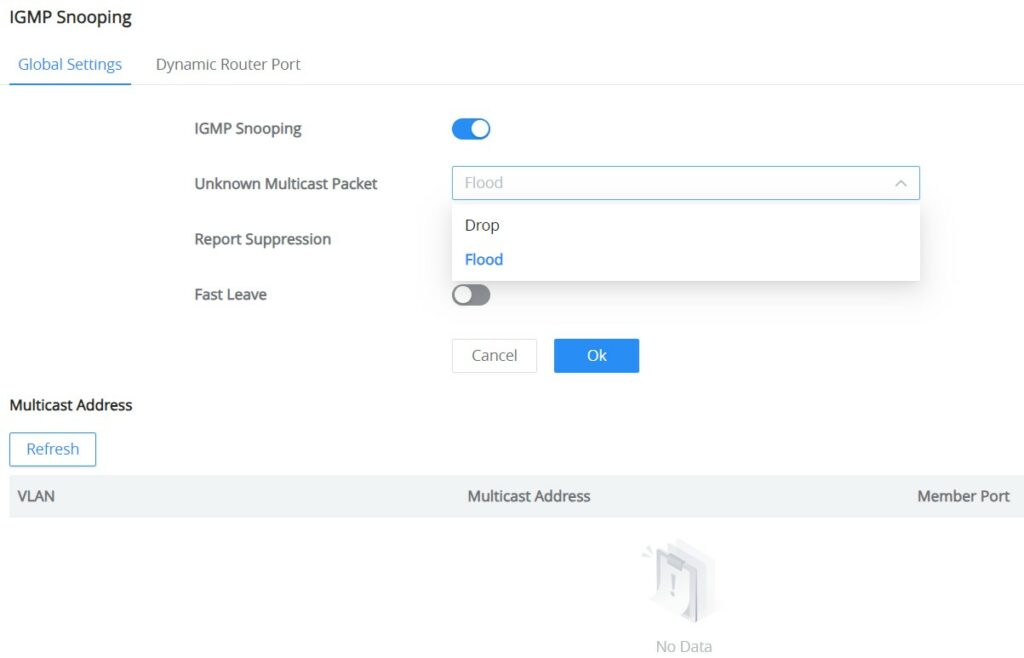
The GWN7711(P) switches support IGMP snooping, which is an IPv4 Layer 2 multicast protocol that optimizes the handling of multicast traffic in a network by intelligently forwarding traffic only to the ports where interested hosts are located, based on the monitoring of IGMP messages.
On the Global Settings tab, the users can enable the IGMP Snooping feature by toggling ON the feature, and for Unknown Multicast Packet will be either dropped or flooded as shown below:
IGMP snooping dynamically identifies router ports by monitoring IGMP General Query messages and optimizes the forwarding of multicast traffic to those ports for efficient use of network bandwidth.
The Dynamic Router Port tab displays all the discovered dynamic router ports, the users can click on the “Refresh” button to refresh the list.
QOS
The popularity of the network and the diversification of services have led to a surge in Internet traffic, resulting in network congestion, increased forwarding delay, and even packet loss in severe cases, resulting in reduced service quality or even unavailability. Therefore, to carry out these real-time services on the network, it is necessary to solve the problem of network congestion. The best way is to increase the bandwidth of the network, but considering the cost of operation and maintenance, this is not realistic. The most effective solution is to apply” Guaranteed ” policies to govern network traffic. QoS technology is developed under this background. QoS is quality of service, and its purpose is to provide end-to-end service quality assurance for various business needs. QoS is a tool for effectively utilizing network resources. It allows different traffic flows to compete for network resources unequally. Voice, video, and important data applications can be prioritized in network equipment.
QoS Basic Settings
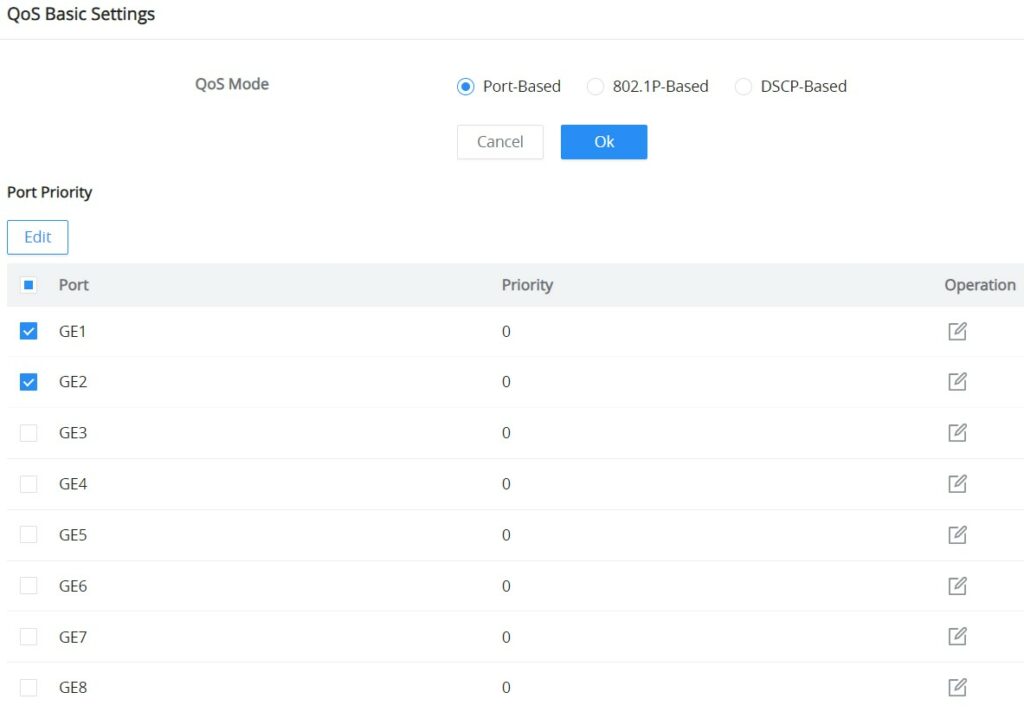
On this page, the user can edit the port priority for each port, supported modes are:
- Port-Based
- 802.1P-Based
- DSCP-Based
Please navigate to QoS → QoS Basic Settings page:
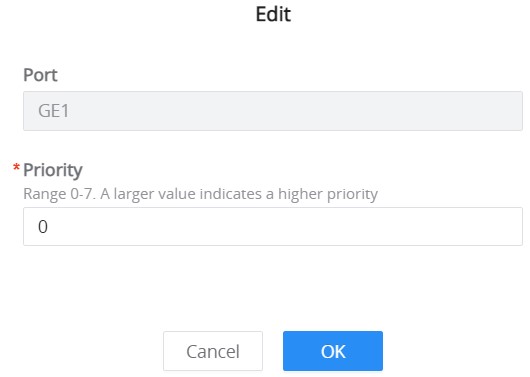
Select one or multiple ports, then click on the “Edit” button to modify the ports’ priority. The priority range is from 0 to 7, a larger value indicates a higher priority, and value 0 is the default value.
Priority Mapping
Priority mapping is used to realize the conversion between the QoS priority carried in the packet and the internal priority of the device ( also known as the local priority, which is the priority used by the device to differentiate the service level of the packet ) so that the device provides the Differentiated QoS service quality. Users can use different QoS priority fields in different networks according to network planning.
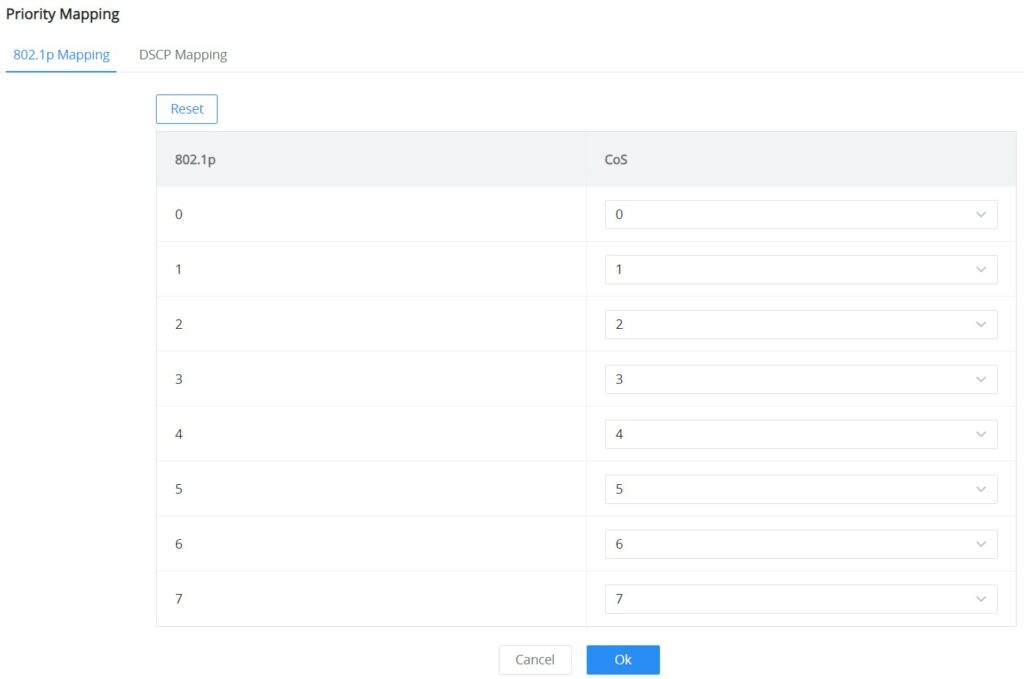
- 802.1p Mapping
On this tab, the user can map between 802.1p and CoS (Class of Service) where 0 is the lowest priority and 7 is the highest priority for 802.1p, and by default, CoS is set to be the same (it’s recommended to keep it by default only if necessary or a specific network requires it).
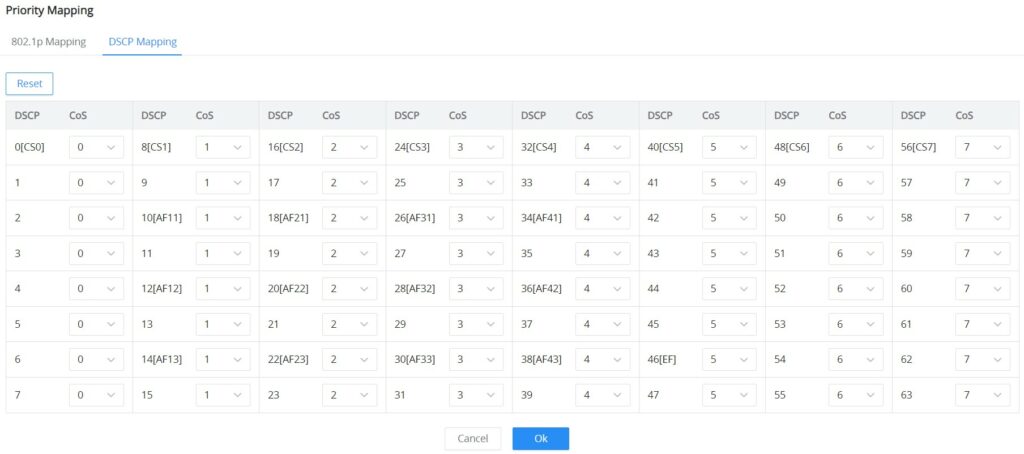
- DSCP Mapping
On this tab, the user can map between CoS and DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point), in this case, 802.1p and CoS mapping must be configured first. (it’s recommended to keep the default settings to keep the consistency between all switches only if it’s necessary or the network requires it)
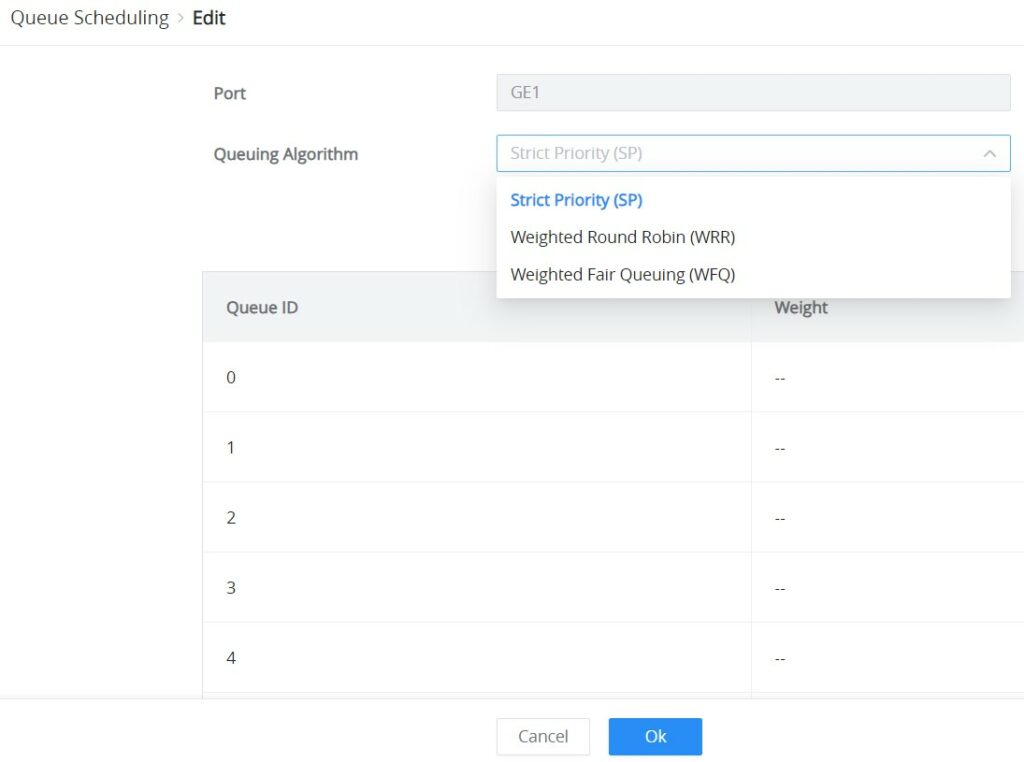
Queue Scheduling
When congestion occurs in the network, the device will determine the processing order of forwarding packets according to the specified scheduling policy, so that high-priority packets are preferentially scheduled.
Queue scheduling algorithm: queue scheduling according to the switch interface.
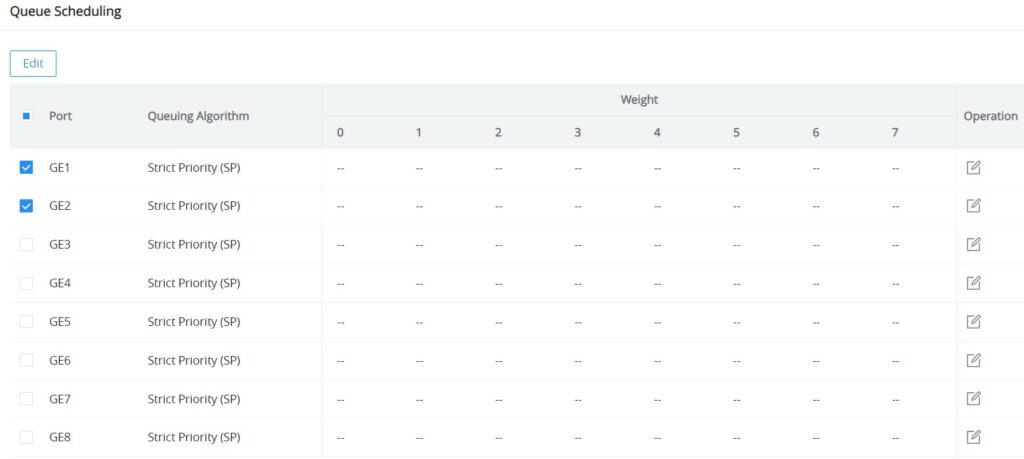
- Strict priority (SP) scheduling: The flow with the highest priority is served first, and the flow with the second highest priority is served until there is no flow at that priority. Each interface of the switch supports 8 queues ( queues 0-7 ), queue 7 is the highest priority queue, and queue 0 is the lowest priority queue. Disadvantage: When congestion occurs, if there are packets in the high-priority queue for a long time, the packets in the low-priority queue cannot be scheduled, and data cannot be transmitted.
- Weighted Round Robin (WRR) scheduling: each priority queue is allocated a certain bandwidth, and provides services for each priority queue according to the priority from high to low. When the high-priority queue has used up all the allocated bandwidth, it is automatically switched to the next priority queue to serve it.
- Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) scheduling: Based on ensuring fairness (bandwidth, delay) as much as possible, priority considerations are added, so that high-priority packets have more opportunities for priority scheduling than low-priority packets. WFQ can automatically classify flows by their “session” information (protocol type, source and destination IP addresses, source, and destination TCP or UDP ports, priority bits in the ToS field, etc.) Place each flow evenly into different queues, thus balancing the latency of the individual flows as a whole. When dequeuing, WFQ allocates the bandwidth that each flow should occupy at the egress according to the flow priority (Precedence). The smaller the priority value is, the less bandwidth is obtained; otherwise, the more bandwidth is obtained.
Select one or multiple ports, then click on the “Edit” button to modify the ports Queuing Algorithm. The default algorithm is set to Strict Priority (SP).
If Weighted Round Robin (WRR) or Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) is selected, the Weight option can be configured accordingly, the higher the Weight the higher the traffic priority.
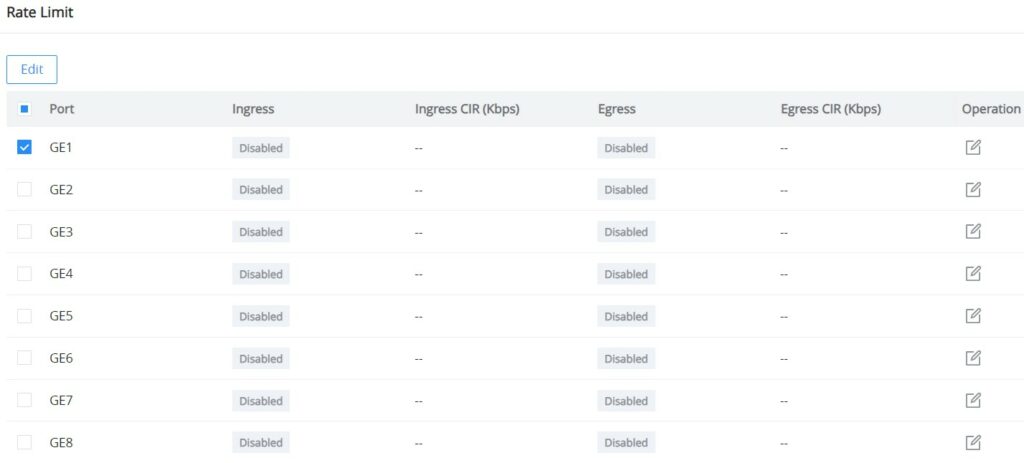
Rate Limit
Interface rate limit can limit the total rate of all packets sent or received on an interface. The interface rate limit also uses the token bucket to control the flow. If an interface rate limit is configured on an interface of the device, all packets sent through this interface must first be processed through the token bucket of the interface rate limiter. If there are enough tokens in the token bucket, the packet can be sent; otherwise, the packet will be discarded or cached.
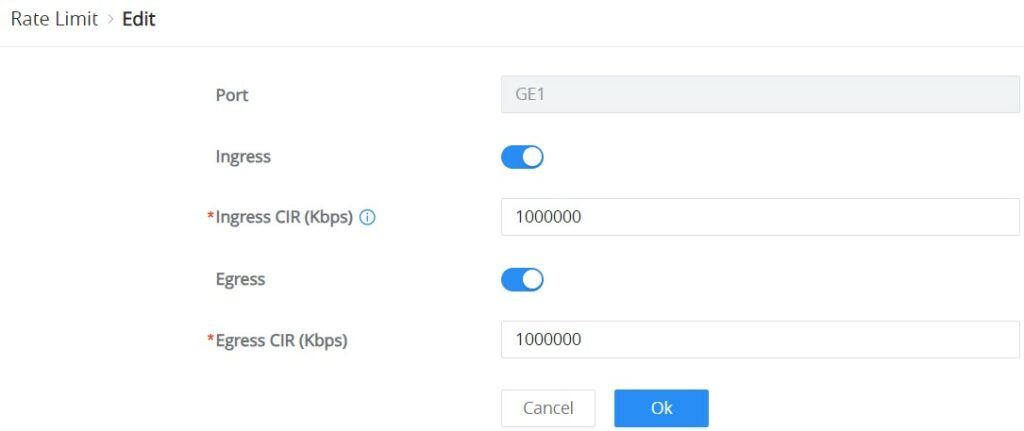
To configure Rate Limit, please navigate to QoS → Rate Limit, then select one or multiple ports, click on the “Edit” button to edit the port(s).
Enable the Ingress (incoming traffic to the switch) and then set the rate limit (in Kbps), and then enable Egress (outgoing traffic) and set the rate limit (in Kbps).
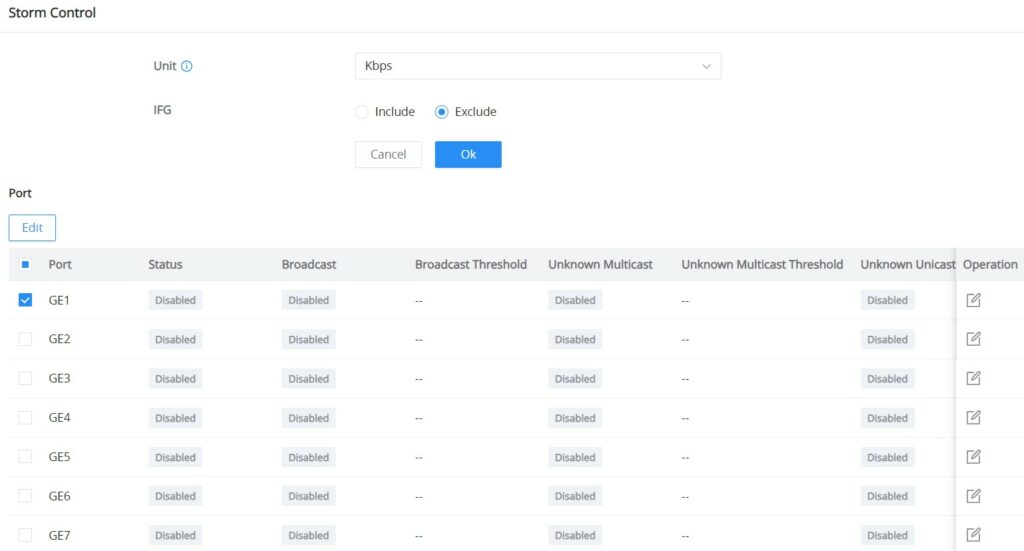
Storm Control
The GWN7711(P) switches support a storm control feature that prevents broadcast, unknown multicast, or unknown unicast by monitoring and limiting excessive traffic on a port. It helps prevent network congestion and performance problems caused by an overwhelming amount of packets. Thresholds are set to limit traffic when defined limits are exceeded.
Navigate to QoS → Storm Control, then select the unit that Storm Control will use:
- Kbps
- pps (packet per second)
Select one or multiple ports then click on the “Edit” button or icon under column operation to edit the selected port(s). Please refer to the figure and table below:
Unit | Select Unit:
|
IFG | Select IFG (Inter Frame Gap):
|
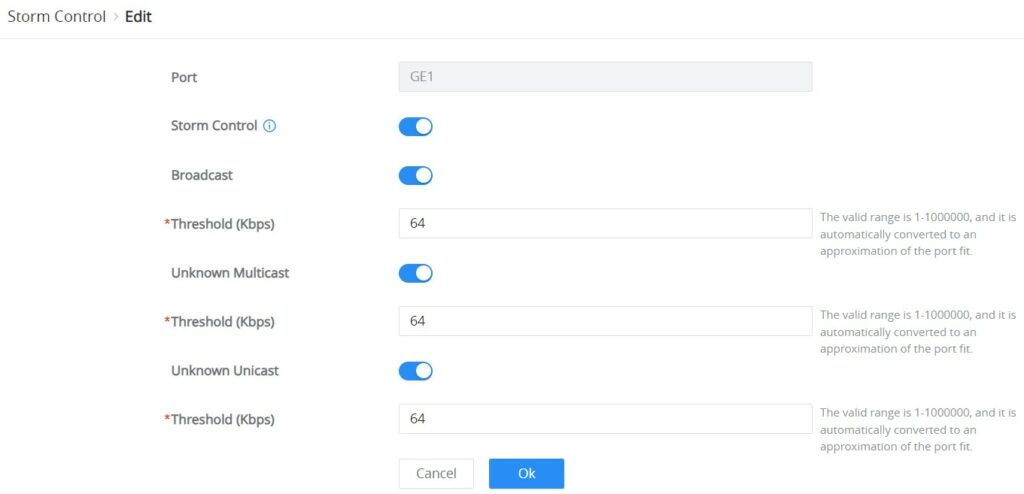
Storm Control → Edit | |
Port | Displays the selected port. |
Storm Control | Select whether to enable Storm Control on the selected port or not. |
Broadcast | Set whether to enable the storm threshold setting for broadcast packets. If Enabled Please enter a Treshhold (Kbps). Note: The valid range is 1-1000000, and it is automatically converted to an approximation of the port fit. |
Unknown Multicast | Set whether to enable the storm threshold setting for the Unknown Multicast packets If Enabled Please enter a Treshhold (Kbps). Note: The valid range is 1-1000000, and it is automatically converted to an approximation of the port fit. |
Unknown Unicast | Set whether to enable the storm threshold setting for the Unknown Unicast packets. If Enabled Please enter a Treshhold (Kbps). Note: The valid range is 1-1000000, and it is automatically converted to an approximation of the port fit. |
Storm Control
POE
Power Over Ethernet (PoE) refers to supplying power over an Ethernet network, also known as a local area network-based power supply system PoL or Active Ethernet.
Usually, the terminal devices of the access point need to use a DC power supply, but due to insufficient wiring, these devices need unified power management. At this time, the switch interface provides the power supply function, which can solve the above problems and realize the precise control of the port PoE power supply.
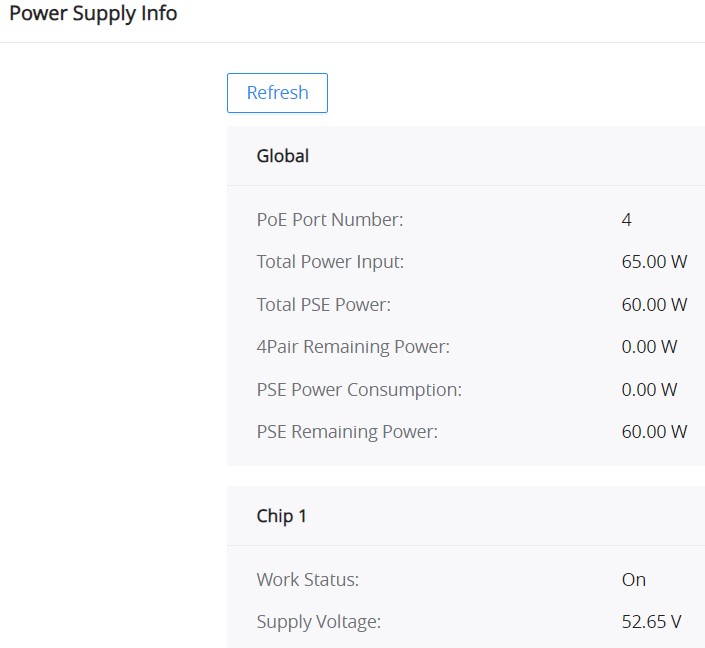
Power Supply Info
This page Displays the Power Supply Info like the number of PoE, Total, Remaining PoE Power, etc, and even the Supply Voltage.
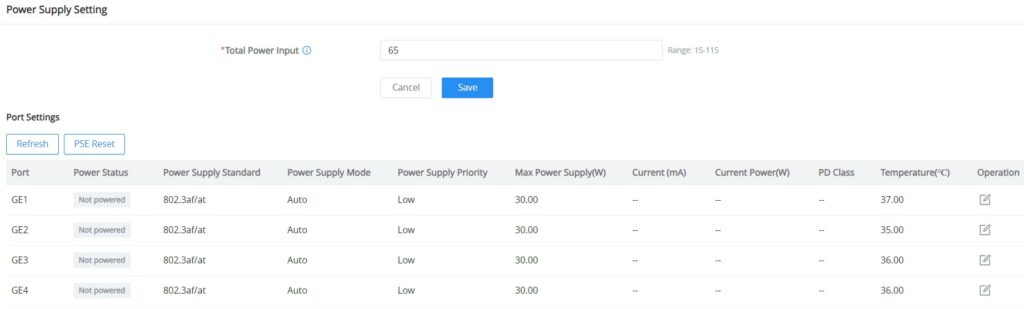
Power Supply Setting
On this page, the user can configure the total power input and configure PoE on each port that supports PoE. On the GWN7711P switch model, the ports 1-4 support PoE/PoE+.
Total Power Input: Configure proper power based on the selected power supply.
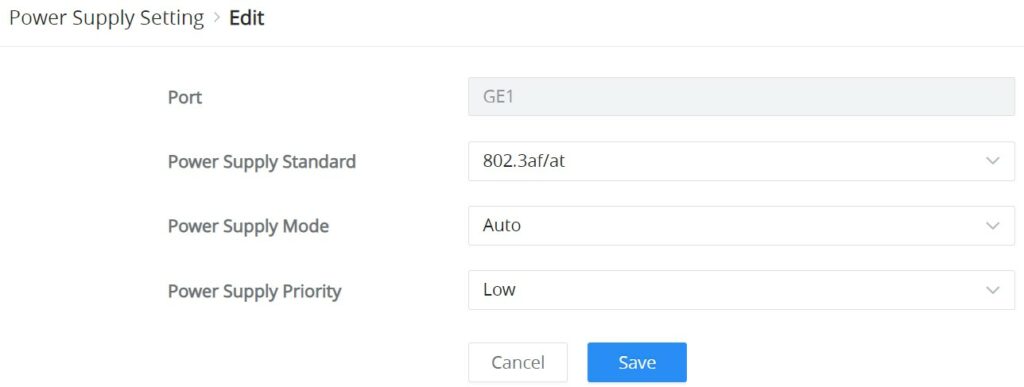
To edit the PoE parameters on the supported port, click on the “Edit icon” under the operation column, then select from the drop-down lists the power supply standard, power supply mode, and power supply priority.
MONITORING
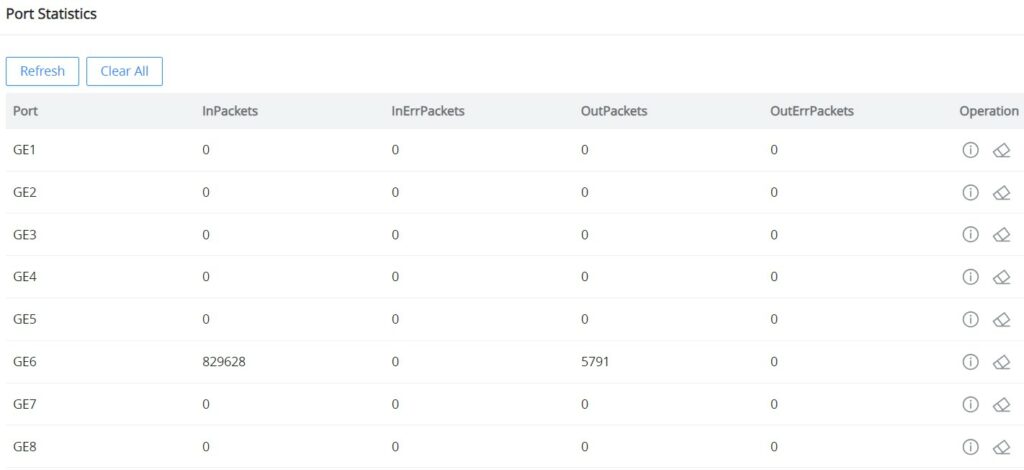
Port Statistics
For monitoring or even sometimes troubleshooting, the Flow Statistics displays in real time the flow of data with different units like Octects, Packets, Transmission Rate, and OutErrPackets.
To refresh the statistics, click on the “Refresh” button, and to clear all the statistics click on the “Clear All” button.
To clear the data for a specific port click on the “clear icon” under the operation column.
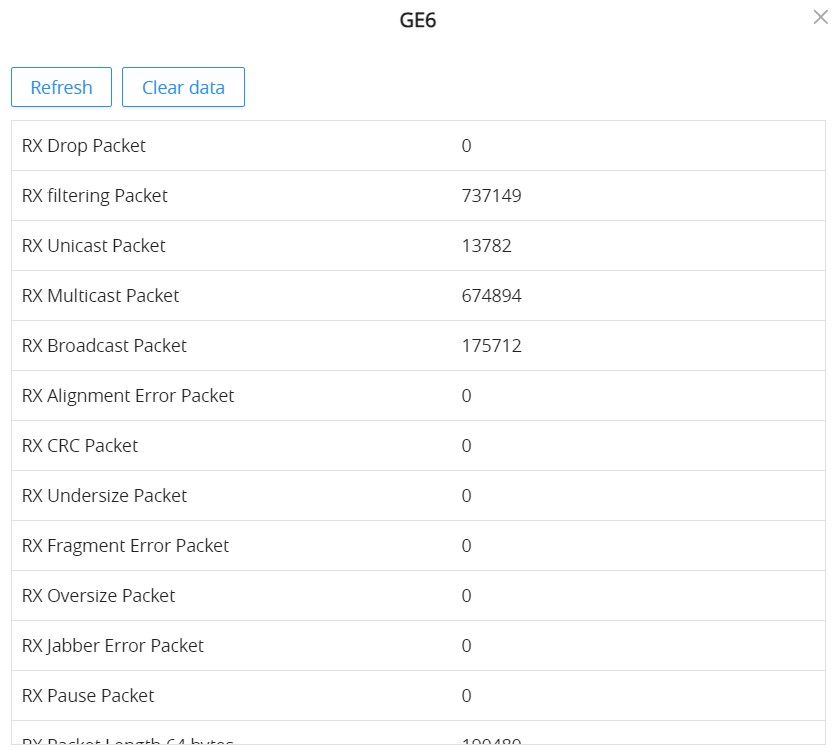
For more details, click on the “Exclamation mark icon” under the operation column next to each port.
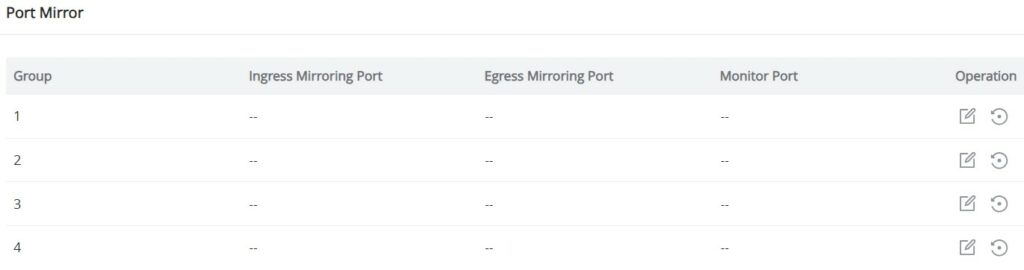
Port Mirror
Mirroring refers to copying the packets from the specified source to the destination port. The specified source is called the mirroring source, the destination port is called the observing port, and the copied packet is called the mirroring packet.
Mirroring can make a copy of the original packet without affecting the normal processing of the original packet by the device, and send it to the monitoring device through the observation port to determine whether the service running on the network is normal.
GWN7711(P) switch supports up to 4 groups, to configure/edit a group, click on the “Edit icon” under the operation column.
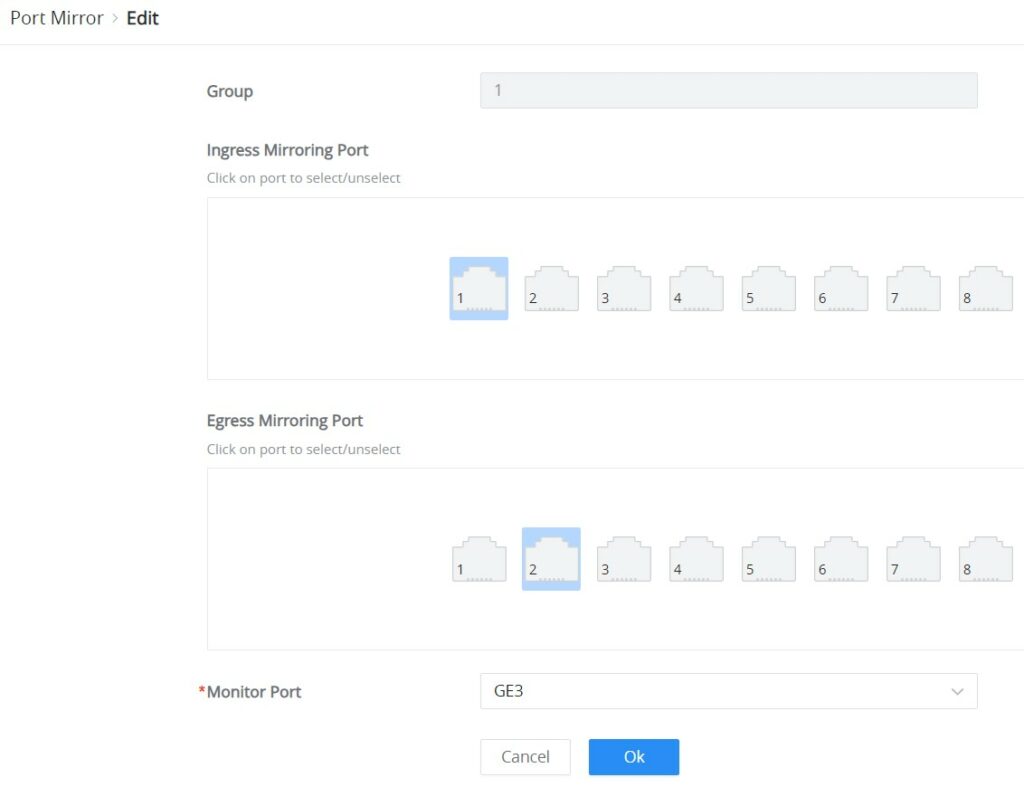
To start mirroring a port, first select the Ingress (incoming traffic to the switch) Mirroring port, then select the Egress (outgoing traffic) Mirroring port, and then select from the drop-down list the Monitor port (Monitor port cannot be the same as the Mirroring port), please refer to the figure below:
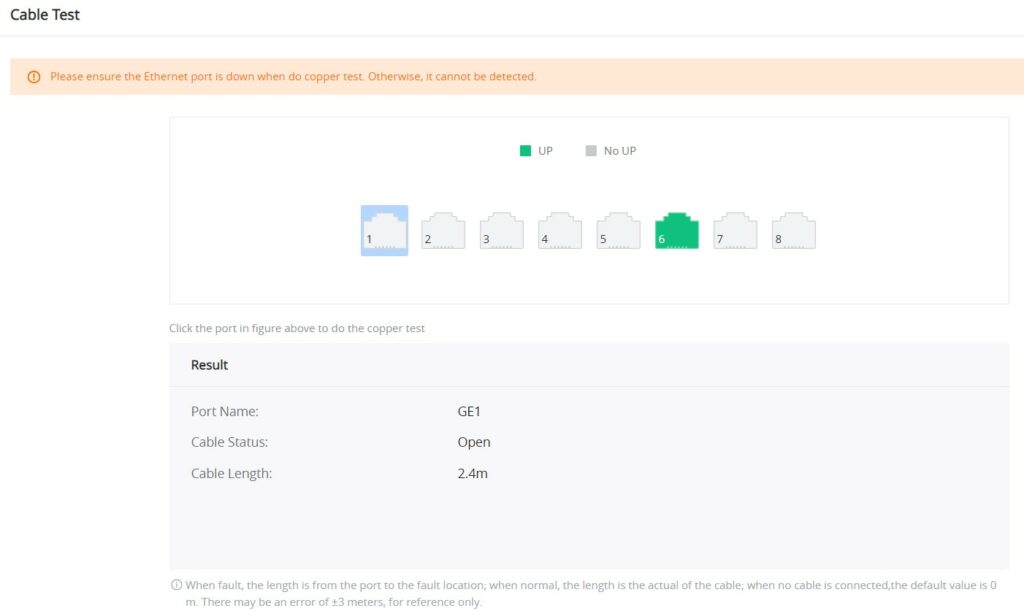
Cable Test
The Cable Test can detect whether the cable connected to the switch is faulty and the location of the fault. Using this function can assist in the daily engineering installation diagnosis.
Please navigate to Maintenance → Cable Test.
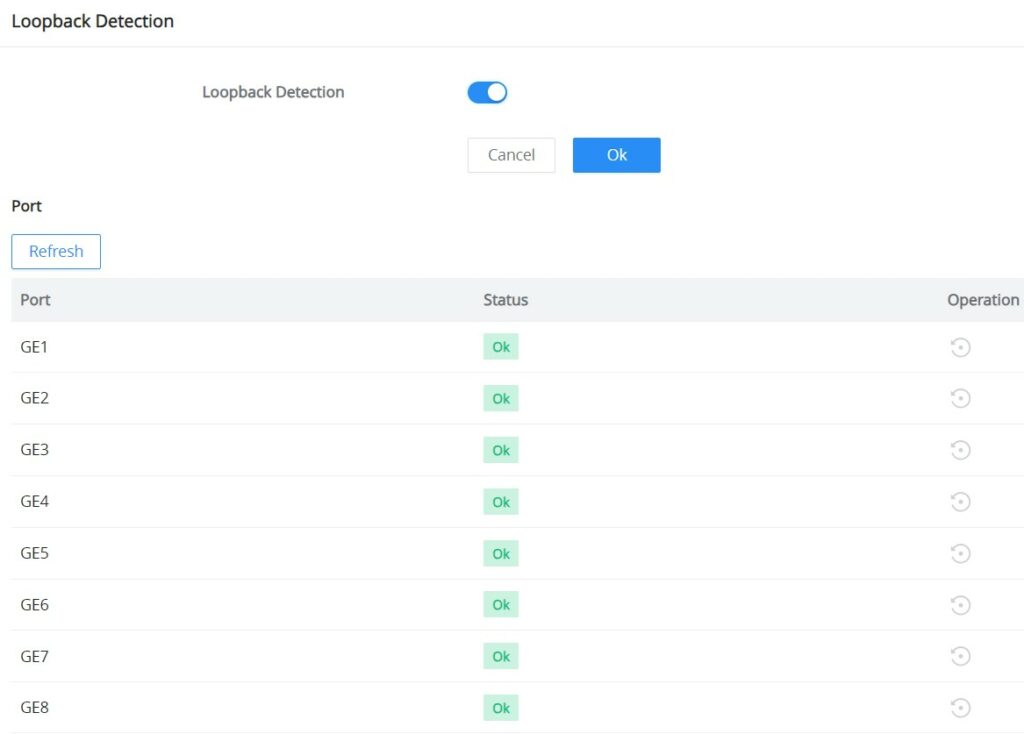
Loopback Detection
The GWN7711(P) switches support loopback detection, a feature commonly used in computer networking to identify and mitigate network loops that can cause broadcast storms and negatively impact network performance. Network loops occur when there is more than one path between switches on a network and data circulates endlessly, consuming network bandwidth and potentially causing network outages.
To enable loopback detection, toggle the feature by navigating to Monitoring → Loopback Detection.
MAINTENANCE
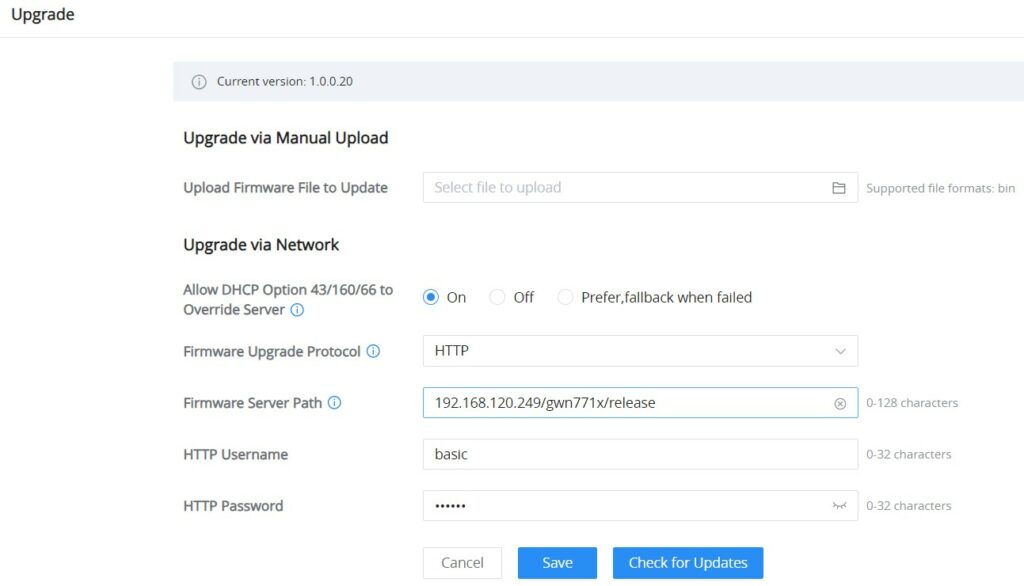
Upgrade
GWN7711(P) Switches support manual upload firmware upgrade via a BIN file that can downloaded from the Grandstream Firmware page: https://www.grandstream.com/support/firmware
Upgrade Via Network is also supported by specifying the Firmware Server Path (For example firmware.grandstream.com).
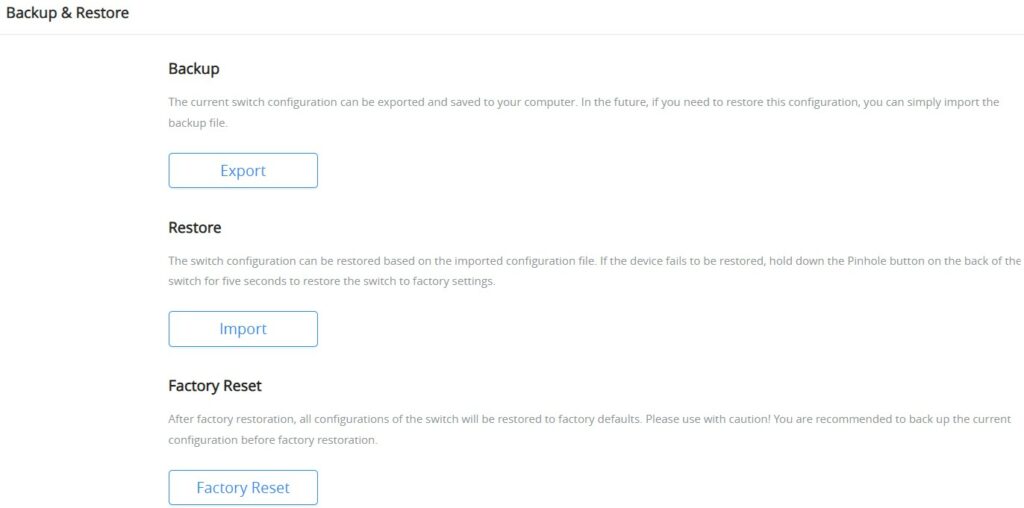
Backup & Restore
On this page, the user can back up the configuration, restore from a previously saved configuration file or factory reset the GWN7711(P).
- Backup: The current switch configuration can be exported and saved to your computer. In the future, if you need to restore this configuration, you can simply import the backup file.
- Restore: The switch configuration can be restored based on the imported configuration file. If the device fails to be restored, hold down the Pinhole button on the back of the switch for five seconds to restore the switch to factory settings.
- Factory Reset: After factory restoration, all configurations of the switch will be restored to factory defaults. Please use it with caution! You are recommended to back up the current configuration before factory restoration.
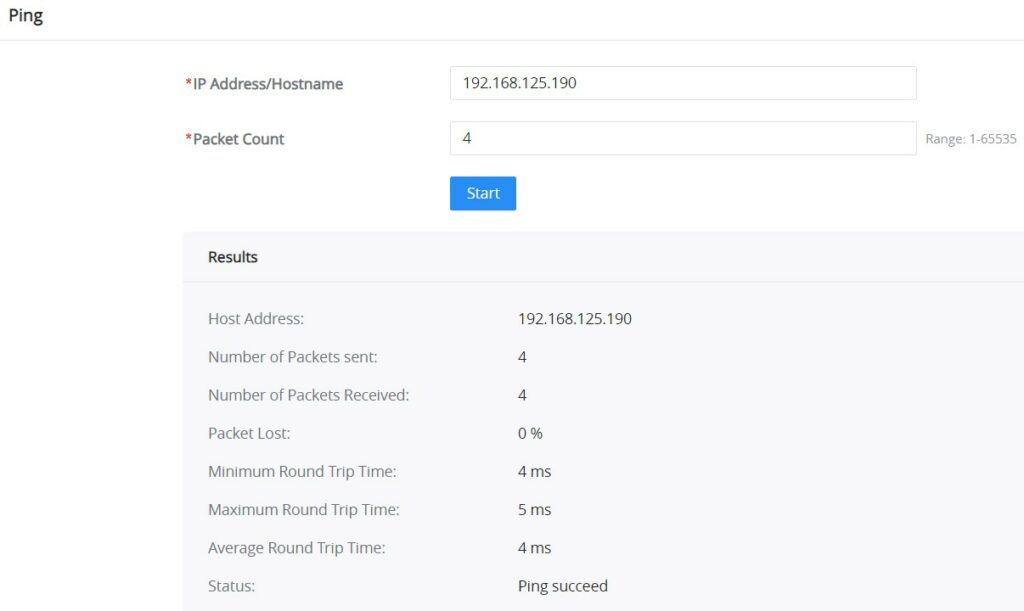
Ping
The user on this page can enter the IP Address or Hostname and then click “Start”, the results of the ping command will be shown below.
CHANGE LOG
This section documents significant changes from previous versions of the GWN7711(P) switches user manuals. Only major new features or major document updates are listed here. Minor updates for corrections or editing are not documented here.
Version 1.0.0.20
- This is the initial release.