OVERVIEW
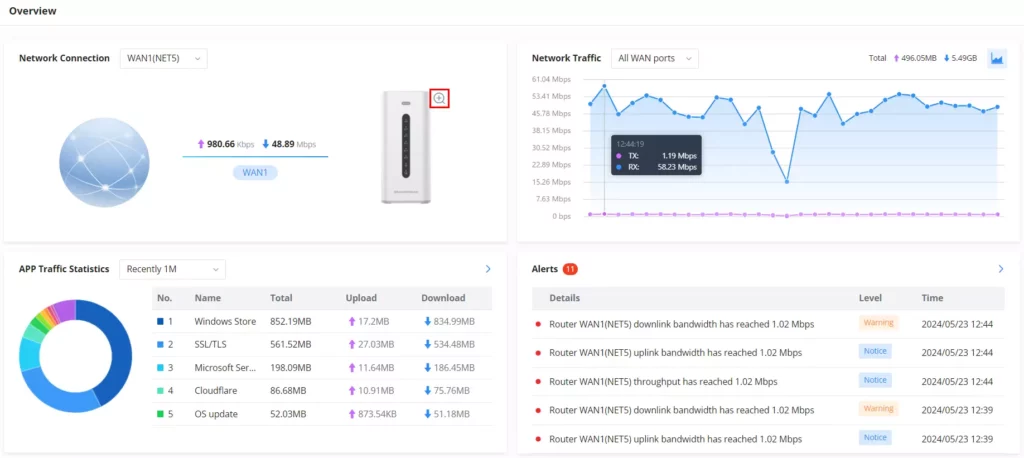
Overview Page
The overview page provides an overall view of the GCC601X(W)’s information presented in a Dashboard style for easy monitoring. Please refer to the figure and table below:
- Under Network Traffic and APP Traffic Statistics, the users can hover the mouse cursor over the graphs to display more details.
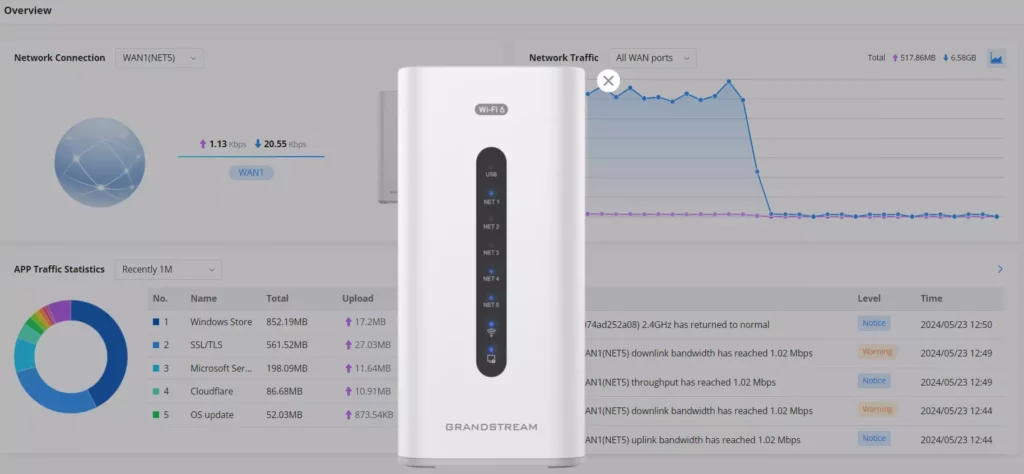
- Under Network Connection, the users can click on the “Zoom icon” to display a virtual GCC device with live LED indicators.
Network Connection | Displays the current state of the network connection for the selected WAN port and shows the current upload and download speed. Note: the user can select the WAN port from the drop-down list. |
Network Traffic | Shows network traffic in real time. Note: the user can select the WAN port from the drop-down list or select All WAN ports. |
Alerts | Shows Alerts General, Important or Emergency with details and time. |
APP Traffic Statistics | Displays traffic statistics based on apps usage (%). |
Overview page
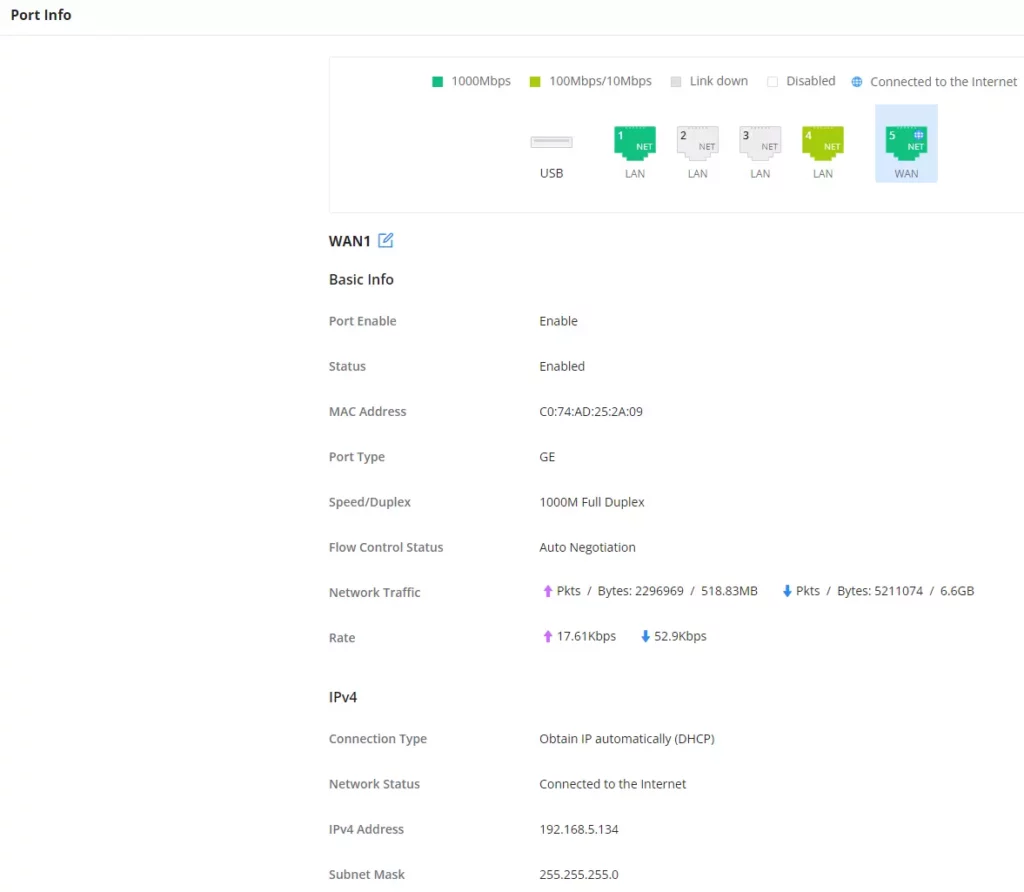
Port Info
The Port Info page displays an overview of all ports status including the USB Port, Gigabits ports, and SFP ports, indicating the links up with a green color and links down with a grey color, furthermore, the user can click on the port icon to get more info about the select link, refer to the figure below:
Navigate to Overview → Port Info:
NETWORK SETTINGS
Port Configuration
To access port configuration, please access the user interface of the GCC601X(W) and then navigate to Network Settings → Port Configuration.
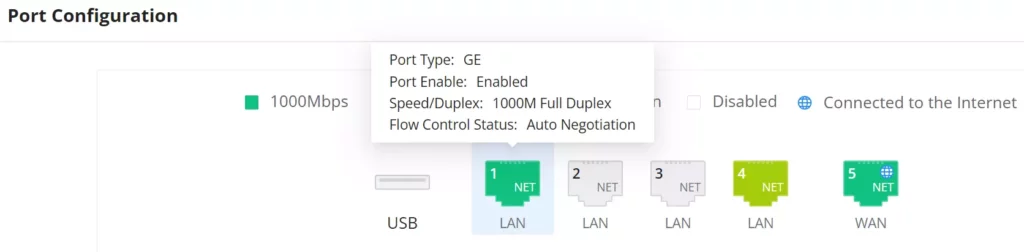
- Port Status
On the top, you can find the status of all the ports.
- Purple color: port speed is 2.5Gbps (works only with SFP ports and 2.5Gbps SFP module).
- Green color: port speed is 1Gbps.
- Light green color: port speed is 100Mbps/10Mbps.
- Grey color: link down.
- White color: port disabled.
- Internet icon: port connected to the internet (for WAN ports).
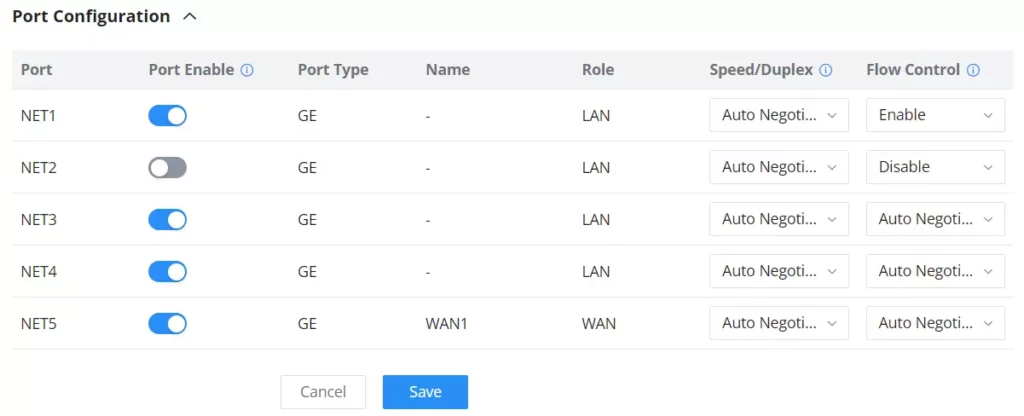
- Port Configuration
Port configuration page allows the user to configure the settings related to all the ports; this includes the gigabit Ethernet ports as well as the SFP ports. The settings that can be edited include flow control, speed and duplex mode.
Port | This field indicates the port number. |
Port enabled | Toggle ON or OFF the port. Note: When set to disabled, this physical port is disabled and all port-based configurations do not take effect. |
Port Type | This field indicates the port type.
|
Name | This indicates the port name. |
Role | This indicates the port role.
|
Speed/Duplex | In this setting, the user can configure the duplex mode as well as the speed of the port. When the mode is set to Auto Negotiation, the GCC device will determine based on the settings negotiated with the device connected. |
Flow Control | The user can enable or disable flow control using this option. Note: When the setting is set to Auto Negotiation, the GCC device will determine based on the settings negotiated with the device connected. |
Port configuration – part 2
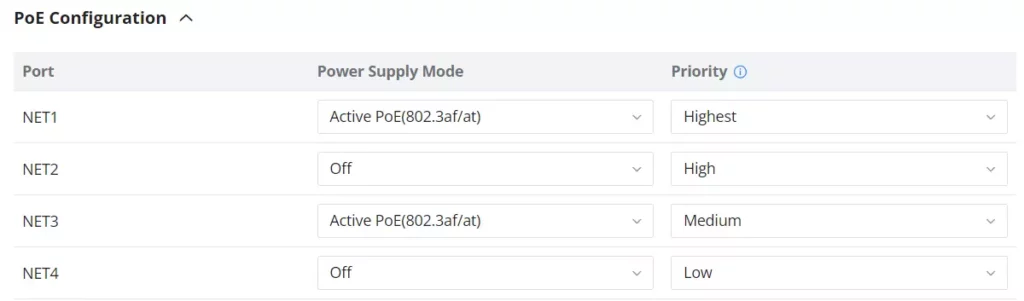
- PoE Configuration
The user can also control the power limit on each PoE port of the GCC601X(W).
Port | This field indicates the port number. |
Power Supply Mode | This option configures the power supply mode for the port, there are two options:
|
Priority | Specifies the priority of the port in terms of power supply. Options include: - Highest - High - Medium - Low Note: When setting the same priority, the power supply rules are as follows: |
Port configuration – PoE configuration
WAN
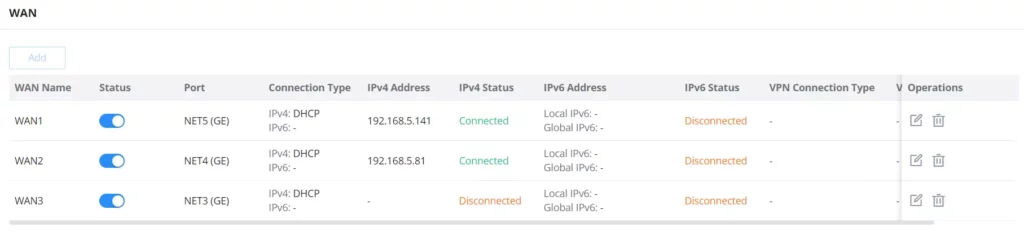
The WAN ports can be connected to a DSL modem or a router. WAN port support also sets up static IPv4/IPv6 addresses and configures PPPoE.
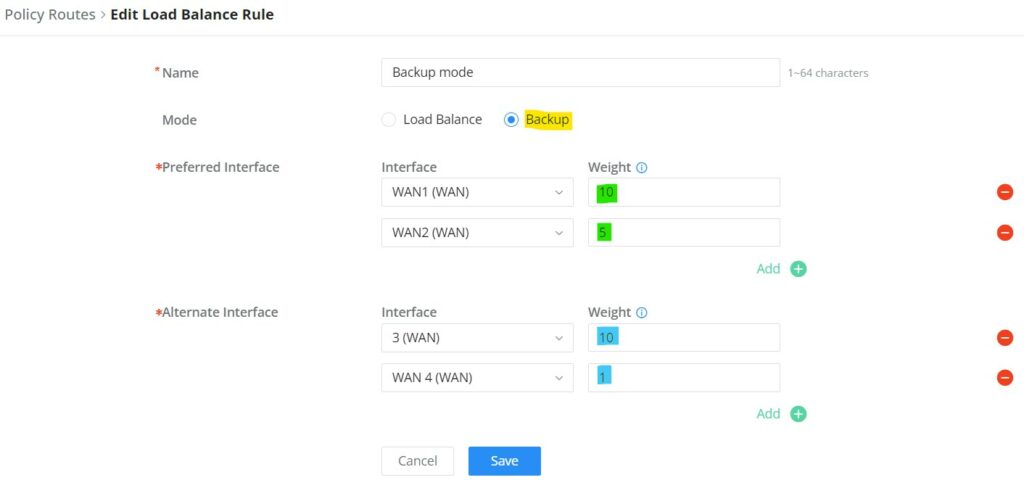
On this page, the user can modify the setting for each WAN port and also can delete or even add another WAN, Adding a WAN port will reduce the LAN ports number. In the case where there is more than one WAN port, load balancing or backup (Failover) can be configured between multiple WAN ports.
Click on to add another WAN port or click on the “edit icon” to edit the previously created ones.
Please refer to the following table for network configuration parameters on the WAN port.
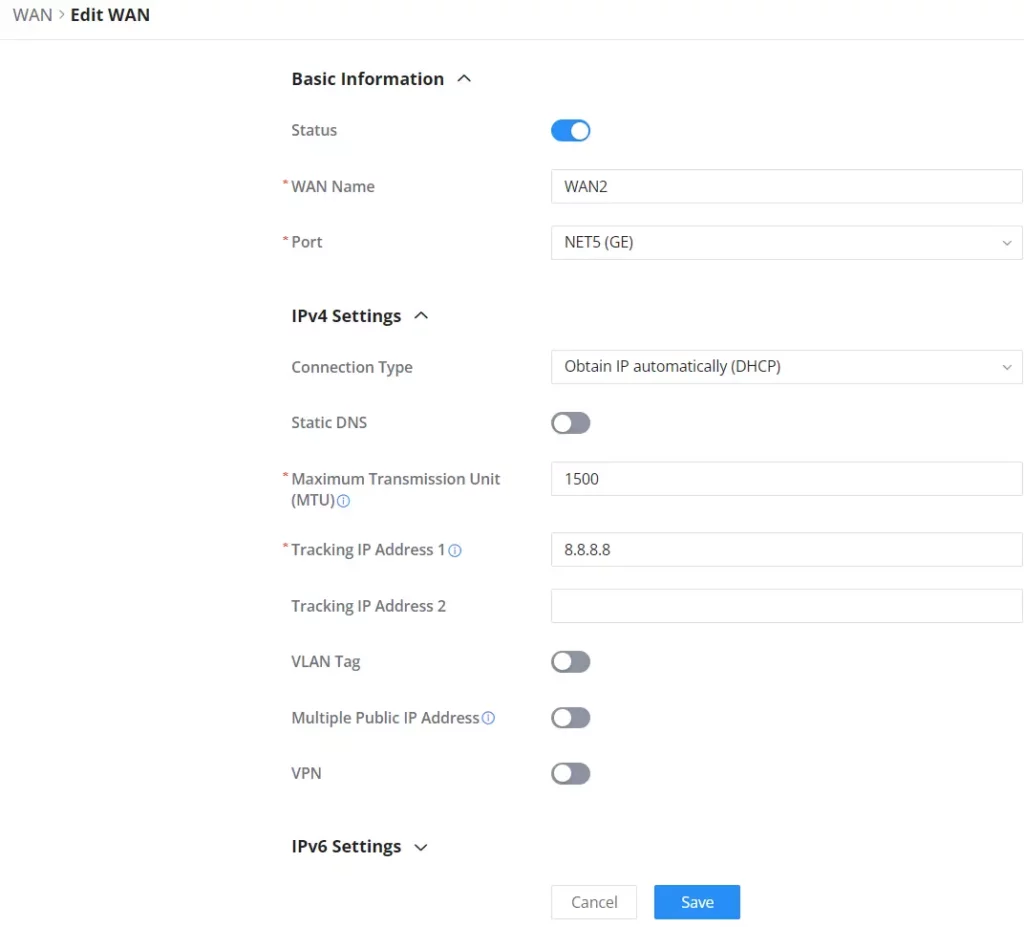
Basic Information | |
Status | Click to enable or disable the WAN |
WAN Name | Enter a name for the WAN port |
Port | Select from the drop-down list the port to be used as a WAN |
IPv4 Settings | |
Connection Type |
The default setting is “Obtain IP automatically (DHCP)”. |
Static DNS | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable static DNS |
Preferred DNS Server | Enter the preferred DNS Server, ex: 8.8.8.8 |
Alternative DNS Server | Enter the altenative DNS Server, ex: 1.1.1.1 |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | Configures the maximum transmission unit allowed on the wan port.
|
Tracking IP Address 1 | Configures tracking IP address of WAN port to determine whether the WAN port network is normal. |
Tracking IP Address 2 | Add another alternative address for Tracking IP Address |
VLAN Tag | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable VLAN Tag |
VLAN Tag ID | Enter the VLAN Tag ID with the priority Note: priority is 0~7 with 7 being the highest priority. Default is 0. |
Multiple Public IP Address | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable Multiple Public IP Address Note: Please use with Port Forward function, so that you can access to router via public IP address. |
Public IP Address | Enter a public IP address Note: Click on "Plus" or "minus" icons to add or delete public IP addresses. |
VPN | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable VPN |
VPN Connection Type |
|
Username | Enter the username to authenticate into the VPN server. |
Password | Enter the password to authenticate into the VPN server. |
Server Address | Enter the IP address or the FQDN of the VPN server. |
MPEE Encryption (if PPTP is selected) | When PPTP is chosen as the VPN Connection Type, the user can choose to toggle on or off the MPEE Encryption. |
IP Type |
|
VPN Static DNS | Enable this option to use the statically assigned DNS server addresses. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This configures the value of the maximum transmit unit. The valid range for this value is 576 - 1460. Note: Please do not change this value unless it's necessary. |
IPv6 Settings | |
IPv6 | Enable this option to use IPv6 on this specific WAN port. |
Connection Type |
|
IPv6 Address | When the Connection Type is set to Static IP, the user can can enter the static IP address in this field. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Prefix Length | Enter the prefix length. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Default Gateway | Enter the IP address of the default gateway Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Preferred DNS Server | Enter the IP address of the preferred DNS server. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Alternative DNS Server | Enter the IP address of the alternative DNS server Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Static DNS | Enable this option to enter statically assigned DNS. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to DHCPv6. |
IPv6 Relay to VLAN | Once enabled, relay IPv6 addresses to clients on the LAN side. Note: This function will take effect only "IPv6 Relay from WAN" is enabled on VLAN. |
WAN Settings
LAN
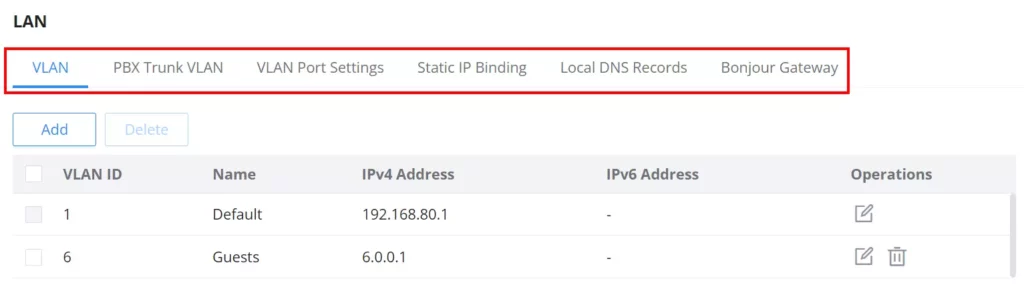
To access the LAN configuration page, log in to the GCC601x(w) WebGUI and go to Network Settings → LAN. VLAN configuration such as adding VLANs or setting up a VLAN port can be found here on this page, as well as the ability to add Static IP Bindings, local DNS Records, and Bonjour Gateway.
VLAN
GCC601X(W) integrates VLAN to enhance security and add more functionalities and features. VLAN tags can be used with SSIDs to separate them from the rest, also the user can allow these VLANs only on specific LANs for more control and isolation and they can be used as well with policy routing.
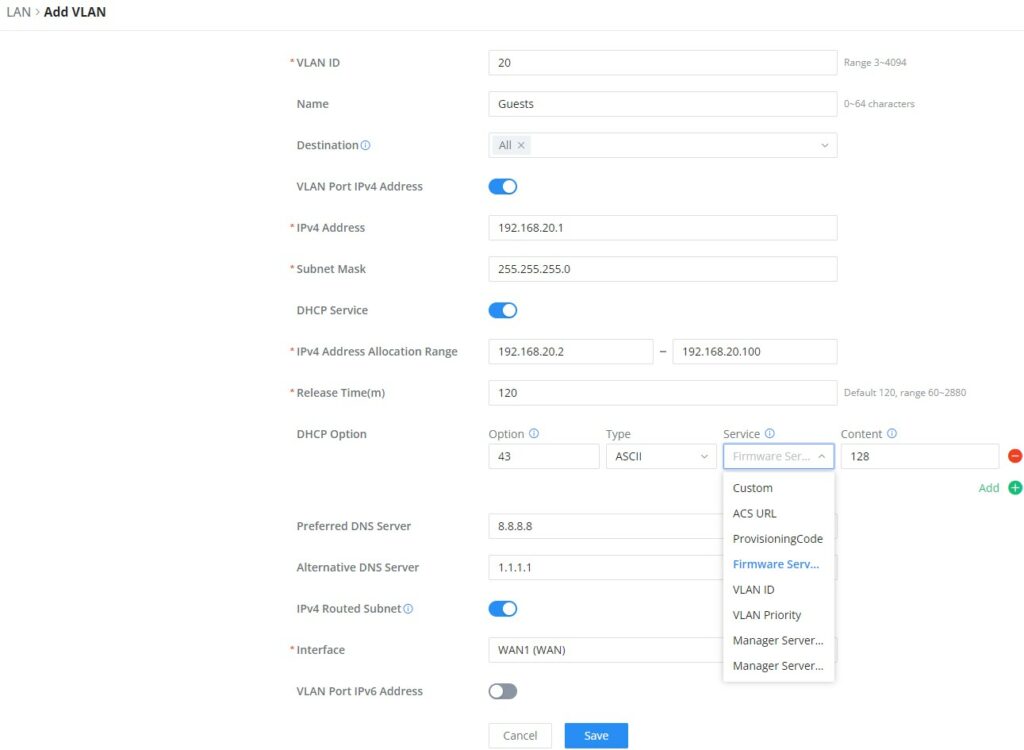
- Add or Edit VLAN
To add or edit a VLAN, Navigate to Network Settings → LAN. Click on “Add” button or click on “Edit” icon.
VLAN ID | Enter a VLAN ID Note: VLAN ID range is from 3 to 4094. |
Name | Enter the VLAN name |
Destination | To fast configure the VLAN's single-way data communication with WANs, other VLANs and VPNs. The option selected by default will be based on "Policy Routing" option to keep the default route accessible. |
VLAN Port IPv4 Address | |
IPv4 address | Enter IPv4 Address |
Subnet Mask | Enter Subnet Mask |
DHCP Server | By default it's "Off", choose "On" to specifiy the IPv4 address Allocation Range |
IPv4 Address Allocation Range | Enter the start and the end of the IPv4 address Allocation Range. |
Release Time(m) | The default value is 120, and the valid range is 60~2880. |
DHCP Option | Select the option, type, service and content for each DHCP option. Click on "Plus" or "Minus" icons to add or delete an entry.
|
Preferred DNS Server | Enter the Preferred DNS Server |
Alternative DNS Server | Enter the Alternative DNS Server |
IPv4 Routed Subnet | Once enabled, clients under the VLAN will be allowed to access the Internet using their real IP addresses. |
Interface | Select the WAN interface from the drop-down list |
VLAN Port IPv6 Address | |
IPv6 Address Source | Select from the drop-down list the WAN port |
Interface ID | Toggle ON or OFF the interface ID |
Customize Interface ID | Enter the interface ID |
IPv6 Preferred DNS Server | Enter the IPv6 Preferred DNS Server |
IPv6 Alternative DNS Server | Enter the IPv6 Alternative DNS Server |
IPv6 Relay form WAN | Once enabled, clients will get IPv6 addresses directly from the WAN side. Note: This function will take effect only "IPv6 Relay to VLAN" is enabled on the WAN side. |
IPv6 Address Assignment | Select from the drop-down list the IPv6 address assignment
|
Add/edit VLAN
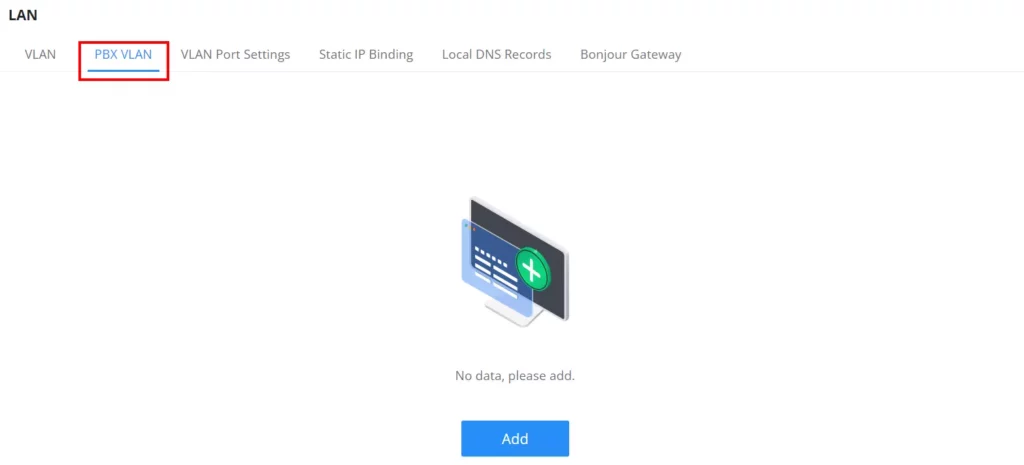
PBX VLAN
PBX VLAN is a specific VLAN configured on a network to support a PBX system (SIP Trunking). It’s a dedicated VLAN used exclusively for the traffic associated with the PBX, separating it from other network traffic for security, performance, and management purposes. This segregation helps ensure that voice traffic from the PBX receives the necessary quality of service (QoS), minimizing potential interference or congestion from other network activities. Additionally, it can enhance security by isolating PBX traffic from other network traffic, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or eavesdropping.
This feature is very helpful in the case where ITSPs/ISPs provide Internet and SIP trunking services on the same network.
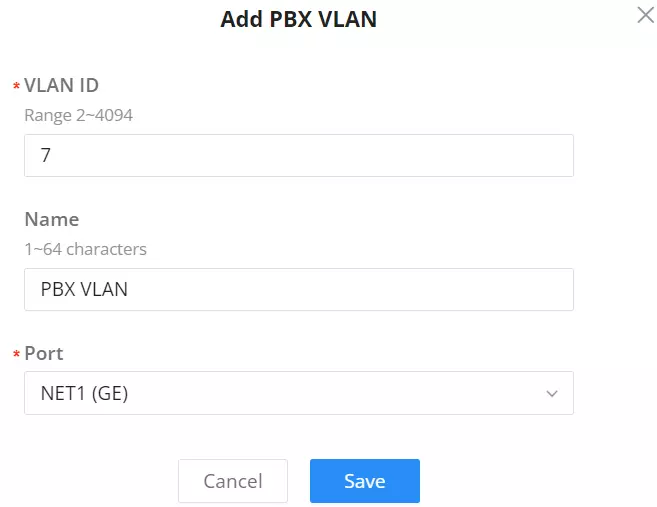
To add a PBX VLAN, navigate to Networking module → Networking Settings → LAN page → PBX VLAN tab. Click on “Add” button to add a PBX VLAN.
Specify a VLAN, name and then select the port as shown below:
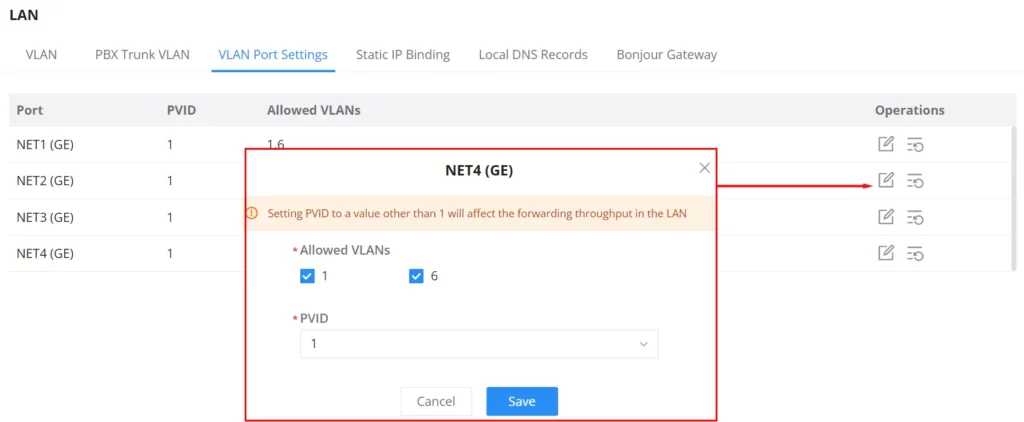
VLAN Port Settings
The user can use LAN ports to allow only specific VLANs on each LAN port and in case there are more than one VLAN then there is an option to choose one VLAN as the default VLAN ID (PVID or Port VLAN Identifier). Click on to edit the VLAN Port Settings or click on
to delete that configuration and bring back the default settings which is by default VLAN 1.
| Allowed VLANs | Choose the VLANS to be allowed on this port. |
| PVID | Select the Port VLAN Identifier or the default VLAN ID |
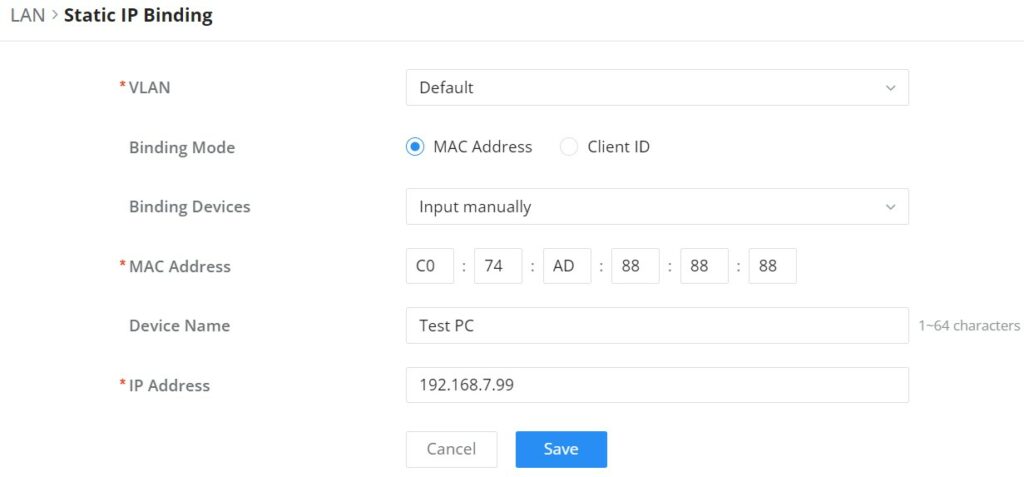
Static IP Binding
The user can set IP static binding to devices in which the IP address will be bound to the MAC address. Any traffic that is received by the router that does not have the corresponding IP address and MAC address combination will not be forwarded.
To configure Static IP Binding, please navigate to Network Settings → LAN → Static IP Binding, refer to the figure and table below:
VLAN | Select the VLAN from the drop-down list. |
Binding Mode | select the binding mode, either using the client MAC address or Client ID. |
Binding Devices | Select the device MAC address from connected devices list. Note: only available bindind mode is set to MAC Address. |
Client ID Type | Select the client ID type, either based on:
Note: only available bindind mode is set to Client ID. |
MAC Address | Enter the MAC Address Note: only available bindind mode or Client ID Type is set to MAC Address |
ASCII | Enter the ASCII Note: only available Client ID Type is set to ASCII |
Hex | Please enter XX:XX:XX:XX format or a valid even-digit hexadecimal number string, the first two digits need to enter the type value. Note: only available Client ID Type is set to Hex |
Device Name | Enter a name for the device |
IP Address | Enter the static IP address based on the VLAN selected previously. |
Static IP Binding
Local DNS Records
Local DNS Records is a feature that allows the user to a DNS records into the GCC601X(W) which can be used to map the domain name to an IP address. This feature can be used when the user needs to access a specific server using a domain name instead of an IP address when they do not want to include the entry in public DNS servers. To add a local DNS record, please navigate to Network Settings → LAN → Local DNS Records, then click “Add“
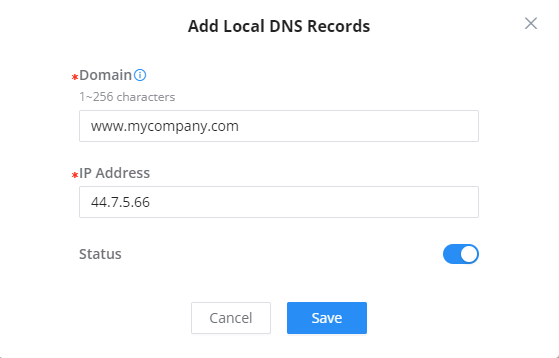
- Enter the domain name in “Domain“
- Then, enter the IP address to which the domain name will be mapped to.
- Toggle on the “Status” for the mapping to take effect.
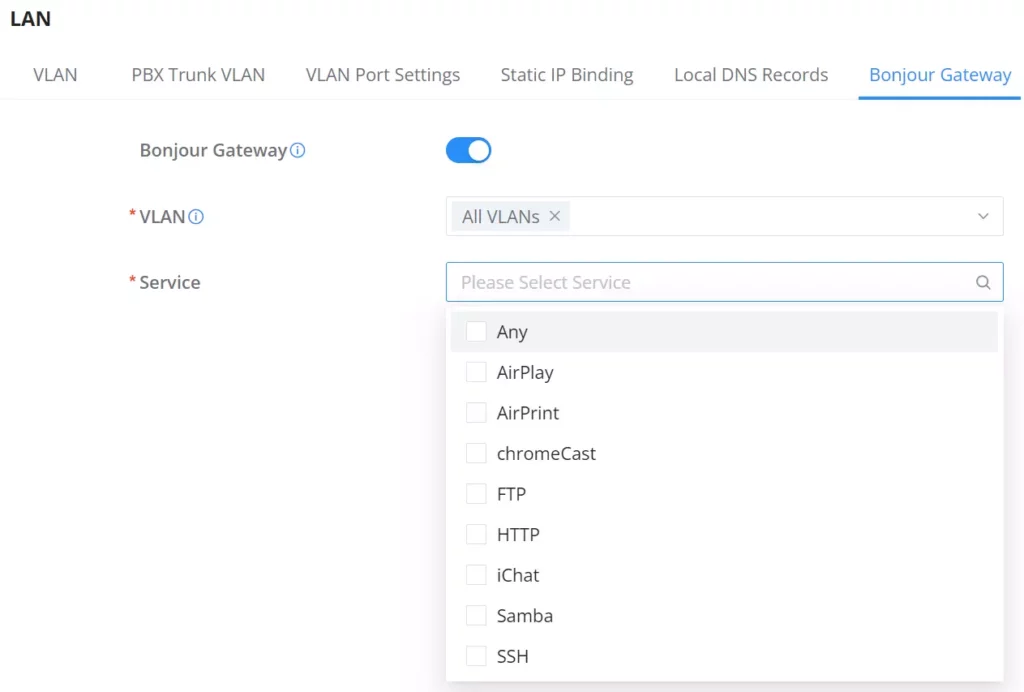
Bonjour Gateway
The Bonjour service is a zero-configuration network that enables the automatic discovery of devices and services on a local network. For example: it can be used on a local network to share printers with Windows® and Apple® devices.
Once enabled, Bonjour services (such as Samba) can be provided to Bonjour supporting clients under multiple VLANs. Once enabled, configure the services of the VLANs and proxies that need to intercommunicate.
To start using Bonjour Gateway, Toggle ON or OFF the service first, then select the VLAN and the services as shown below:
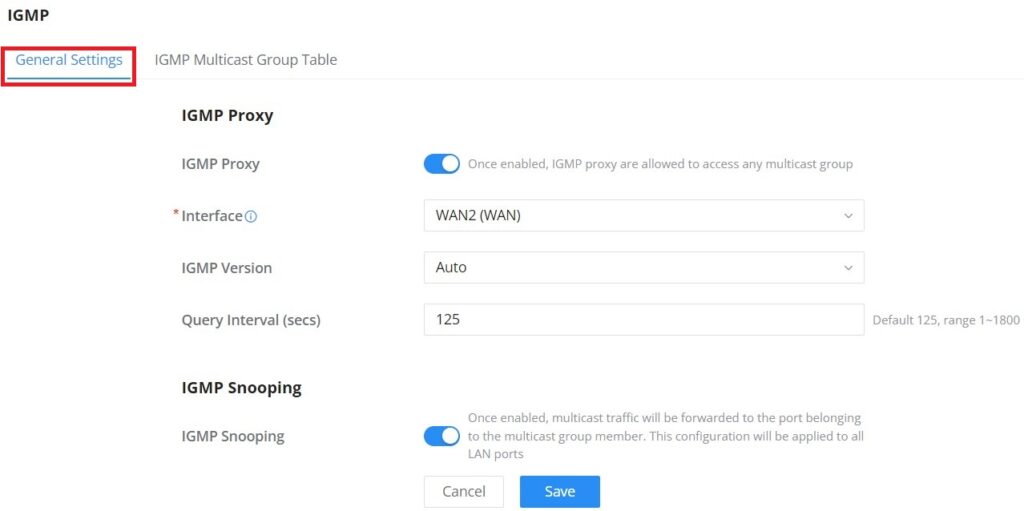
IGMP
When IGMP Proxy is enabled, the GWN router can issue IGMP messages on behalf of the clients behind it, then the GCC601X(W) will be able to access any multicast group.
To start using IGMP Proxy:
- Toggle ON IGMP Proxy first.
- Select the WAN interface to be used from the drop-down list (Note: IGMP proxy cannot be enabled on a WAN port with bridge mode enabled)
- Select the version, be default is Auto.
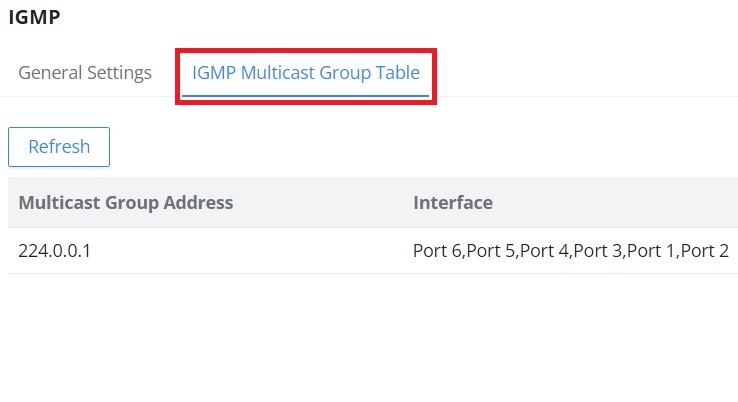
The user can also enable IGMP Snooping. Once enabled, multicast traffic will be forwarded to the port belonging to the multicast group member. This configuration will be applied to all LAN ports.
On the IGMP Multicast Group Table, all the active multicast groups will be displayed here.
Network Acceleration
Network acceleration allows the GCC601X(W) to transfer data at a higher rate when Hardware acceleration is enabled. This ensures a high performance.
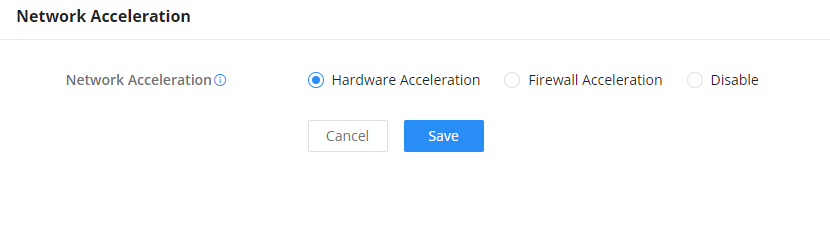
- Hardware Acceleration: All the network traffic will use dedicated hardware acceleration. Once enabled, QoS, rate limit, traffic statistic will not take effect.
- Firewall Acceleration: Only IDS/IPS and app traffic authorize by the firewall will use dedicated hardware acceleration. Once enabled, QoS rate limit will not take effect.
VPN
VPN stands for “Virtual Private Network” and it encrypts data in real-time to establish a protected network connection when using public networks.
VPN allows the GCC601X(W) to be connected to a remote VPN server using PPTP, IPSec, L2TP, OpenVPN®, and WireGuard® protocols, or configure an OpenVPN® server and generate certificates and keys for clients.
GCC601X(W) supports the following VPN functions:
- PPTP: Client and server
- IPSec: Site-to-site and client-to-site (Beta)
- OpenVPN®: Client and server
- L2TP: Client
- WireGuard®: Server
VPN page can be accessed from the GCC601X(W) Web GUI → VPN.
PPTP
A data-link layer protocol for wide area networks (WANs) based on the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and developed by Microsoft enables network traffic to be encapsulated and routed over an unsecured public network such as the Internet. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) allows the creation of virtual private networks (VPNs), which tunnel TCP/IP traffic through the Internet.
PPTP Clients
To configure the PPTP client on the GCC601X(W), navigate under VPN → PPTP → PPTP Clients and set the following:
1. Click on “Add” button.
The following window will pop up.
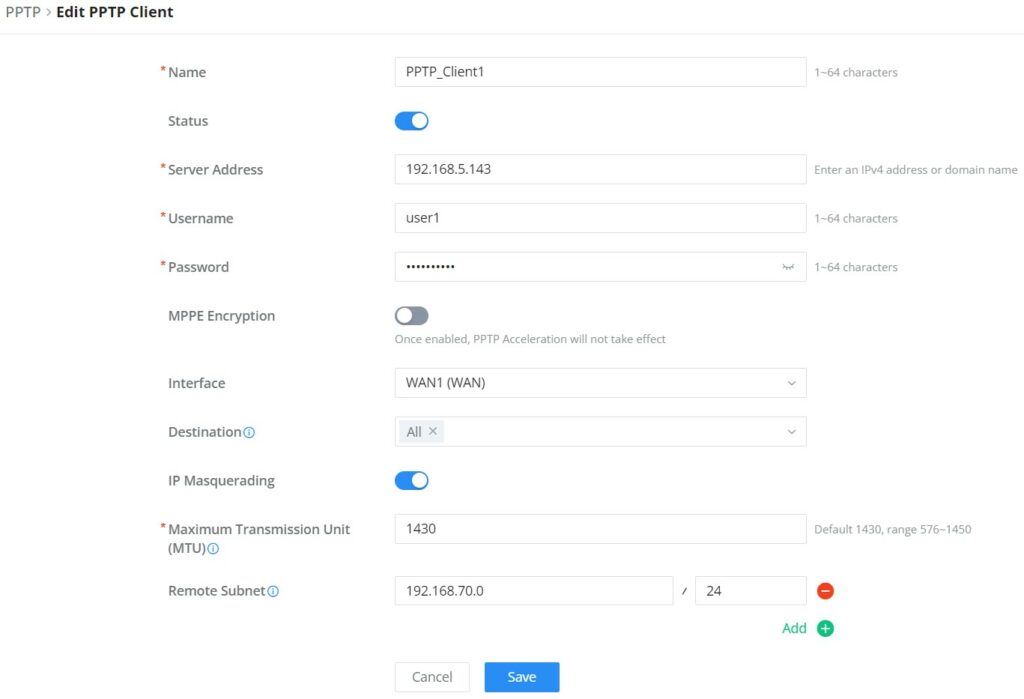
Name | Enter a name for the PPTP client. |
Status | Toggle on/off the VPN client account. |
Server Address | Enter the IP/Domain of the remote PPTP Server. |
Username | Enter the Username for authentication with the VPN Server. |
Password | Enter the Password for authentication with the VPN Server. |
MPPE Encryption | Enable / disable the MPPE for data encryption. By default, it’s disabled. |
Interface | Choose the interfaces. Note: Set forwarding rules in firewall automatically to allow traffic forwarded from VPN to the selected WAN port. If remote device is allowed to access, please set the corresponding forwarding rules in firewall. |
Destination | Choose to which destination group or WAN to allow traffic from the VPN, this will generate automatically a forwarding rule under the menu Firewall → Traffic Rules → Forward. |
IP Masquerading | This feature is a form of network address translation (NAT) which allows internal computers with no known address outside their network, to communicate to the outside. It allows one machine to act on behalf of other machines. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. |
Remote Subnet | Configures the remote subnet for the VPN. The format should be “IP/Mask” where IP could be either IPv4 or IPv6 and mask is a number between 1 and 32. example: 192.168.5.0/24 |
PPTP Client Configuration
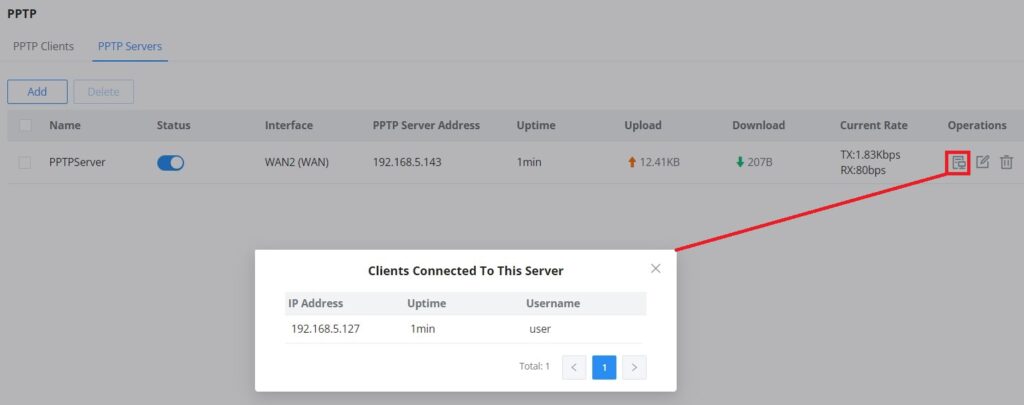
PPTP Servers
To add a PPTP Server, please navigate to Web UI → VPN → PPTP page → PPTP Servers tab, then click the “Add” button.
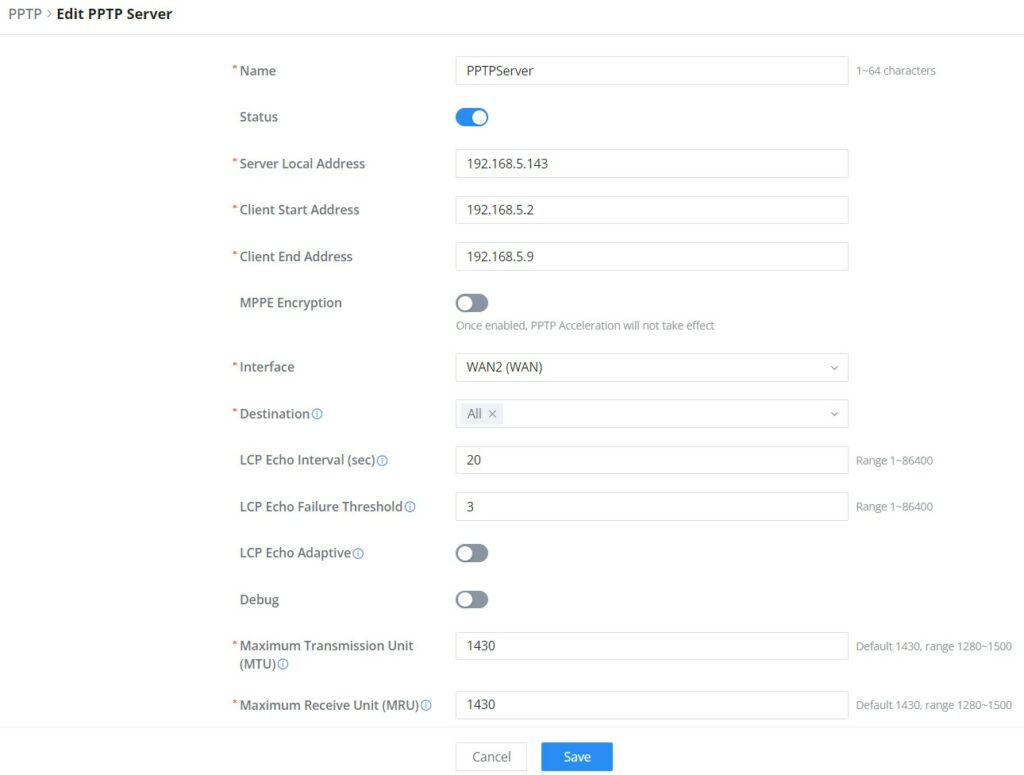
Name | Enter a name for the PPTP Server. |
Status | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable the PPTP Server VPN. |
Server Local Address | Specify the server local address |
Client Start Address | specify client start IP address |
Client End Address | specify client end IP address |
MPPE Encryption | Enable / disable the MPPE for data encryption. By default, it’s disabled. |
Interface | Select from the drop-down list the exact interface (WAN port). |
Destination | Select the Destination from the drop-down list (WAN or VLAN). Note: When selecting "All", subsequent new interfaces will be automatically included. |
LCP Echo Interval (sec) | Configures the LCP echo send interval. |
LCP Echo Failure Threshold | Set the maximum number of Echo transfers. If it is not answered within the set request frames, the PPTP server will consider that the peer is disconnected and the connection will be terminated. |
LCP Echo Adaptive |
|
Debug | Toggle On/Off to enable or disable debug. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. By default is 1450. |
Maximum Receive Unit (MRU) | MRU indicates the size of the received packets. By default is 1450. |
Preferred DNS Server | specify the preferred DNS server. Ex: 8.8.8.8 |
Alternative DNS Server | specify the alternative DNS server. Ex: 1.1.1.1 |
PPTP Server
- Create the remote user credentials:
To create the remote user account which will be required to be entered on the client side and and authenticated on the server side, please refer to the Remote Users section.
To view the clients connected to this server, click on the “Client List” icon as shown below:
IPSec
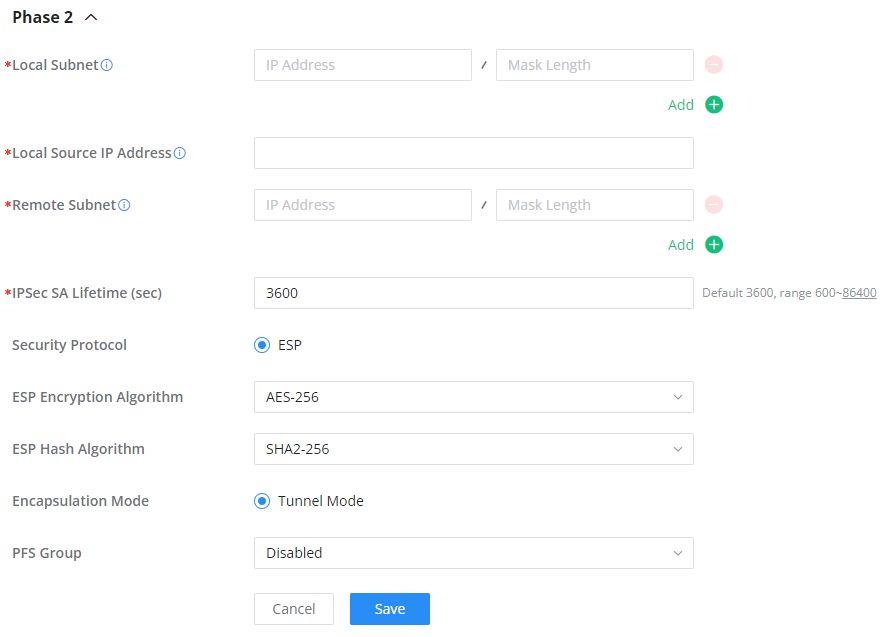
IPSec or Internet Protocol Security is mainly used to authenticate and encrypt packets of data sent over the network layer. To accomplish this, they use two security protocols – ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload) and AH (Authentication Header), the former provides both authentications as well as encryption whereas the latter provides only authentication for the data packets. Since both authentication and encryption are equally desirable, most of the implementations use ESP.
IPSec supports two different encryption modes, they are Tunnel (default) and Transport mode. Tunnel mode is used to encrypt both payloads as well as the header of an IP packet, which is considered to be more secure. Transport mode is used to encrypt only the payload of an IP packet, which is generally used in gateway or host implementations.
IPSec also involves IKE (Internet Key Exchange) protocol which is used to set up the Security Associations (SA). A Security Association establishes a set of shared security parameters between two network entities to provide secure network layer communication. These security parameters may include the cryptographic algorithm and mode, traffic encryption key, and parameters for the network data to be sent over the connection. Currently, there are two IKE versions available – IKEv1 and IKEv2. IKE works in two phases:
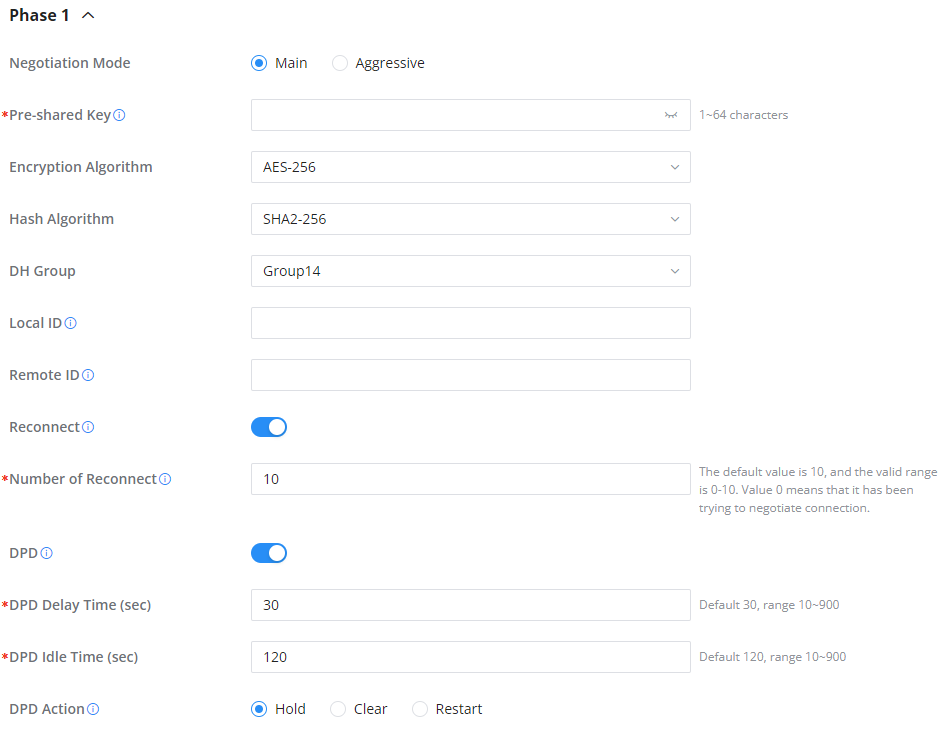
Phase 1: ISAKMP operations will be performed after a secure channel is established between two network entities.
Phase 2: Security Associations will be negotiated between two network entities.
IKE operates in three modes for exchanging key information and establishing security associations – Main, Aggressive, and Quick mode.
• Main mode: is used to establish phase 1 during the key exchange. It uses three two-way exchanges between the initiator and the receiver. In the first exchange, algorithms and hashes are exchanged. In the second exchange, shared keys are generated using the Diffie-Hellman exchange. In the last exchange, verification of each other’s identities takes place.
• Aggressive mode: provides the same service as the main mode, but it uses two exchanges instead of three. It does not provide identity protection, which makes it vulnerable to hackers. The main mode is more secure than this.
• Quick mode: After establishing a secure channel using either the main mode or aggressive mode, the quick mode can be used to negotiate general IPsec security services and generate newly keyed material. They are always encrypted under the secure channel and use the hash payload that is used to authenticate the rest of the packet.
IPSec Site-to-Site
To build an IPSec secure tunnel between two sites located in two distant geographical locations, we can use the sample scenario below:
The branch office router needs to connect to the Headquarters office via an IPSec tunnel, on each side we have a GCC601X(W). Users can configure the two devices as follows:
The branch office router runs a LAN subnet 192.168.1.0/24 and the HQ router runs a LAN subnet 192.168.3.0, the public IP of the branch office router is 1.1.1.1 and the IP of the HQ router is 2.2.2.2.
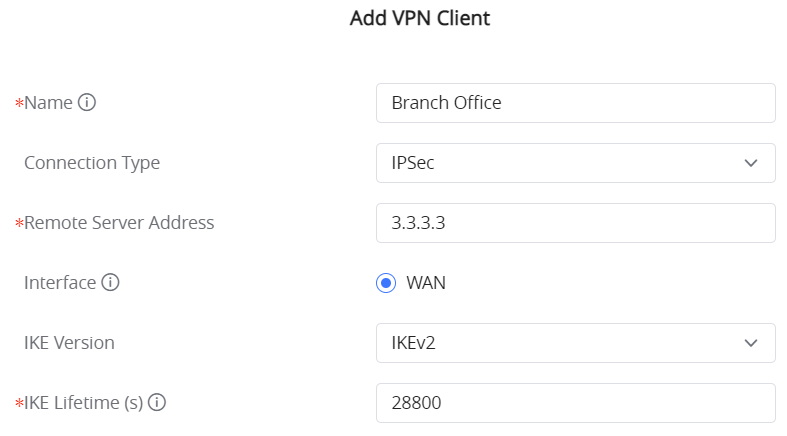
Go under VPN → IPSec → Site-to-Site then click on to add a VPN Client.
○ Phase 1
○ Phase 2
After this is done, press “Save” and do the same for the HQ Router. The two routers will build the tunnel and the necessary routing information to route traffic through the tunnel back and from the branch office to the HQ network.
- Create the remote user credentials:
To create the remote user account which will be required to be entered on the client side and and authenticated on the server side, please refer to the Remote Users section.
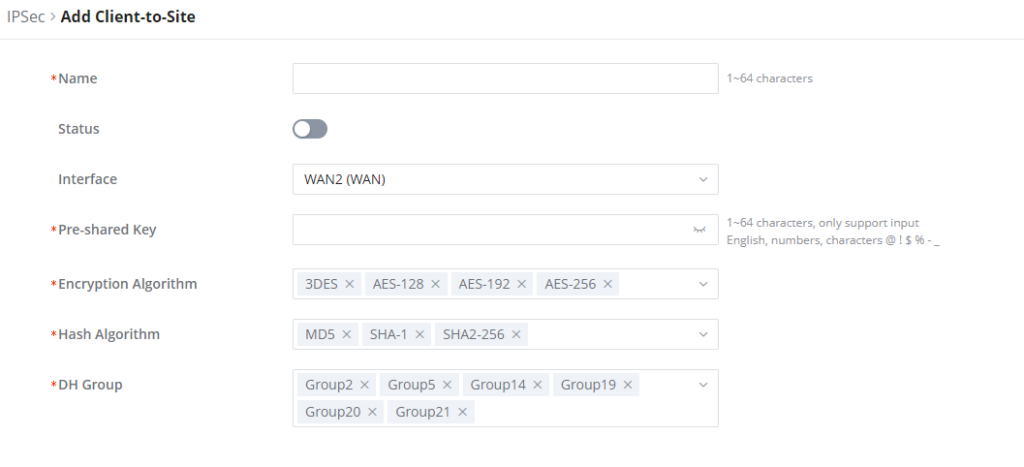
IPSec Client-to-Site
Go under VPN → IPSec → Client-to-Site then fill in the following information:
OpenVPN®
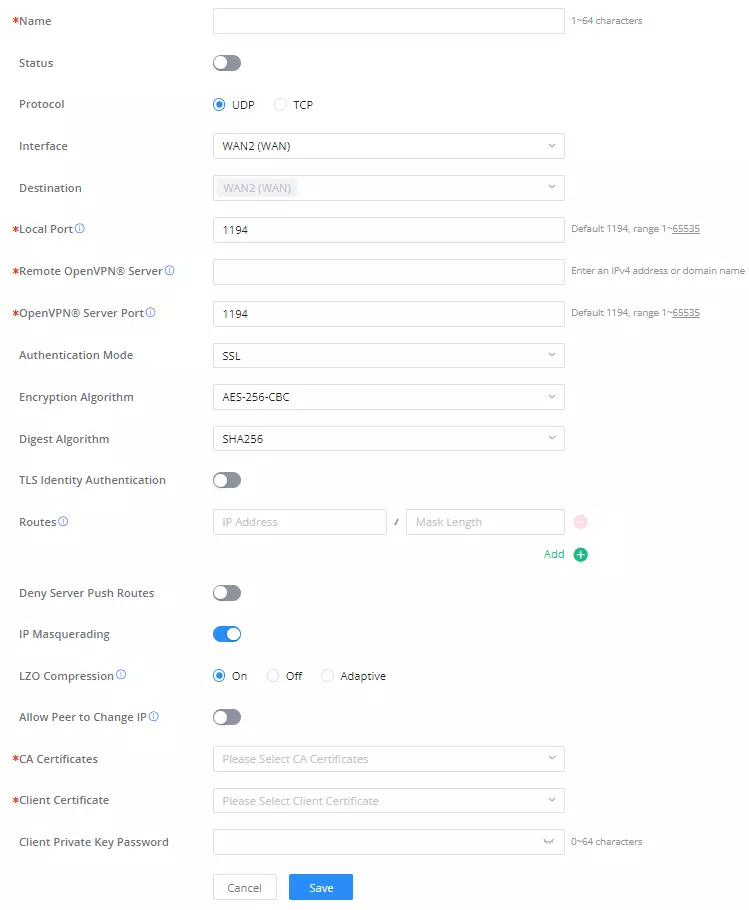
OpenVPN® Client
There are two ways to use the GCC601X(W) as an OpenVPN® client:
1. Upload client certificate created from an OpenVPN® server to the GCC601X(W).
2. Create client/server certificates on the GCC601X(W) and upload the server certificate to the OpenVPN® server.
Go to VPN → OpenVPN® → OpenVPN® Clients and follow the steps below:
Click on button. The following window will pop up.
Clickafter completing all the fields.
Name | Enter a name for the OpenVPN® Client. |
Status | Toggle on/off the client account. |
Protocol | Specify the transport protocol used.
Note: The default protocol is UDP. |
Interface | Select the WAN port to be used by the OpenVPN® client. |
Destination | Select the WANs, VLANs and VPNs (clients) destinations that will be used by this OpenVPN® client. |
Local Port | Configures the client port for OpenVPN®.The port between the OpenVPN® client and the client or between the client and the server should not be the same. |
Remote OpenVPN® Server | Configures the remote OpenVPN® server. Both IP address and domain name are supported. |
OpenVPN® Server Port | Configures the remote OpenVPN® server port |
Authentication Mode | Choose the authentication mode.
|
Encryption Algorithm | Choose the encryption algorithm. The encryption algorithms supported are:
|
Digest Algorithm | Select the digest algorithm. The digest algorithms supported are:
|
TLS Identity Authentication | Enable TLS identity authentication direction. |
TLS Identity Authentication Direction | Select the indentity authentication direction.
|
TLS Pre-Shared Key | Enter the TLS pre-shared key. |
Routes | Configures IP address and subnet mask of routes, e.g., 10.10.1.0/24. |
Deny Server Push Routes | If enabled, client will ignore routes pushed by the server. |
IP Masquerading | This feature is a form of network address translation (NAT) which allows internal computers with no known address outside their network, to communicate to the outside. It allows one machine to act on behalf of other machines. |
LZO Compression | Select whether to activate LZO compression or no, if set to “Adaptive”, the server will make the decision whether this option will be enabled or no. |
Allow Peer to Change IP | Allow remote change the IP and/or Port, often applicable to the situation when the remote IP address changes frequently. |
CA Certificates | Click on “Upload” and select the CA certificate |
Client Certificate | Click on “Upload” and select the Client Certificate. |
Client Private Key Password | Enter the client private key password. |
OpenVPN® Client
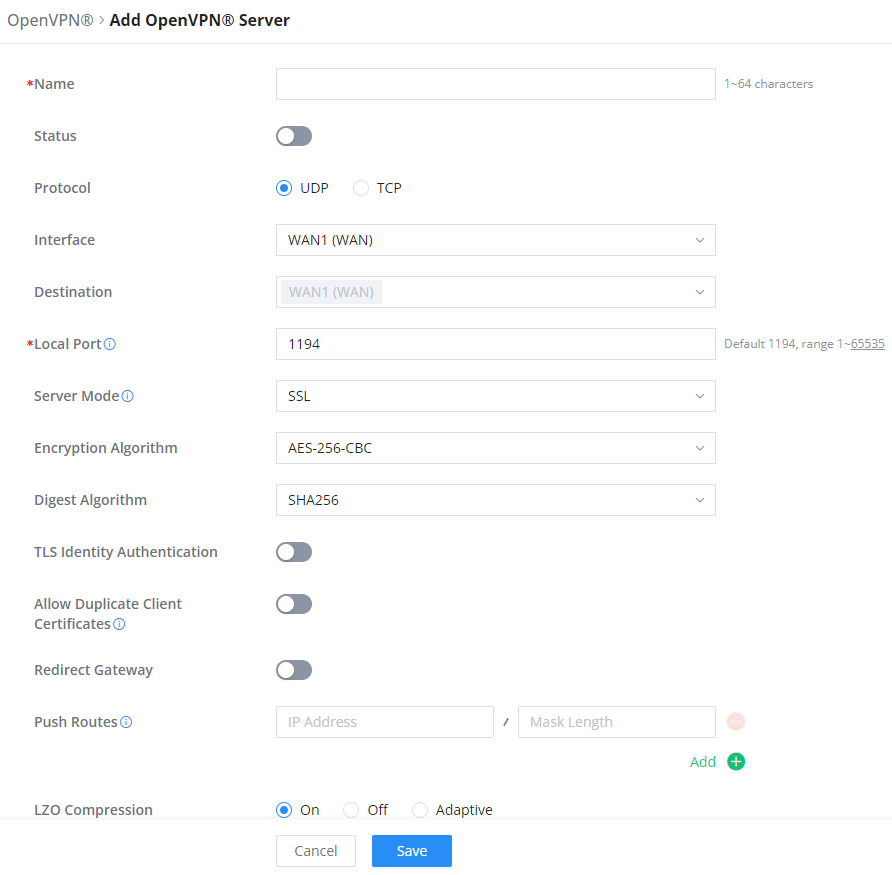
OpenVPN® Server
To use the GCC601X(W) as an OpenVPN® server, you will need to start creating OpenVPN® certificates and remote users.
To create a new VPN server, navigate under Web UI → VPN → OpenVPN® page → OpenVPN® Servers tab.
Clickafter completing all the fields.
Refer to the table below:
Name | Enter a name for the OpenVPN® server. |
Status | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable the OpenVPN® Server. |
Protocol | Choose the Transport protocol from the dropdown list, either TCP or UDP. The default protocol is UDP. |
Interface | Select from the drop-down list the exact interface (WAN). |
Destination | Select from the drop-down list the destination (WAN or VLAN). |
Local Port | Configure the listening port for OpenVPN® server. The default value is 1194. |
Server Mode | Choose the server mode the OpenVPN® server will operate with. 4 modes are available:
|
Encryption Algorithm | Choose the encryption algorithm from the dropdown list to encrypt data so that the receiver can decrypt it using same algorithm. |
Digest Algorithm | Choose digest algorithm from the dropdown list, which will uniquely identify the data to provide data integrity and ensure that the receiver has an unmodified data from the one sent by the original host. |
TLS Identicy Authentication | This option uses a static Pre-Shared Key (PSK) that must be generated in advance and shared among all peers. This feature adds extra protection to the TLS channel by requiring that incoming packets have a valid signature generated using the PSK key. |
TLS Identity Authentication Direction | Select from the drop-down list the direction of TLS Identity Authentication, three options are available (Server, Client or Both). |
TLS Pre-Shared Key | If TLS Identicy Authentication is enabled, enter the TLS Pre-Shared Key. |
Allow Duplicate Client Certificates | Click on "ON" to allow duplicate Client Certificates |
Redirect Gateway | When redirect-gateway is used, OpenVPN® clients will route DNS queries through the VPN, and the VPN server will need to handle them. |
Push Routes | Specify route(s) to be pushed to all clients. Example: 10.0.0.1/8 |
LZO Compression Algorithm | Select whether to activate LZO compression or no, if set to “Adaptive”, the server will make the decision whether this option will be enabled or no. |
Allow Peer to Change IP | Allow remote change the IP and/or Port, often applicable to the situation when the remote IP address changes frequently. |
CA Certificate | Select a generated CA from the dropdown list or add one. |
Server Certificate | Select a generated Server Certificate from the dropdown list or add one. |
IPv4 Tunnel Network/Mask Length | Enter the network range that the GCC601X(W) will be serving from to the OpenVPN® client. Note: The network format should be the following 10.0.10.0/16. The mask should be at least 16 bits. |
Create OpenVPN® Server
- Create the remote user credentials:
To create the remote user account which will be required to be entered on the client side and and authenticated on the server side, please refer to the Remote Users section.
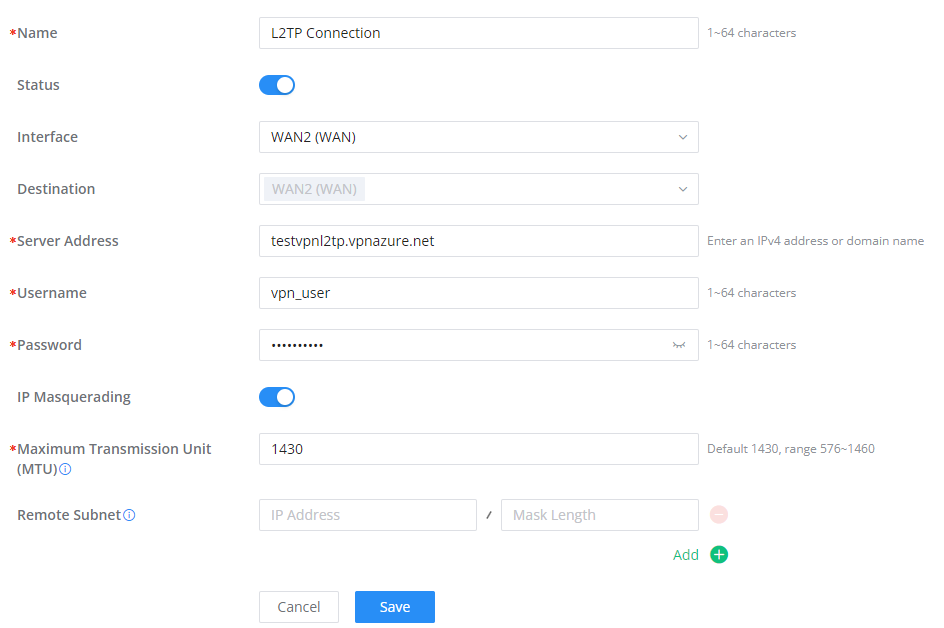
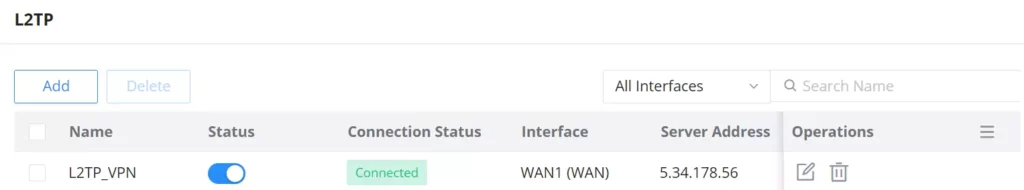
L2TP
To configure the L2TP client on the GCC601X(W) router, navigate under “VPN → VPN Clients” and set the followings:
1. Click on “Add” button and the following window will pop up.
Name | Set a name for this VPN tunnel. |
Status | Toggle on/off this L2TP account. |
Interface | Select the WAN port to be used by VPN. |
Destination | Select the WANs, VLANs destinations that will be using this VPN. |
Server Address | Enter the VPN IP address or FQDN. |
Username | Enter VPN username that has been configured on the server side. |
Password | Enter VPN password that has been configured on the server side. |
IP Masquerading | This feature is a form of network address translation (NAT) which allows internal computers with no known address outside their network, to communicate to the outside. It allows one machine to act on behalf of other machines. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. |
Remote Subnet | Enter the remote Subnet that has been configured on the server side. |
L2TP Client Configuration
Click on “Save” button after completing all the fields.
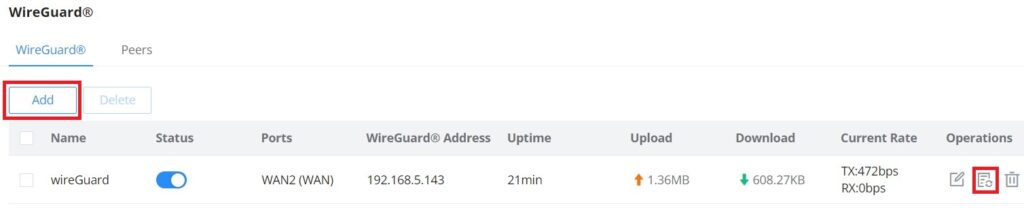
WireGuard®
WireGuard® is a free and open-source VPN solution that encrypts virtual private networks, easy to use, high performance, and secure. GCC601X(W) series supports WireGuard® VPN with automatic peer generation and QR code scanning for mobile phones and devices with camera support.
To start using WireGuard® VPN, please navigate to the Web UI → VPN → WireGuard® page. Click on the “Add” button to add a WireGuard® server as shown below:
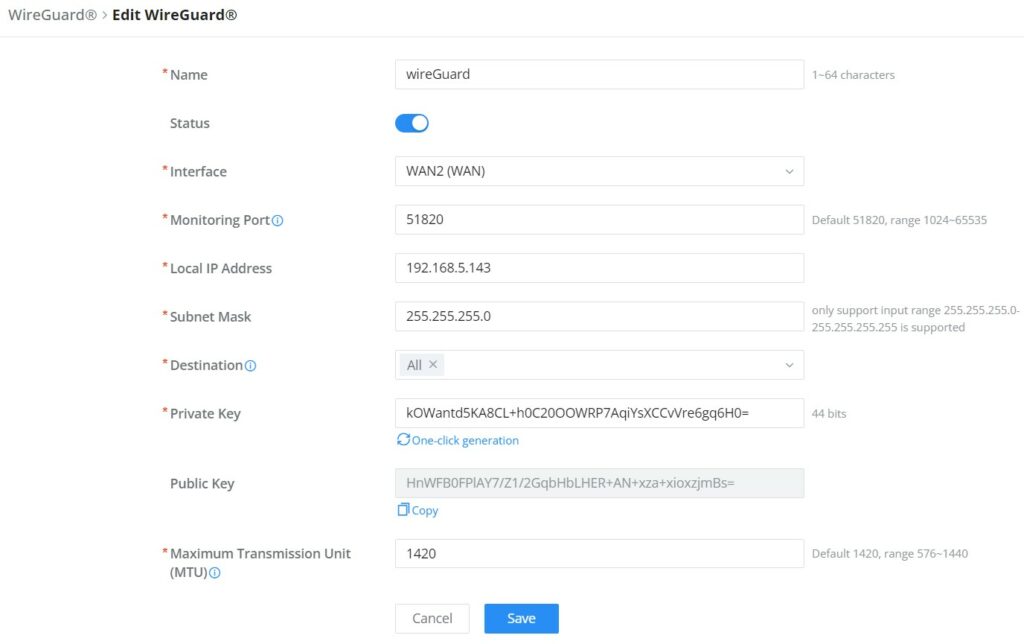
Please refer to the figure and table below when filling up the fields.
Name | Specify a name for Wireguard® VPN. |
Status | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable the Wireguard® VPN. |
Interface | Select from the drop-down list the WAN port. |
Monitoring Port | Set the local listening port when establishing a WireGaurd® tunnel. Default: 51820 |
Local IP Address | Specify the network that WireGuard® clients (Peers) will get IP address from. |
Subnet Mask | Configures the IP address range available to the Peers. |
Destination | Select the Destination(s) from the drop-down list. Note: When selecting "All", subsequent new interfaces will be automatically included. |
Private Key | Click on "One-Click Generation" text to generate a private key. |
Public Key | The public key will be generated according to the private key. Click on "Copy" text to copy the public key. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. By default is 1450. |
Add/Edit WireGuard®
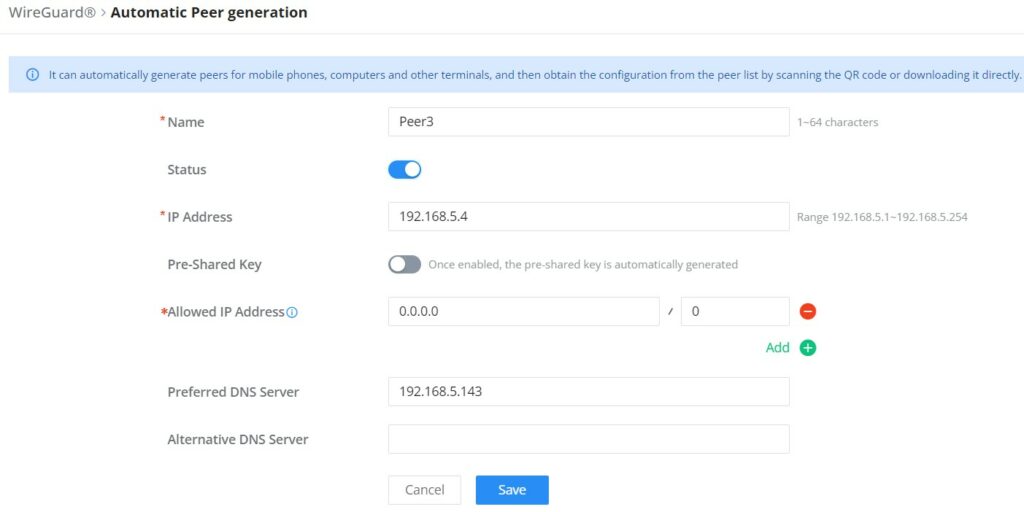
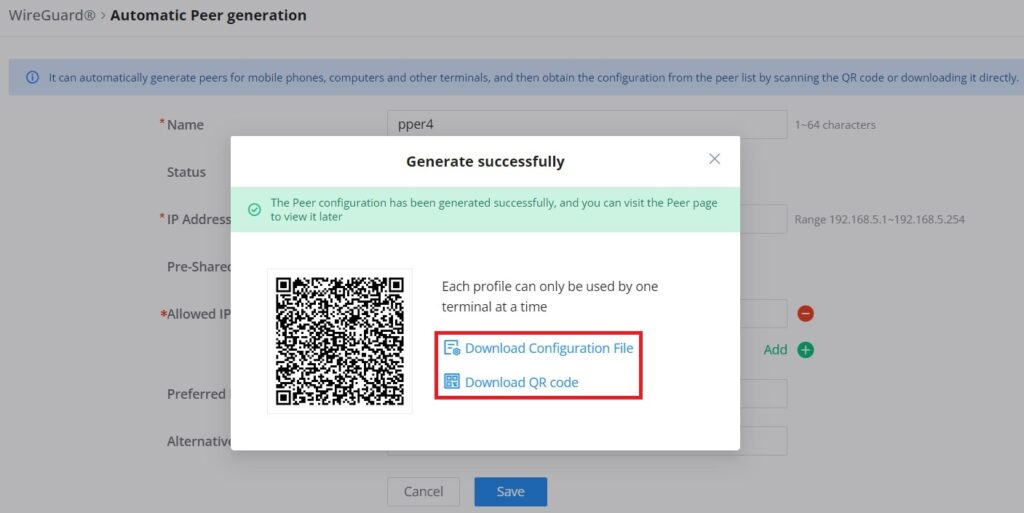
Once finished configuring WireGuard®, click on the “Automatic peer generation” icon to generate peers very quickly and easily as shown in the figures below:
Enter a name and toggle status ON then click on the “Save” button.
Now, the user can either download the configuration file and share it, or download a QR code for devices like mobile phones to scan.
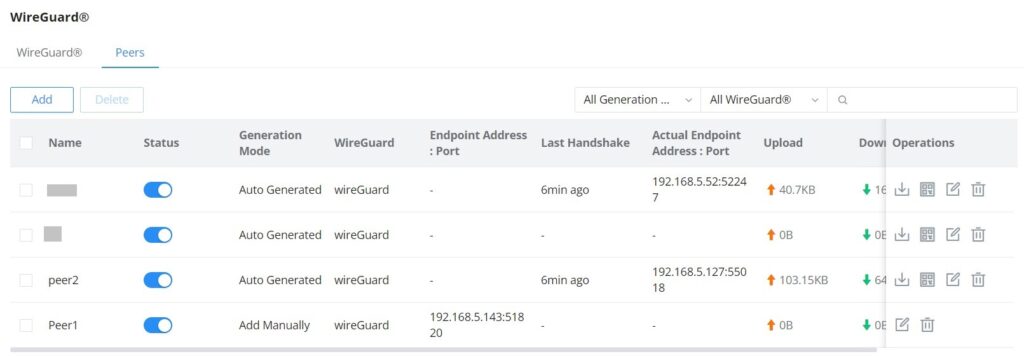
Peers
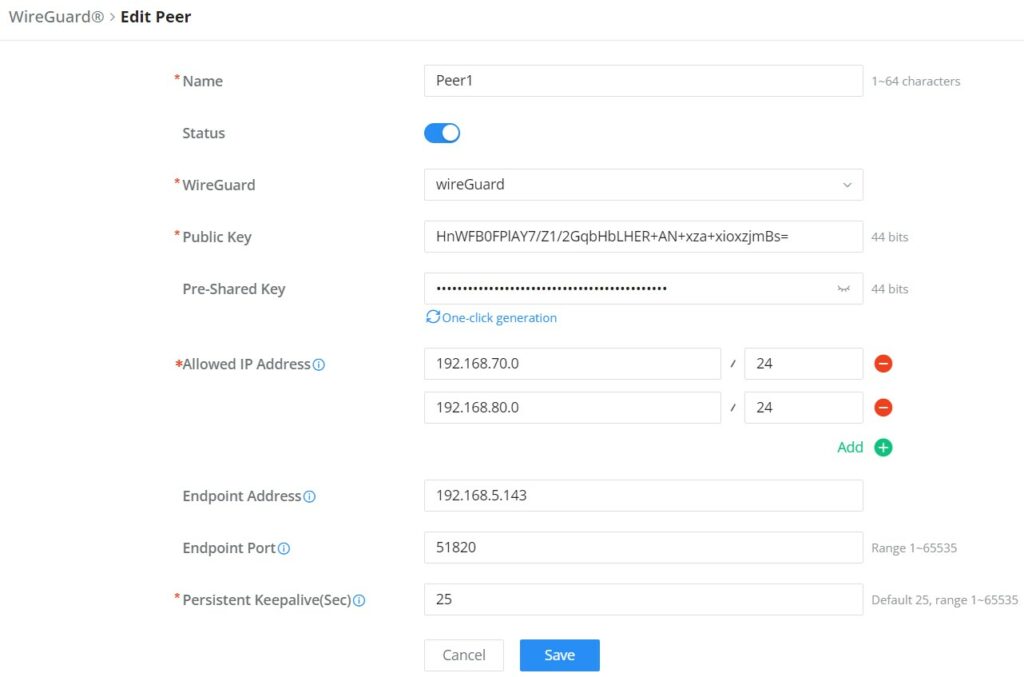
On the peers’ tab, the user can create peers manually by clicking on the “Add” button.
Please refer to the figure below when filling up the fields.
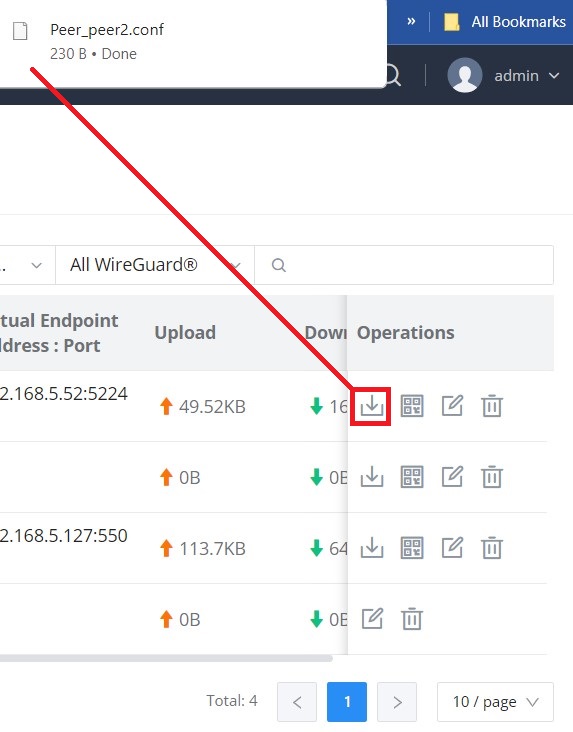
The user can download the config file after adding the peer.
Or scanning the QR code for devices with camera support.
Remote Users
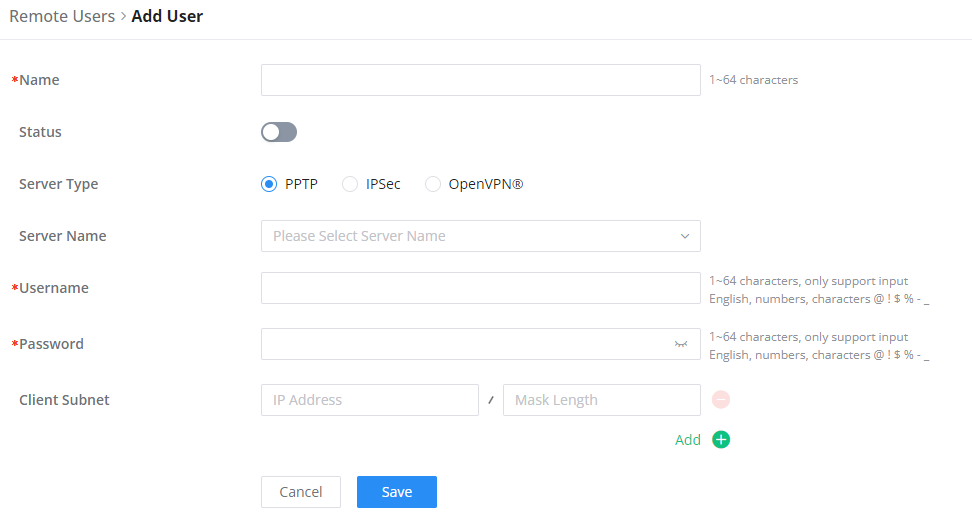
To create the VPN user accounts, please navigate to VPN → Remote Users then click “Add”. The account configured will be used for the client to authenticate into the VPN server. The remote client user that can be created in this section is for PPTP, IPSec, and OpenVPN.
Name | Enter a name for the user. This name will not be used to log in. |
Status | Enable or disable this account. |
Server Type | Choose the type of the server.
|
Server Name | Enter the server's name. |
Username | Enter the username. This username will be used to log in. |
Password | Enter the password. |
Client Subnet | Specify the client subnet. |
Add VPN Remote Users
To authenticate a remote user into the VPN server successfully, the username and password are used alongside the client certificate. To create a client certificate please refer to the Certificates section.
To configure the VPN clients for each VPN server type, please refer to the respective VPN client configuration above.
ROUTING
Policy Routes
In this section, the user can create a policy route to either load balance or backup (Failover) between 2 or more WAN ports. This feature allows a network administrator to make advanced routing decisions for traffic passing through the router and for high granularity control over policies that dictate what WAN port and even VLAN, traffic should use. Traffic controlled this way can be balanced across multiple VLANs.
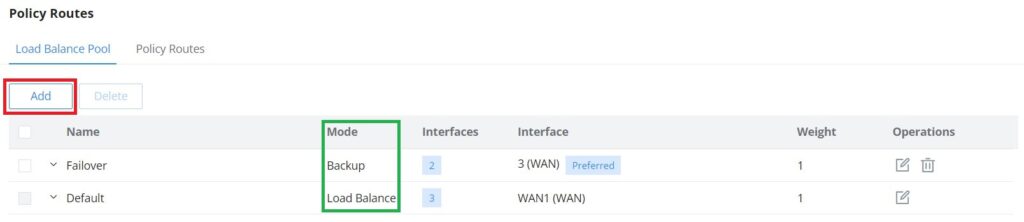
Load Balance Pool
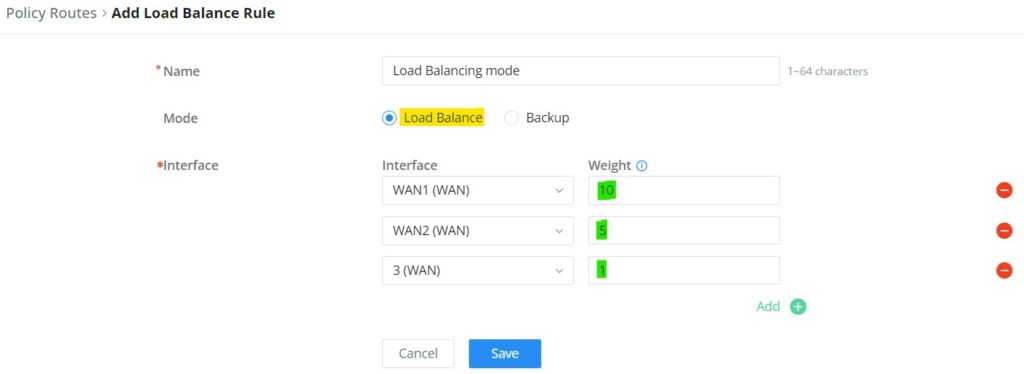
To create a load balance rule, navigate to the Routing → Policy Routes page → Load Balance Pool tab, click on the “Add” button, then select the mode (Load Balance or Backup), after selecting the WAN ports from the drop-down list and specify the Weight for each port added. Please refer to the figures below:
Policy Route
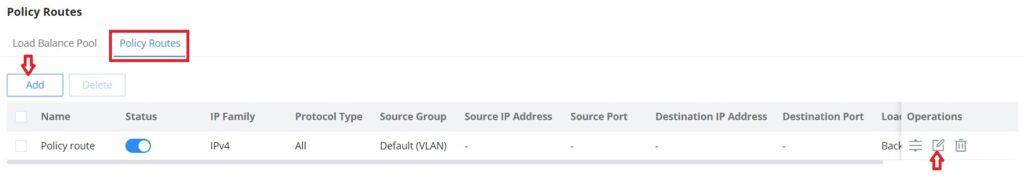
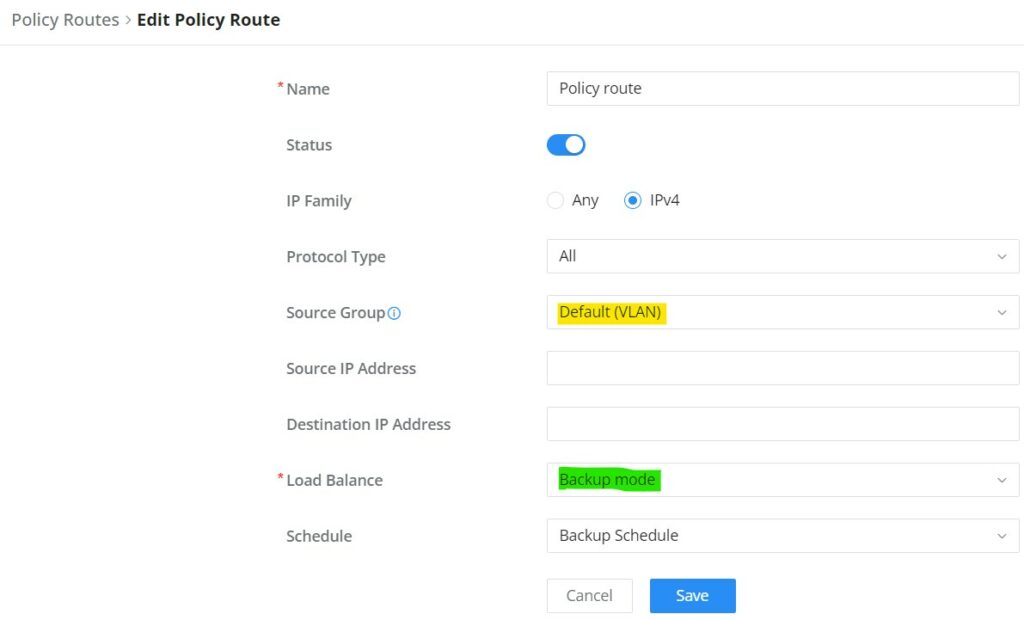
On the second tab (Policy Routes), the user can specify which Networks (VLAN) can use which Load Balance rule (must be created first), also the user can specify the protocol type, source, and destination IP and even assign a schedule for it.
To create a Policy Route, please navigate to Routing → Policy Routes page → Policy Routes tab, then click on the “Add” button as shown below:
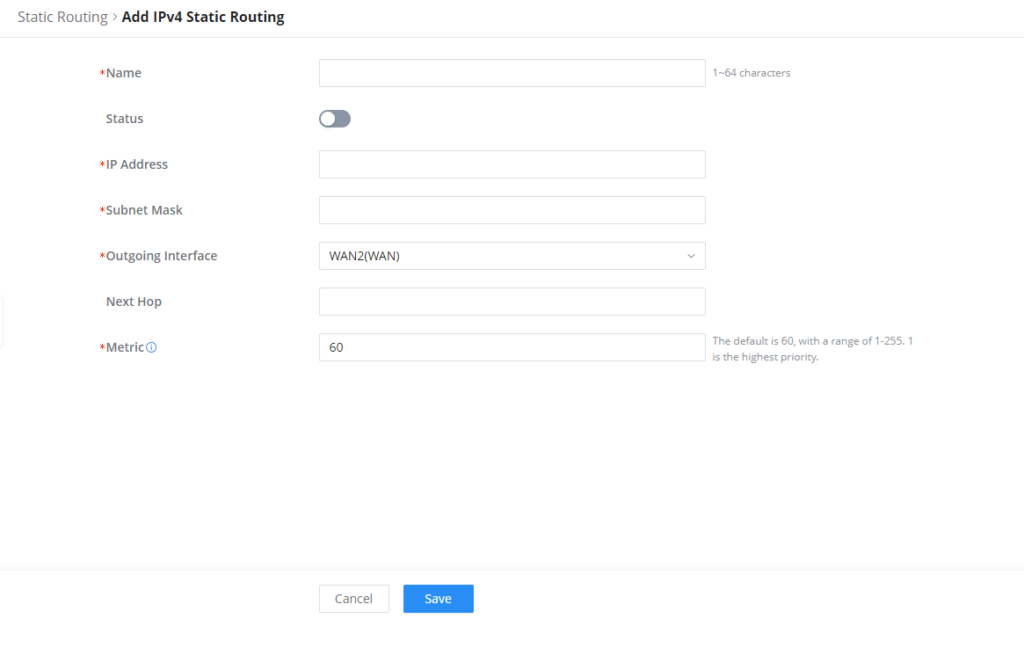
Static Routes
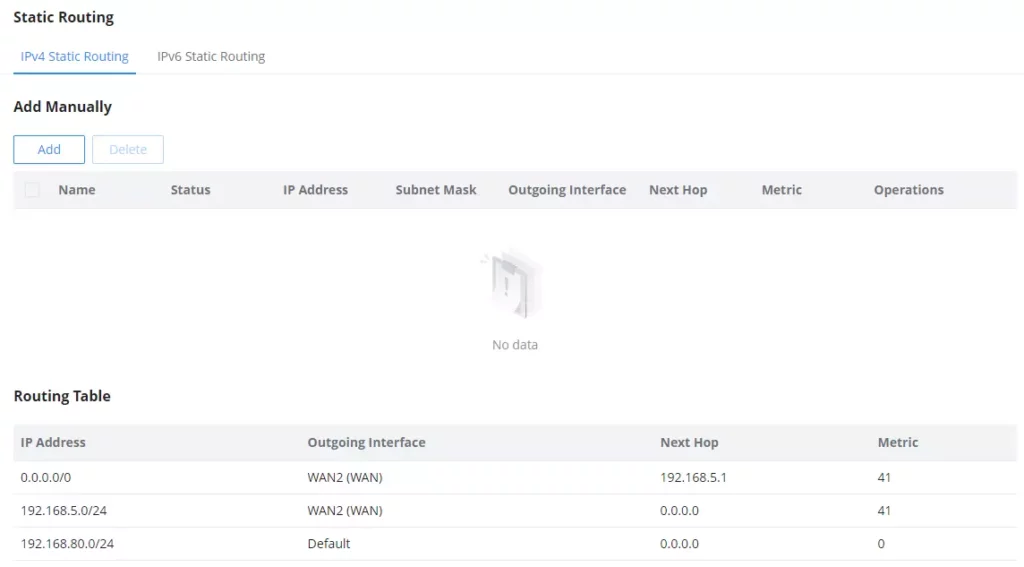
Static routing is a form of routing by manually configuring the routing entries, rather than using dynamic routing traffic for any service that requires a static address that never changes.
GCC601X(W) supports setting manually IPv4 or IPv6 Static Routes which can be accessed from GCC601X(W)WebGUI Routing → Static Routing.
To add a new Static Route, the user needs to click on .
Name | Specify a name for the Static Routing |
Status | enable or disable the Static Routing |
IP Address | Specify the IP address |
Subnet Mask | Enter the Subnet Mask |
Outgoing Interface | Select the interface |
Next Hop | Specify the next Hop |
Metric | When there are multiple routings in the network that can reach the same destination, the priority of routing rules can be adjusted by setting metric, and the packets will be forwarded according to the path with the smallest metric. |
Add IPv4 Static Routing
TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT
Traffic Statistics
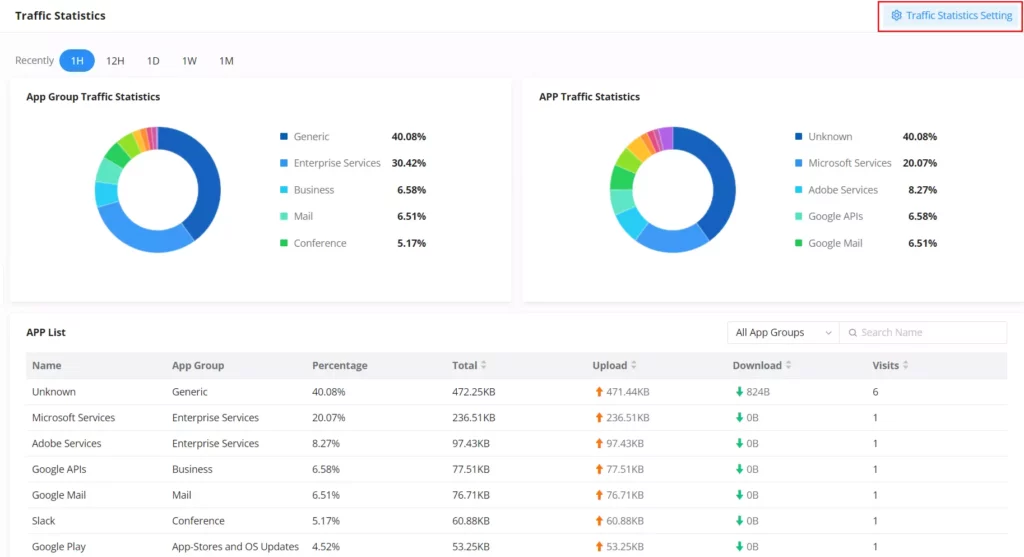
When traffic statistics are enabled, the GCC601X(W) will start identifying the traffic and generating statistics. The statistics will be represented graphically as shown in the screenshot below. The feature displays the name and the type of the service generating the traffic to easily identify which services are being used and which clients are using them.
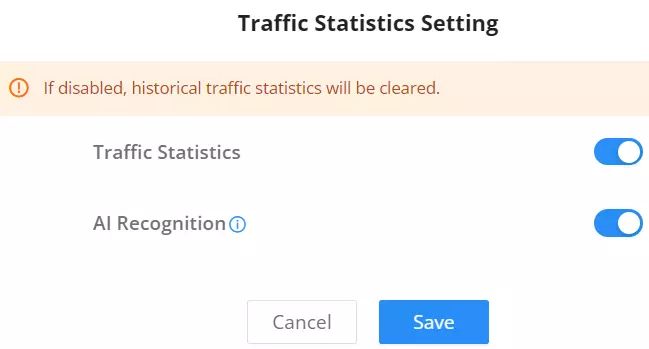
To enable traffic statistics, navigate to the Traffic Management → Traffic Statistics page, on the top right corner, click on “Traffic Statistics Settings” as shown in the figure above, then toggle ON “Traffic Statistics“.
The users have also the option to enable AI Recognition, when enabled, AI deep learning algorithms will be used to optimize the accuracy and reliability of application classification, which may consume more CPU and memory resources.
QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) is a feature that allows the prioritization of the latency-sensitive traffic exchanged between the WAN and the LAN hosts. This will offer more control over the usage of a limited bandwidth and ensure that all application services are not affected by the amount of traffic exchanged.
General Settings
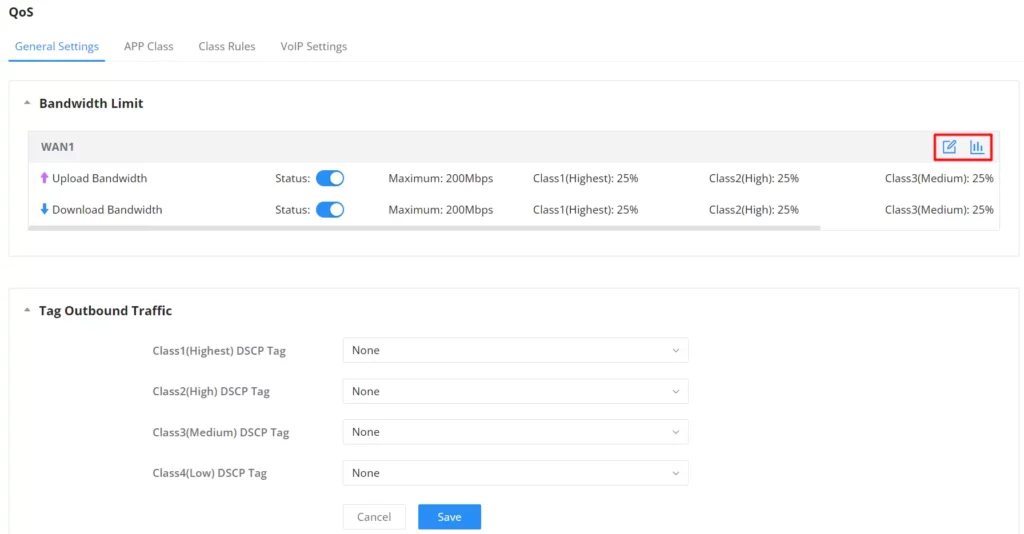
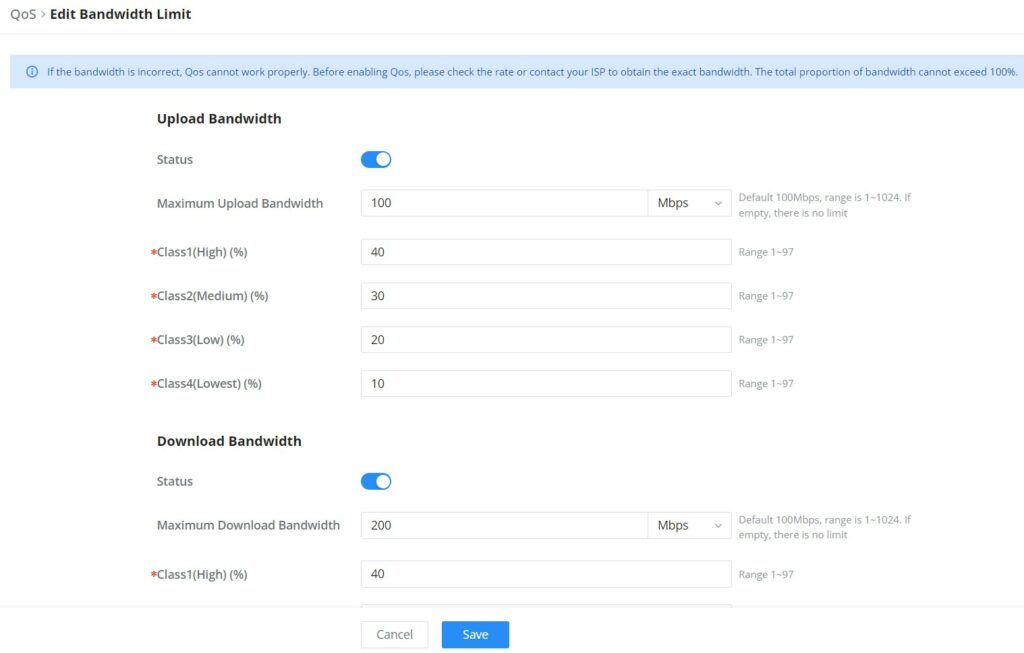
On this page, the user will be able to allocate a percentage of the download and the upload bandwidth to 4 classes. These classes can be assigned to applications to determine which application traffic will be prioritized, this includes the inbound and the outbound traffic. Also, it’s possible to tag outbound traffic with DSCP tags for each class.
To set Upload/Download bandwidth percentage for each class, click on the edit button .
Upload/Download Bandwidth | |
Status | Toggle QoS for the WAN port on/off |
Maximum Upload/Download Bandwidth | Specify the maximum upload/download speed for the WAN port. |
Class1 (High) | Specify the bandwidth percentage allocated for Class1. |
Class2 (Medium) | Specify the bandwidth percentage allocated for Class2. |
Class1 (Low) | Specify the bandwidth percentage allocated for Class3. |
Class1 (Lowest) | Specify the bandwidth percentage allocated for Class4. |
Edit Bandwidth limit
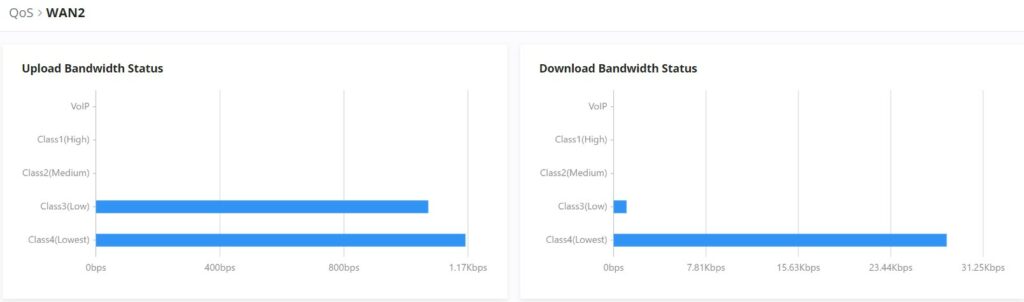
Click on bandwidth statistics icon to get a general overview of the upload/download bandwidth status.
APP Class
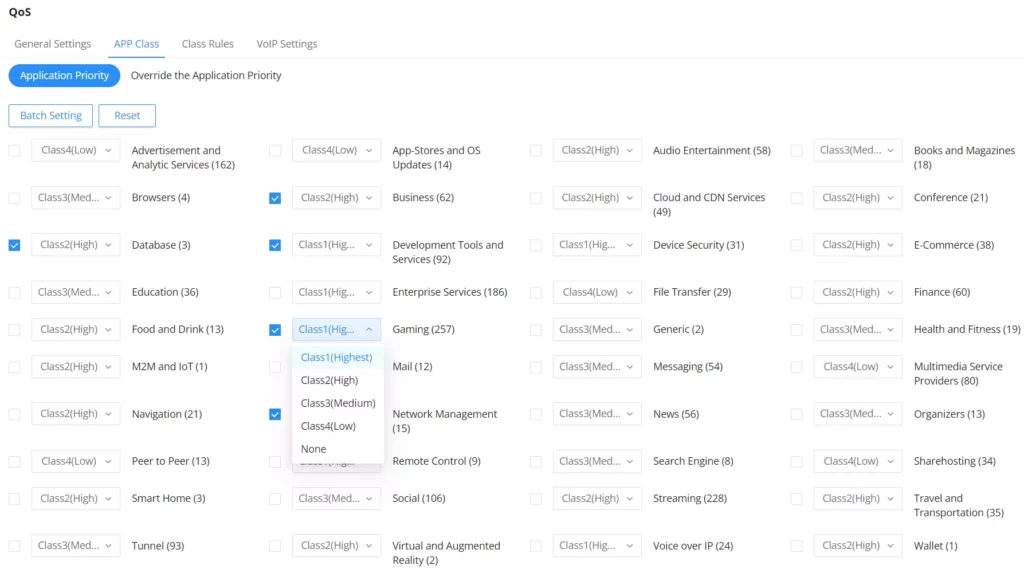
GCC601X(W) can prioritize the traffic of applications by category or individually. The priority level can be set in 4 classes, class 1 having the highest priority and class 4 having the lowest priority. To access APP Class settings, please access the web GUI of the router then navigate to Traffic Management → QoS → APP Class.
- Application Priority
Under Application Priority, the users can select a category then specify the priority (Highest, High, Medium, low or none), please check the figure below:
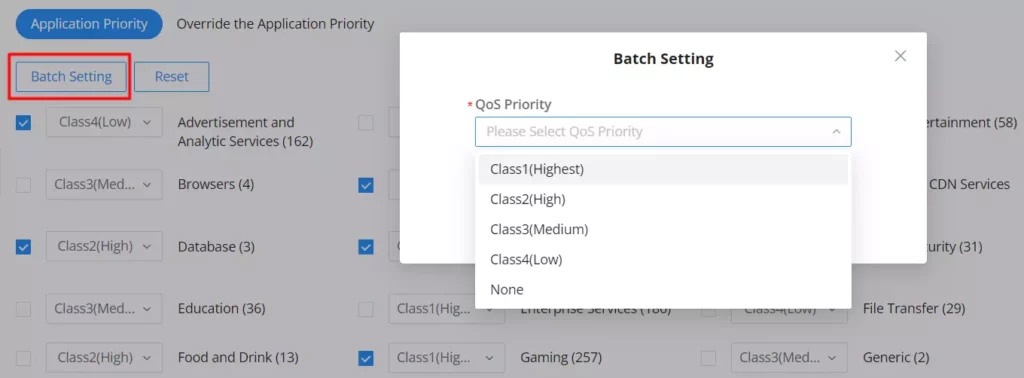
It’s also possible to select many categories and then click on “Batch Settings” to apply QoS Priority on all of them at once.
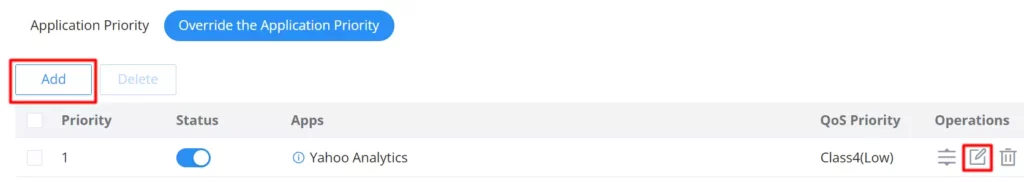
- Override the Application Priority
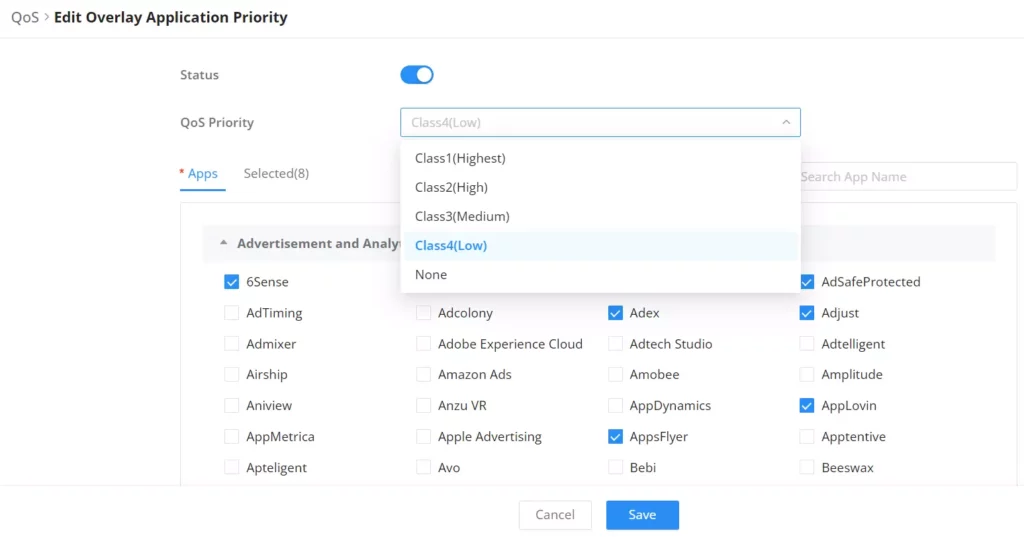
The previous option (Application Priority) applies the priority on the whole category, if the users want to make an exception or add a specific application, under “Override the Application Priority“, click on “Add” button as shown below:
Then, select the specific applications even from different categories, after that select the QoS priority from the drop-down list. This will override the Application Priority applied on the whole category.
Class Rules
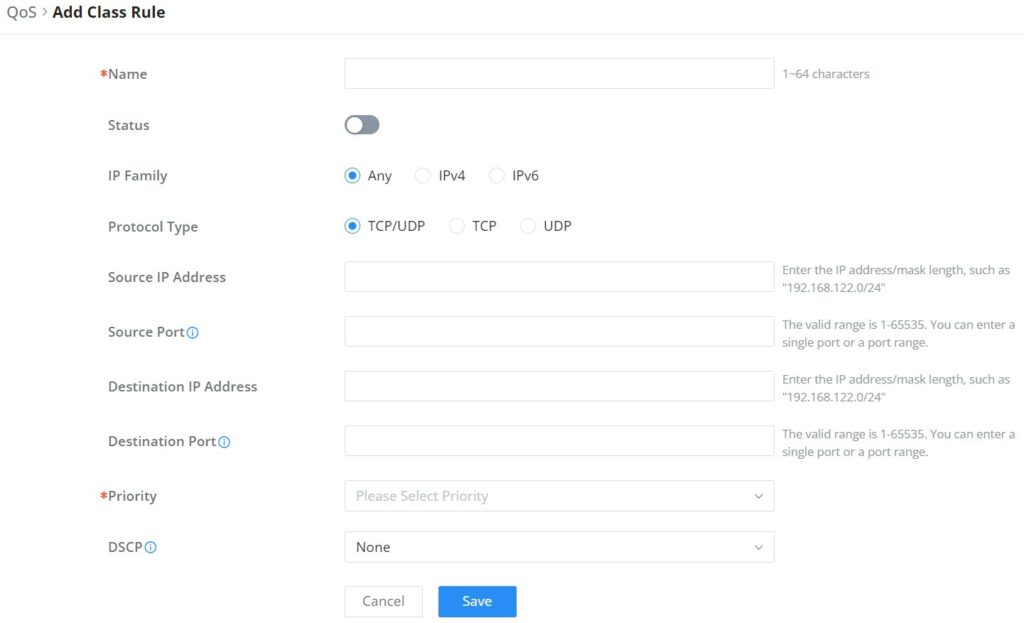
QoS class rules are rules that set the QoS based on source and/or destination IP addresses, and source and destination ports.
Name | Enter the name of the class. The character limit is 1-94 characters. |
Status | Enable or disable the class's status. |
IP Family | Choose the IP family:
|
Protocol Type | Choose the protocol type:
|
Source IP Address | Enter the source IP address/mask length. E.g.,"192.168.122.0/24" |
Source Port | Enter a single port number, multiple port numbers, or a range of ports number. Example: - To enter a single port number, type the port number such as "3074". - To enter multiple port numbers, type the port numbers with a comma in between each port number, such as "3074, 5060, 10000". - To enter a range of port, enter the first port number in the range, then type a dash (-) and enter the last port number in the range. E.g., "10000-20000" Note: The valid range of port numbers that can be entered is 1-65535. |
Destination IP Address | Enter the destination IP address/mask length. E.g.,"192.168.122.0/24" |
Destination Port | Enter a single port number, multiple port numbers, or a range of ports number. Example: - To enter a single port number, type the port number such as "3074". - To enter multiple port numbers, type the port numbers with a comma in between each port number, such as "3074, 5060, 10000". - To enter a range of port, enter the first port number in the range, then type a dash (-) and enter the last port number in the range. E.g., "10000-20000" Note: The valid range of port numbers that can be entered is 1-65535. |
Priority | Select the class of priority. |
DSCP | Choose a DSCP value. |
QoS – Add Class Rules
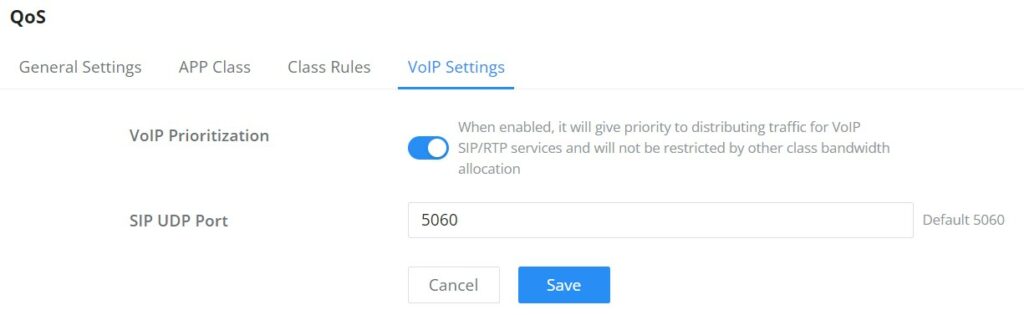
VoIP Settings
VoIP Settings in QoS allow the user to identify and prioritize the VoIP traffic that is forwarded by the GCC601X(W). To configure this option, please access the web UI of the GCC601X(W) and navigate to Traffic Management → QoS → VoIP Settings, then toggle on the “VoIP Prioritization”, which specifies the SIP UDP port, by default the port number is 5060.
Bandwidth Limit
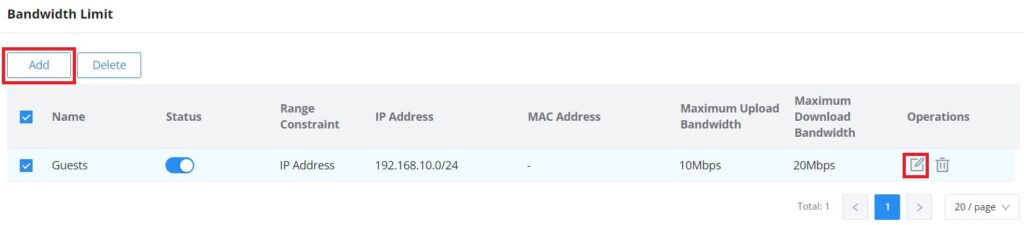
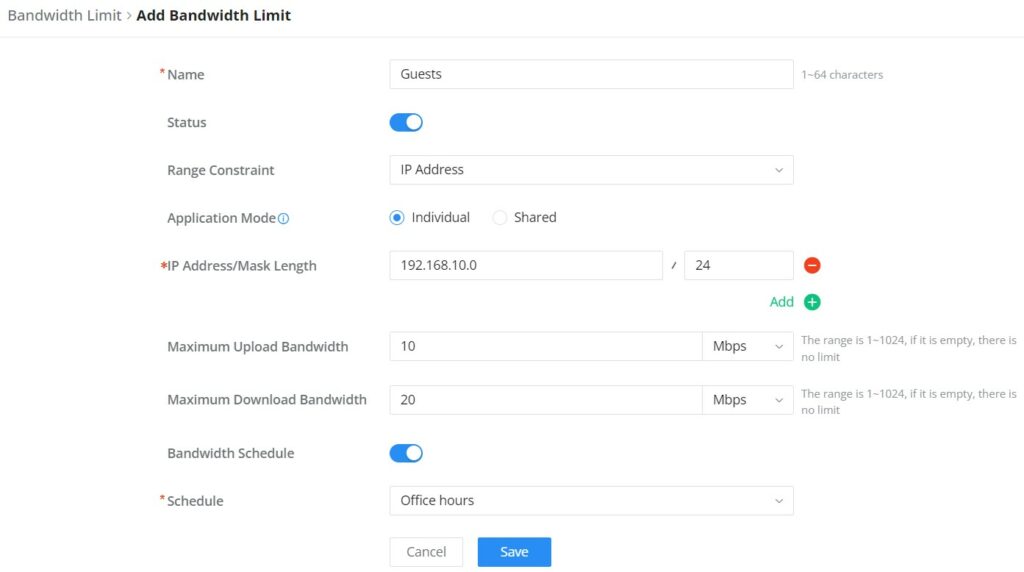
The Bandwidth limit feature helps to limit bandwidth by specifying the maximum upload and download limit, then this limit can be applied to each IP/MAC address or applied to all IP addresses in the IP address range. Navigate to Web UI → Traffic Management → Bandwidth Limit.
To add a bandwidth rule, please click on the “Add” button or click on the “Edit” icon as shown above.
Please refer to the figure below:
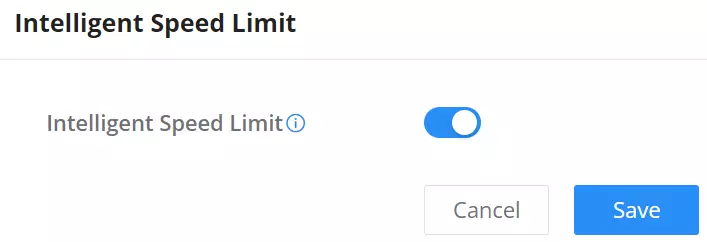
Intelligent Speed Limit
When intelligent speed limit is enabled, it automatically limits the speed of download or upload traffic when the CPU load is high.
To enable Intelligent speed limit, navigate to Traffic Management → Intelligent Speed Limit, then toggle ON the feature.
ACCESS CONTROL
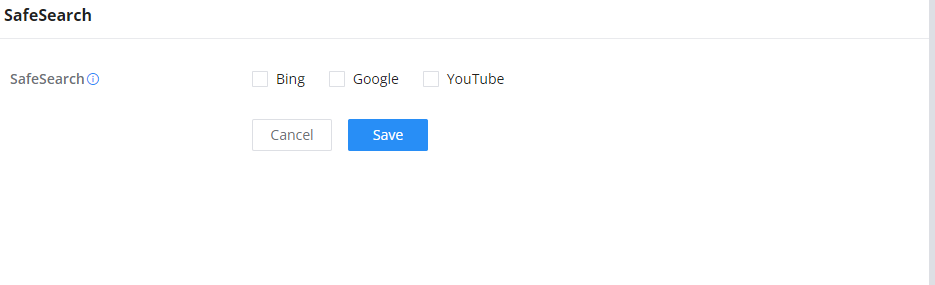
SafeSearch
The GCC601X(W) offers a SafeSearch feature on Bing, Google, and YouTube. Enabling this option will hide any inappropriate or explicit search results from being displayed.
EXTERNAL ACCESS
By default, all the requests initiated from the WAN side are rejected by the GCC601X(W) external access features allow hosts located on the WAN side to access the services hosted on the LAN side of the GCC601X(W).
DDNS
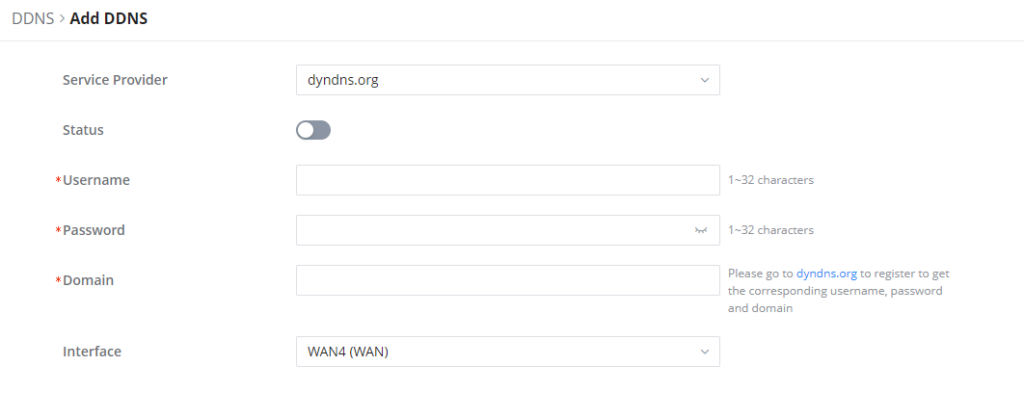
1. Access to GCC601X(W) web GUI, navigate to External Access → DDNS, and click to Add Service.
2. Fill in the domain name created with the DDNS provider under the Service Provider field.
3. Enter your account username and password under the User Name and Password fields.
4. Specify the Domain to which the DDNS Account is applied under Domain.
Service Provider | Select the DDNS provider from the list |
Username | Enter the Username |
Password | Enter the Password |
Domain | Enter the Domain |
Interface | Select the Interface |
DDNS Page
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows forwarding requests initiated from the WAN side of the GCC601X(W) to a LAN host. This is done by configuring either the port only or the port and the IP address in case we want to restrict access over that specific port to one IP address. Once the GCC601X(W) receives the request on the IP address, the GCC601X(W) will verify the port on which the request has been initiated and will forward the request to the host IP address and the port of the host which is configured as the destination.
Port forwarding can be used in the case when a host on the WAN side wants to access a server on the LAN side.
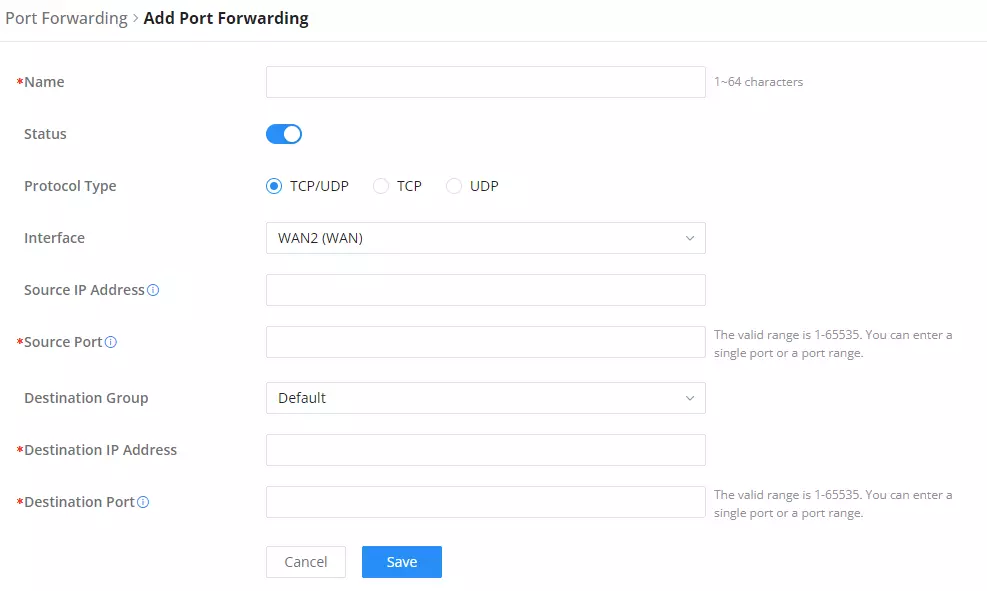
Navigate to External Access → Port Forward:
Refer to the following table for the Port Forwarding option when editing or creating a port forwarding rule:
Name | Enter a name for the port forwarding rule. |
Status | Toggle on/off the rule status. |
Protocol Type | Select a protocol, users can select TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP. |
Interface | Select the WAN port |
Source IP Address | Sets the IP address that external users access to this device. If not set, any IP address on the corresponding WAN port can be used |
Source Port | Set a single or a range of Ports. |
Destination Group | Select VLAN group. |
Destination IP Address | Set the destination IP address. |
Destination Port | Set a single or a range of Ports. |
Port Forwarding page
DMZ
Configuring the DMZ, the GCC601X(W) will allow all external access requests to the DMZ host. This is
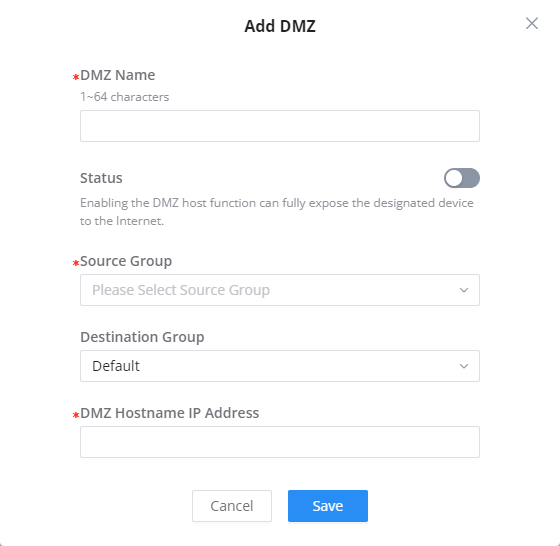
This section can be accessed from Web GUI → External Access → DMZ.
GCC601X(W) supports DMZ, where it is possible to specify a Hostname IP Address to be put on the DMZ.
Enabling the DMZ host function, the computer set as the DMZ host can be completely exposed to the Internet, realizing two-way unrestricted communication.
Refer to the below table for DMZ fields:
DMZ Name | Enter a name for the DMZ rule. |
Status | Toggle on/off the status of the DMZ rule. |
Source Group | Select the interface to allow access to the DMZ host. |
Destination Group | Select the VLAN on which the DMZ host belong. |
DMZ Hostname IP Address | Enter the DMZ host IP address. |
DMZ Page
UPnP
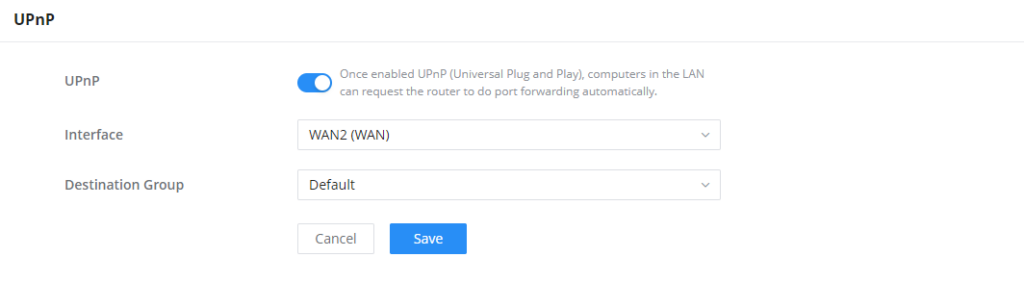
GCC601X(W) supports UPnP that enables programs running on a host to configure automatically port forwarding.
UPnP allows a program to make the GCC601X(W) open necessary ports, without any intervention from the user, without making any check.
UPnP settings can be accessed from GCC601X(W) Web GUI → External Access → UPnP.
UPnP | Click on "ON" to enable UPnP. Note: Once enabled UPnP (Universal Plug and Play), computers in the LAN can request the router to do port forwarding automatically |
Interface | Select the interface (WAN) |
Destination Group | Select the LAN Group |
UPnP Settings
When UPnP is enabled, the ports will be shown in the section below. The information shown includes the application name, IP address of the LAN host that has requested the opening of the port, the external port number, the internet port number, and the transport protocol used (UDP or TCP).
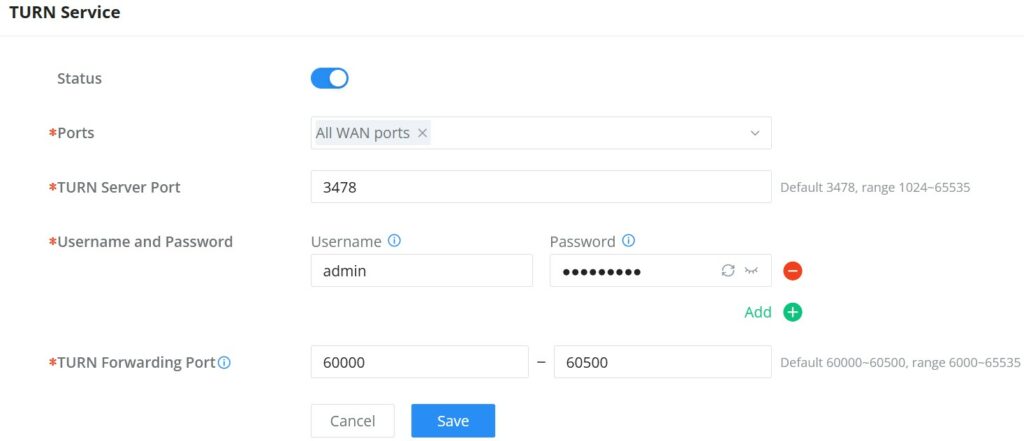
TURN Service
TURN stands for Traversal Using Relays around NAT and it’s a network service that helps establish peer-to-peer connections between devices that are behind a NAT or Firewall. Real-time communication like video conferencing, Voice over IP, etc benefit from TURN service to establish connections between peers when the NAT or the Firewall blocks or modifies the traffic.
Navigate to Web UI → External Access → TURN Service. The service is OFF by default, toggle Status ON to turn on the service. The default TURN Server Port is 3478, also it’s possible to add or remove a username and password by clicking on “minus” and “Plus” icons.
MAINTENANCE
GCC601X(W) offers multiple tools and options for maintenance and debugging to help further troubleshooting and monitoring the GCC601X(W) resources.
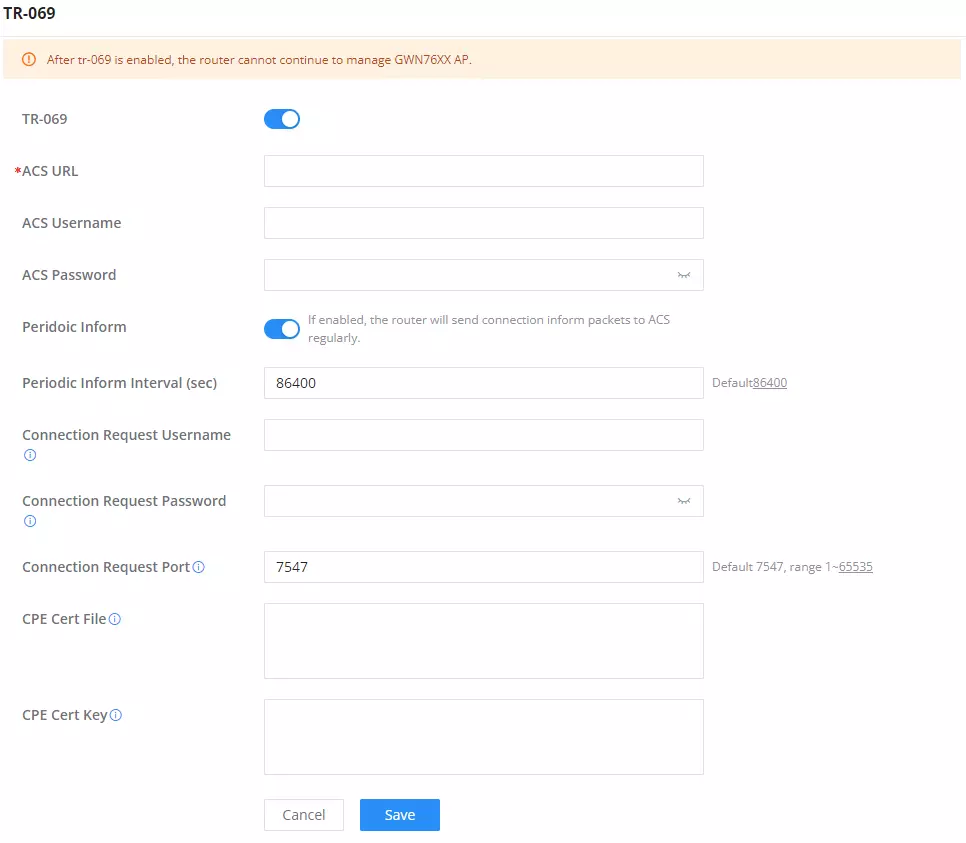
TR-069
It is a protocol for communication between CPE (Customer Premise Equipment) and an ACS (Auto Configuration Server) that provides secure auto-configuration as well as other CPE management functions within a common framework.
TR-069 stands for a “Technical Report” defined by the Broadband Forum that specifies the CWMP “CPE WAN Management Protocol”. It commonly uses HTTP or HTTPS as transport for communication between CPE and the ACS. The message exchange uses SOAP (XML_RPC) for the configuration and management of the device.
TR-069 | Enable/disable TR-069 |
ACS URL | Enter the FQDN or the IP address of the ACS server. |
ACS Username | Enter the username. |
ACS Password | Enter the password. |
Periodic Inform | If enabled, the GCC601X(W) will send connection inform packets to ACS regularly. |
Periodic Inform Interval (sec) | This configures the time duration between each inform sent by the device to the ACS server. |
Connection Request Username | When ACS server sends a connection request to the device, the username that the device authenticates ACS must be consistent with the configuration of ACS side. |
Connection Request Password | The password that the device authenticates ACS must be consistent with the configuration of ACS server. |
Connection Request Port | The port for ACS to send connection request to the GCC601X(W). This port cannot be occupied by other device features. |
CPE Cert File | Enter the certificate that the device needs to use when connecting to ACS through SSL. |
CPE Cert Key | Enter the certificate key that the device needs to use when connecting to ACS through SSL. |
TR-069 page
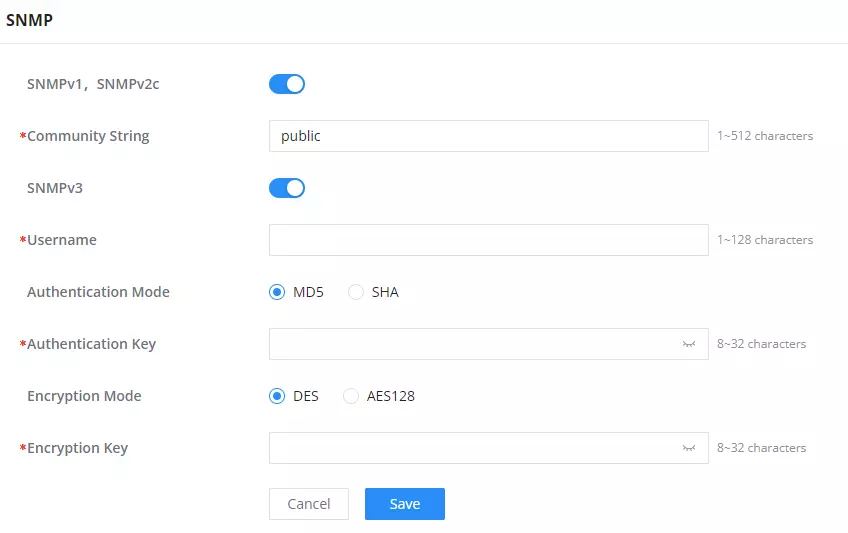
SNMP
GCC601X(W) supports SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) which is widely used in network management for network monitoring for collecting information about monitored devices.
To configure SNMP settings, go to Web GUI → Maintenance → SNMP, in this page, the user can either enable SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, or enable SNMPv3, and enter all the necessary parameters.
To configure SNMPv1 or SNMPv2, please refer to the table below:
SNMPv1, SNMPv2 | Enable/disable SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 |
Community String | Enter the shared password of the community. |
SNMP – SNMPv1 or SNMPv2
To configure SNMPv3, please refer to the table below:
SNMPv3 | Enable/disable SNMPv3. |
Username | Enter a username. |
Authentication Mode | Select the algorithm used for the authentication. |
Authentication Key | Select the authentication password. |
Encryption Mode | Select the encryption protocol used for the encryption of the data. |
Encryption Key | Enter the encryption key. |
SNMP – SNMPv3
System Diagnostics
Many debugging tools are available on GCC601X(W)’s Web GUI to check the status and troubleshoot GCC601X(W)’s services and networks.
To access these tools navigate to “Web UI → System Settings → System Diagnosis“
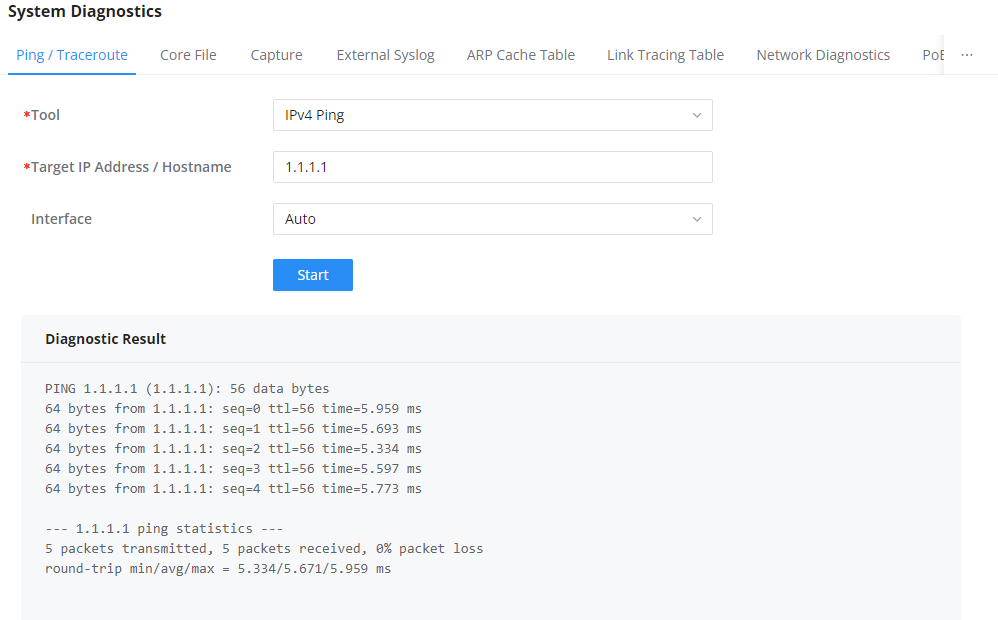
Ping/Traceroute
Ping and Traceroute are useful debugging tools to verify reachability with other clients across the network (WAN or LAN). The GCC601X(W) offers both Ping and Traceroute tools for IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
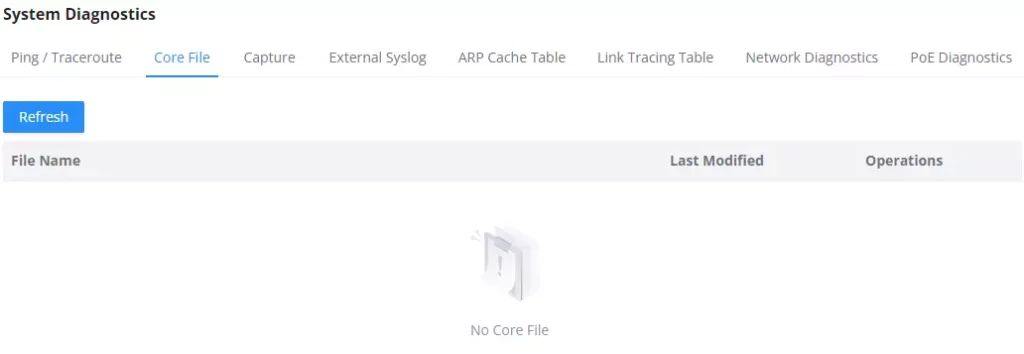
Core File
When a crash event happens on the unit, it will automatically generate a core dump file that can be used by the engineering team for debugging purposes.
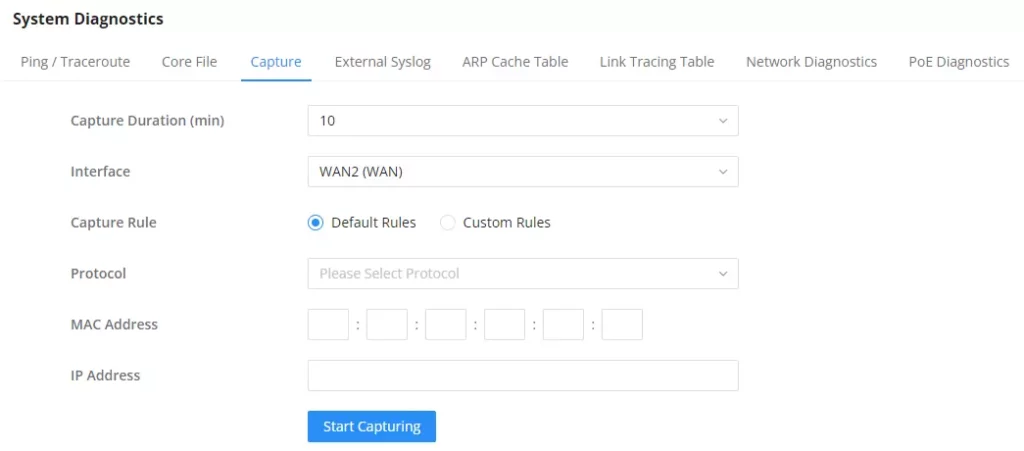
Capture
This section is used to capture packet traces from the GCC601X(W) interfaces (WAN ports and network groups) for troubleshooting purposes or monitoring. It’s even possible to capture based on MAC address or IP Address, once done the user can click on and the file (CAP) will start downloading right away.
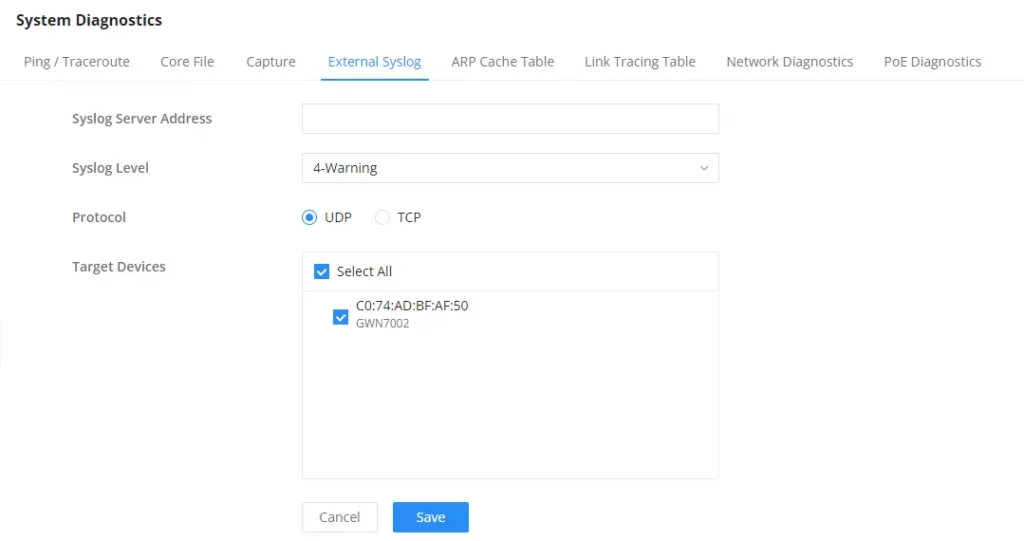
External Syslog
GCC601X(W) supports dumping the Syslog information to a remote server under Web GUI → System Settings → System Diagnosis → External Syslog Tab
Enter the Syslog server Hostname or IP address and select the level for the Syslog information. Nine levels of Syslog are available: None, Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, Warning, Notice, Information, and Debug.
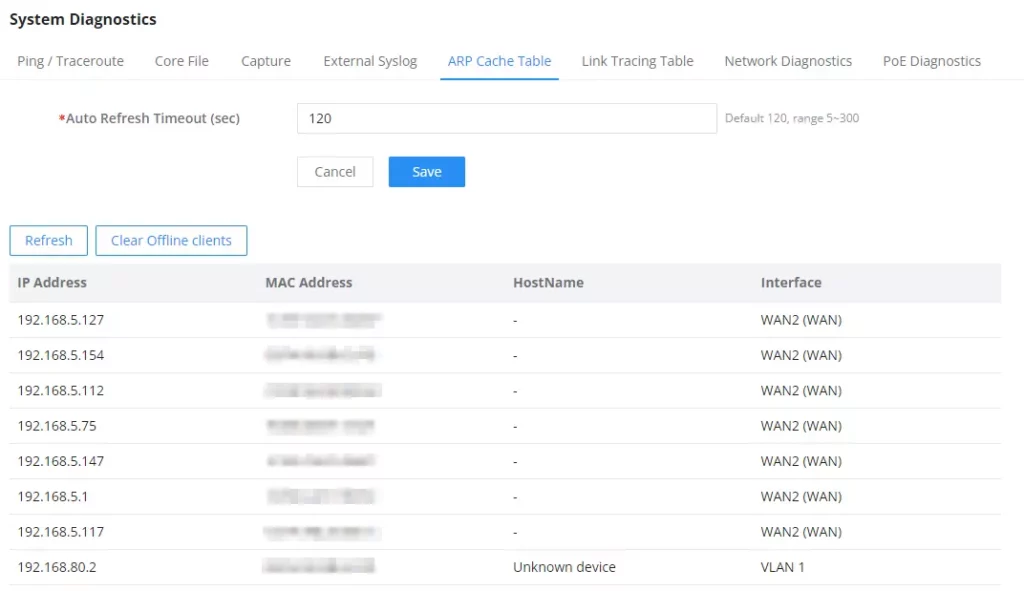
ARP Cache Table
GCC601X(W) keeps an ARP table record of all the devices that have been assigned an IP address from the GCC601X(W). The record will keep the device’s information when the device is offline. To access the ARP Cache Table, please navigate to System Diagnostics → ARP Cache Table.
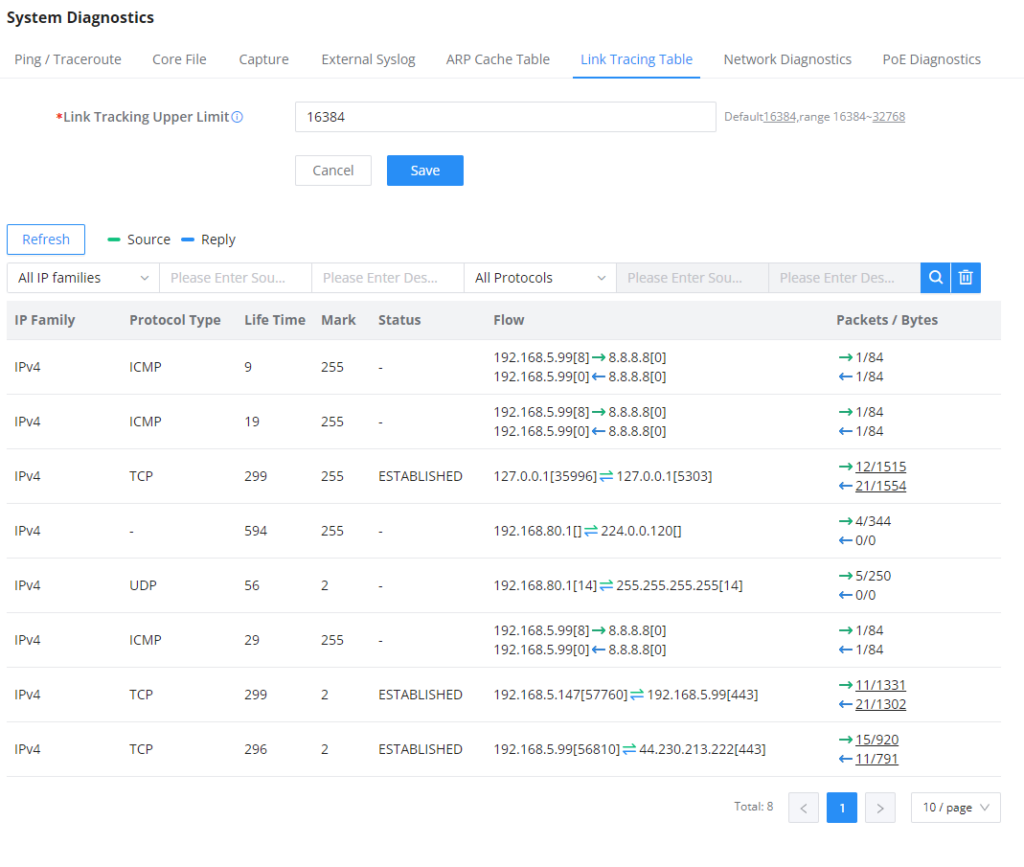
Link Tracing Table
The Link Tracing Table shows the flow of traffic by displaying the source IP address/Port (the green color) and the reply IP address/port (the blue color), also other information can be displayed like IP Family, Protocol Type, Life Time, Status, Packets/Bytes, etc.
Users/Administrators can also delete the flow of certain IP addresses/Ports (Source and Destination) or then click on the “Delete” button to clear the link tracing statistic.
Network Diagnostics
The Network Diagnostics feature allows the user to quickly diagnose the connection link on a specific WAN interface.
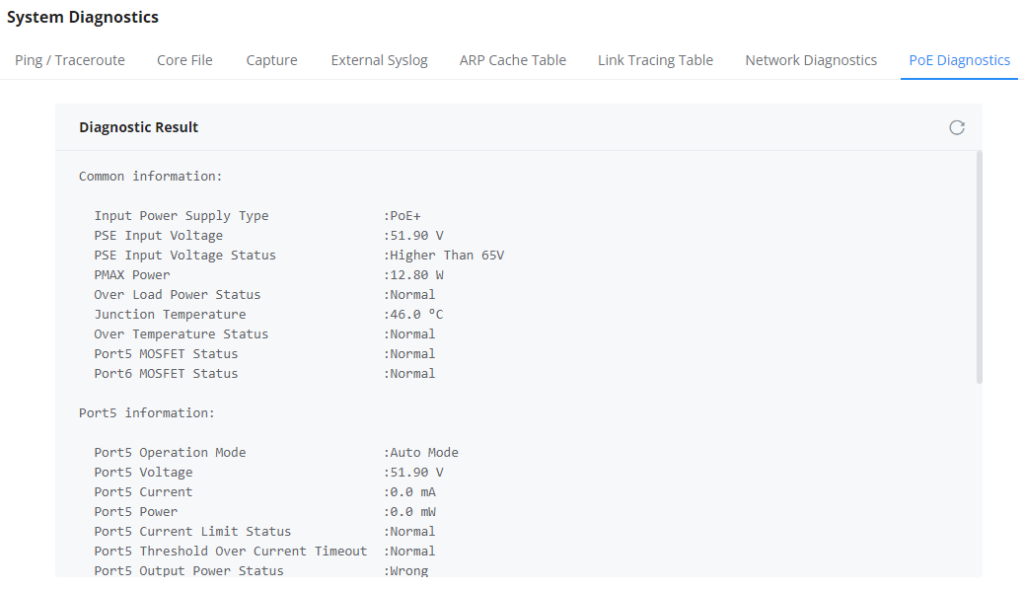
PoE Diagnostics
The PoE Diagnostics page offers insight about the ports and their components as well as the power used and the temperature. The information provided can be useful when the user encounters an issue with the PoE function of the GCC601X(W).
Cloud/Manager Connection Diagnostics
When the GCC601x(W) device is added to GWN.Cloud or GWN Manager, users can check the connection status (connected or not) and even diagnose the problem.
Alerts & Notifications
Alerts
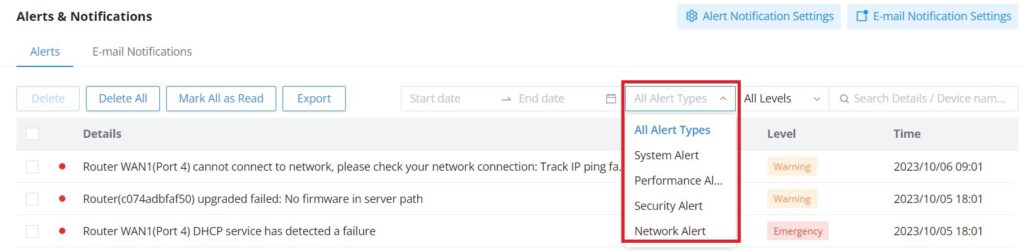
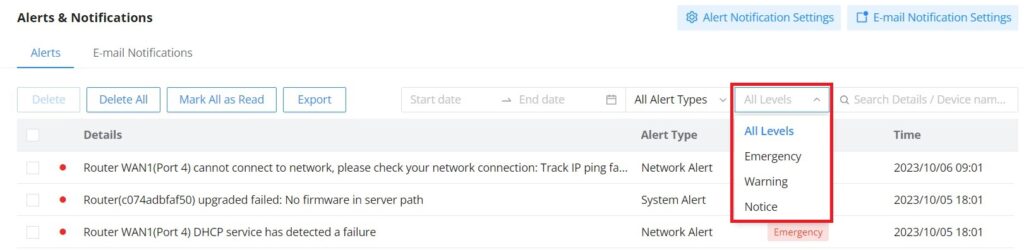
The Alerts page displays alerts about the network, the user can specify to display only certain types like (System, Performance, Security, or Network) or the levels. To check the alerts that have been generated, please navigate to Maintenance → Alerts & Notifications page → Alerts tab.
The alerts can be displayed either by type or level. However, that is not the only way to display them. The user can filter through the alert log using a date interval or search by MAC address or device name.
Alerts Types
The available types are System, Performance, Security, and Network, or the user can choose to display all the types.
Alerts Levels
The user can filter the alert level by the following levels: All Levels, Emergency, Warning or Notice.
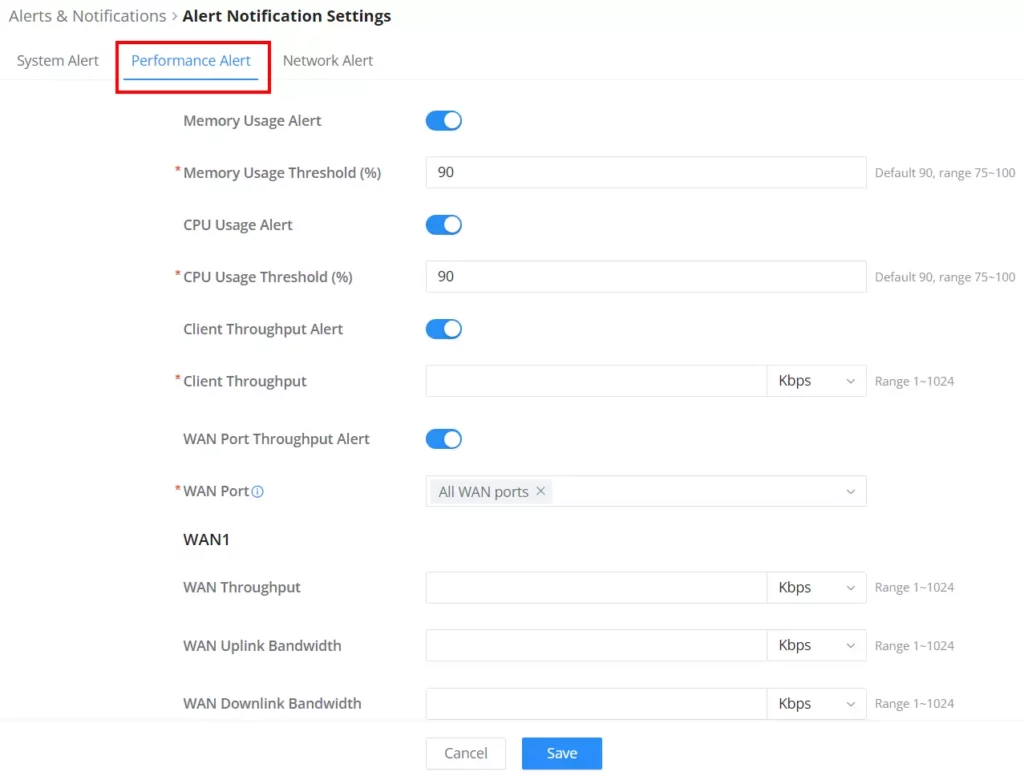
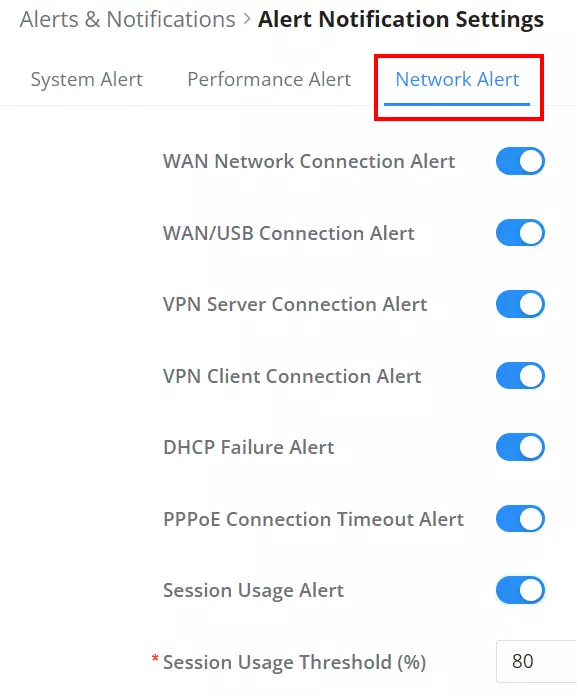
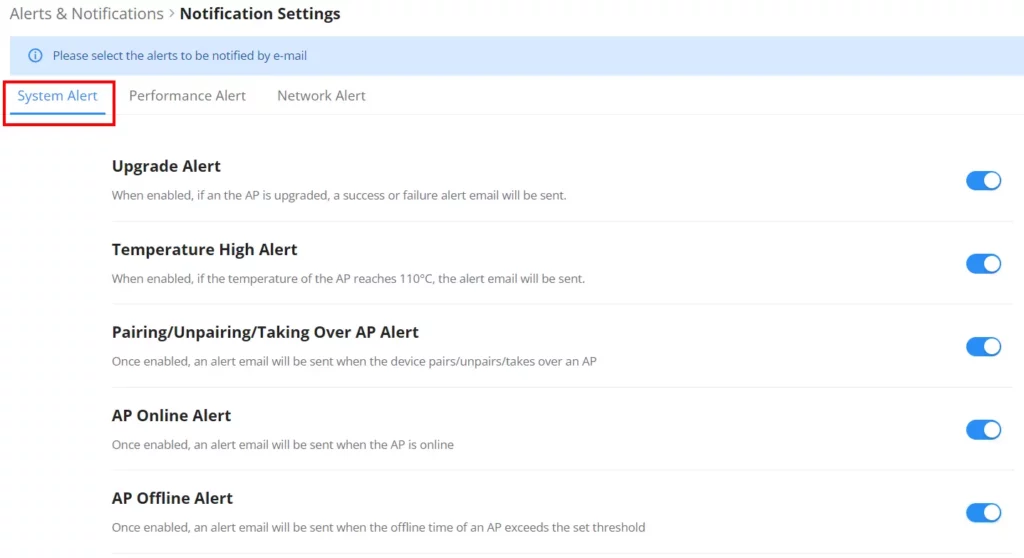
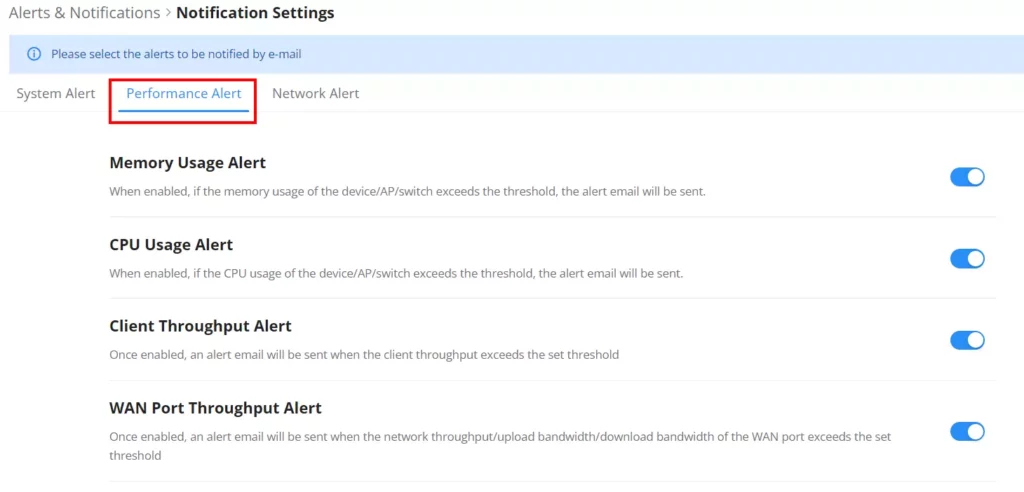
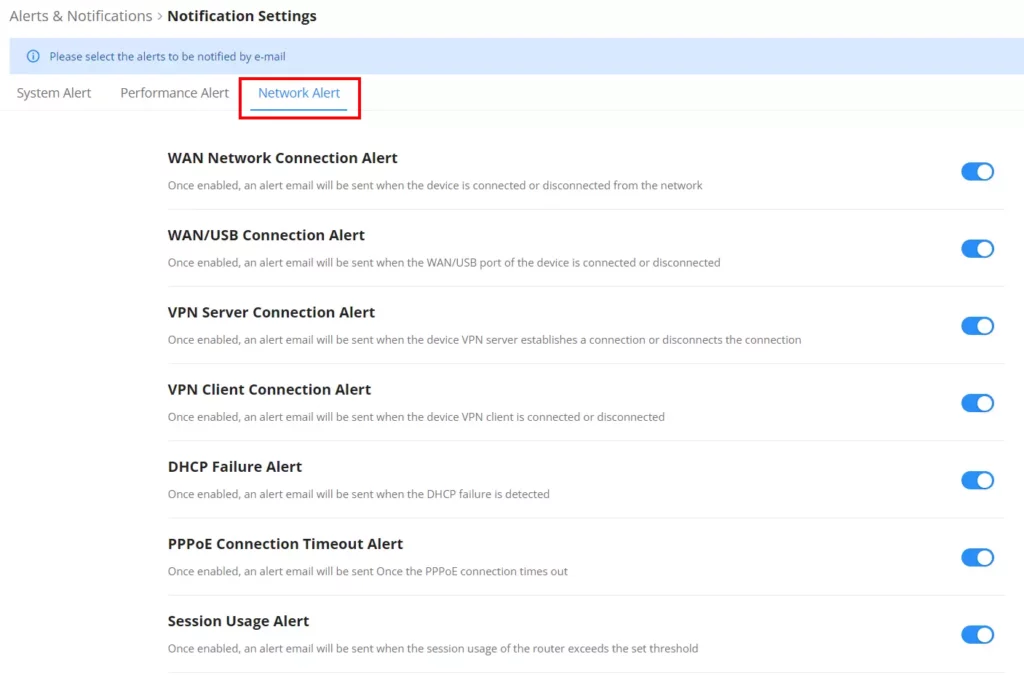
Alert Notification Settings
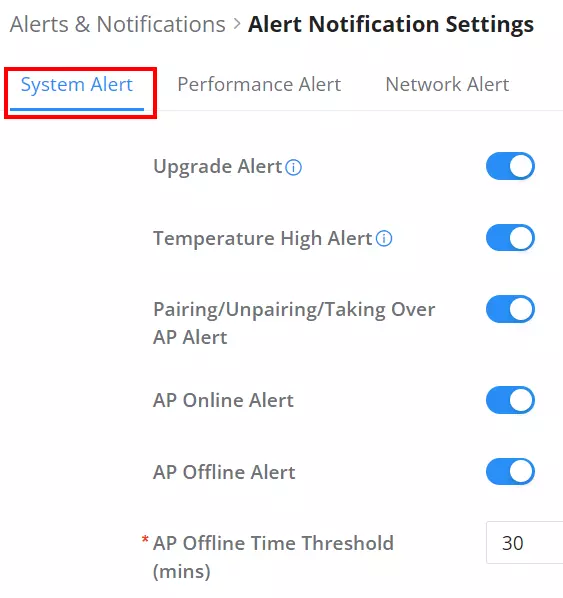
To enable the notifications on the Alerts tab, please click on the “Alert Notification Settings” button as shown below:
The figures below show all the possible alert notifications that the user can enable on the Alerts tab, organized into 4 categories: System Alert, Performance Alert, and Network Alert.
Please refer to the figures below:
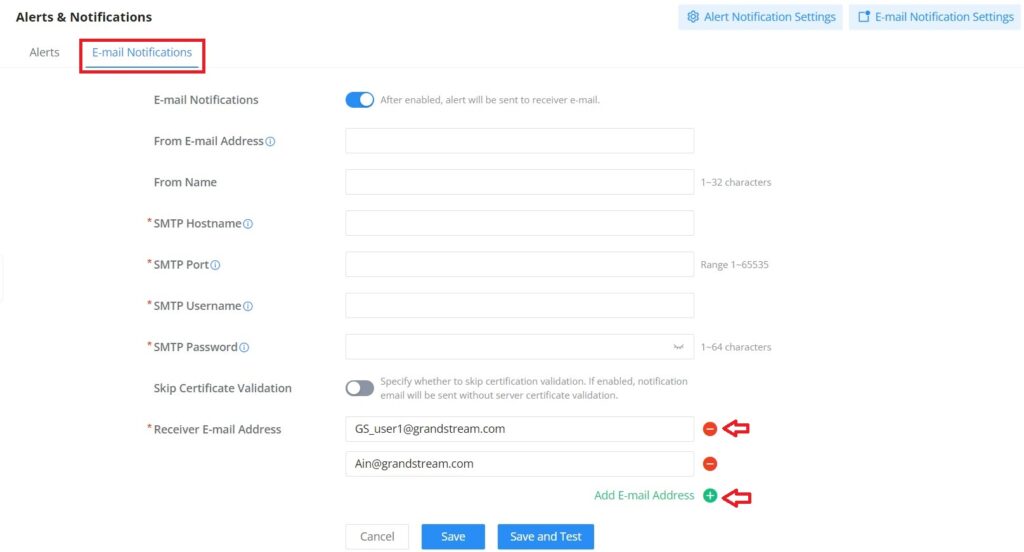
E-mail Notifications
On this tab, the user can set up the E-mails that will receive the notifications, once the feature is enabled, then the user can fill up the fields according to SMTP parameters. Refer to the figure below:
It’s possible to add more than one receiver E-mail address as shown in the figure above.
- Click on the “Minus” icon to delete the receiver’s E-mail address.
- Click on the “Plus” icon to add the receiver’s E-mail address.
E-mail Notification Settings
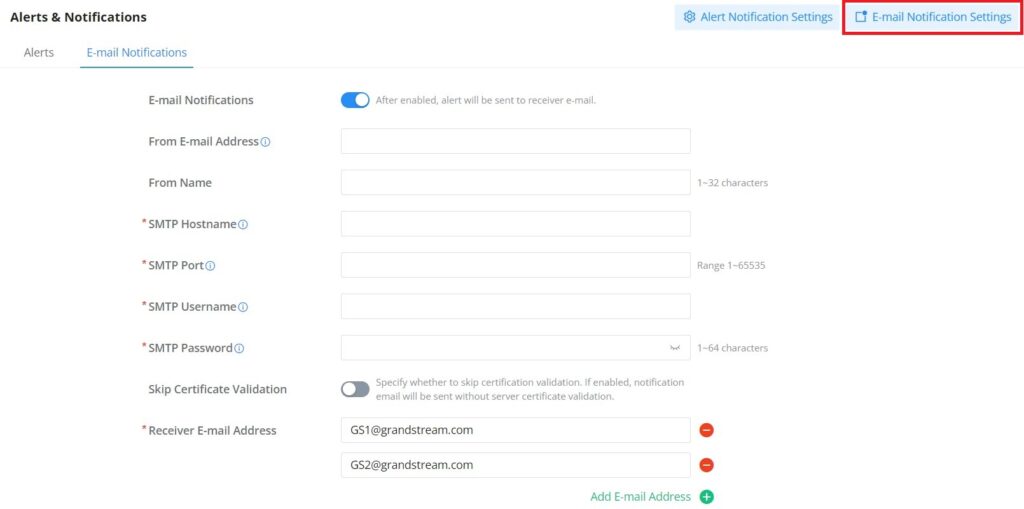
To select what notifications will be sent to the receiver’s E-mail addresses, please click on the “E-mail Notification Settings” button as shown below:
The figures below show all the possible E-mail notifications that the user can send to the pre-configured receiver E-mail Addresses, organized into 4 categories:
- System
- Performance
- Network
SYSTEM SETTINGS
Certificates
CA Certificates
In this section, the user can create a CA certificate. This certificate will authenticate the user when connected to the VPN server created on the device. This authentication will ensure that no identity is being usurped and that the data exchanged remains confidential. To create a certificate, please access the web GUI of the router and access System Settings → Certificates → CA Certificates then click “Add” and fill in the necessary information.
Cert. Name | Enter the Certificate name for the CA. Note: It could be any name to identify this certificate. Example: “CATest”. |
Key Length | Choose the key length for generating the CA certificate. The following values are available:
|
Digest Algorithm | Choose the digest algorithm:
Note: Hash is a one-way function, it cannot be decrypted back. |
Expiration (D) | Enter the validity date for the CA certificate in days. The valid range is 1~999999.. |
Country / Region | Select a country code from the dropdown list. Example: “United Stated of America”. |
State / Province | Enter a state name or province. Example: “Casablanca”. |
City | Enter a city name. Example: “SanBern”. |
Organization | Enter the organization’s name. Example: “GS”. |
Organizational Unit | This field is the name of the department or organization unit making the request. Example: “GS Sales”. |
Enter an email address. Example: “EMEAregion@grandstream.com” |
Add CA Certificate
Certificate
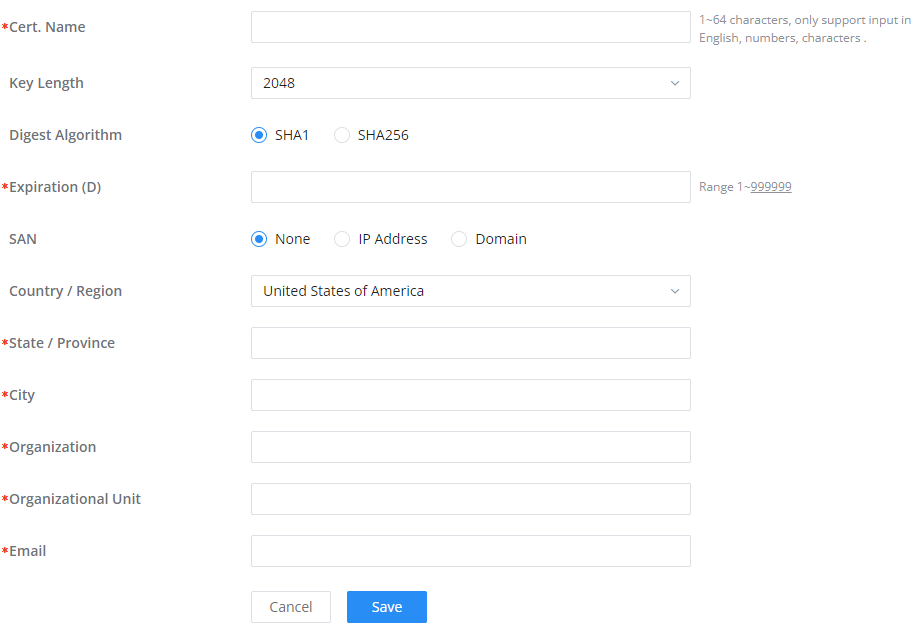
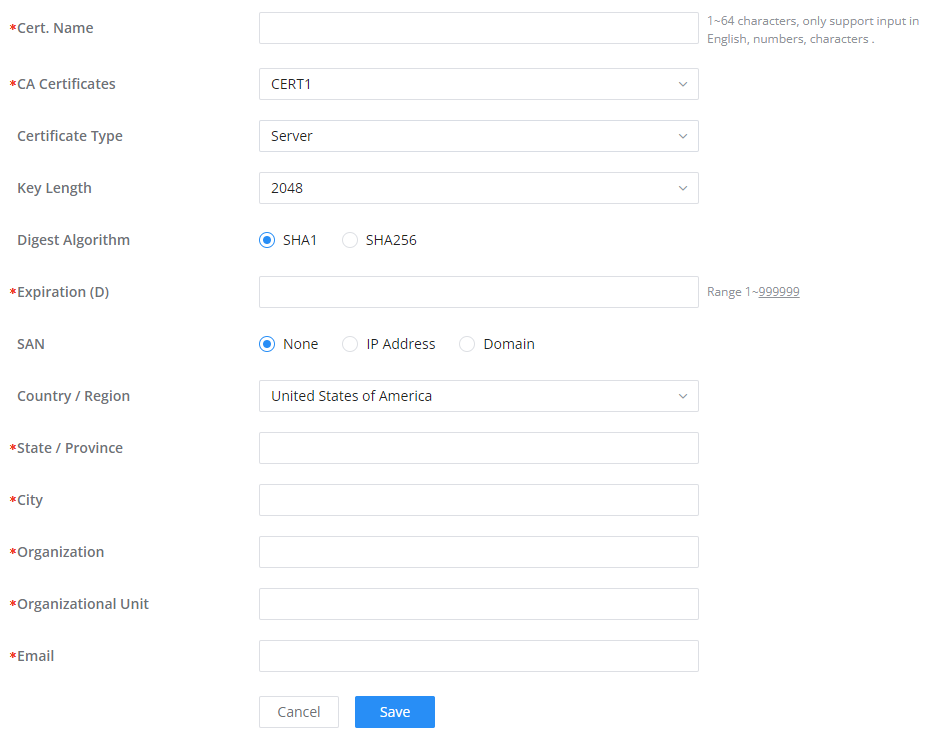
In this section, the user can create a server or a client certificate. To create a certificate please access the web UI of the device, then navigate to System Settings → Certificates → Add Certificate, click “Add“, then enter the necessary information regarding the certificate.
Cert. Name | Enter the certificate's name. |
Key Length | Choose the key length for generating the CA certificate.The following values are available:
|
Digest Algorithm | Select the digest algorithm.
Note: Hash is a one-way function, it cannot be decrypted back. |
Expiration (D) | Select the duration of validity of the certificate. The number entered represents the days that have to elapse before the certificate is considered as expired. The valid range is 1 - 999999. |
SAN | Enter the address IP or the domain name of the SAN (Subject Alternate Name). |
Country / Region | Select a country from the dropdown list of countries. Example: "United States of America". |
State / Province | Enter a state name or a province. Example: California |
City | Enter a city name. Example: "San Diego" |
Organization | Enter the organization’s name. Example: “GS”. |
Organization Unit | This field is the name of the department or organization unit making the request. Example: “GS Sales”. |
Enter an email address. Example: “EMEAregion@grandstream.com” |
Add Certificate
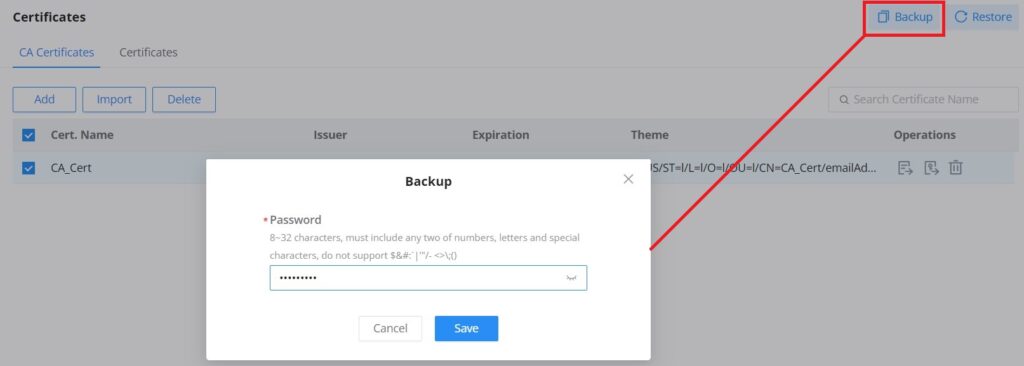
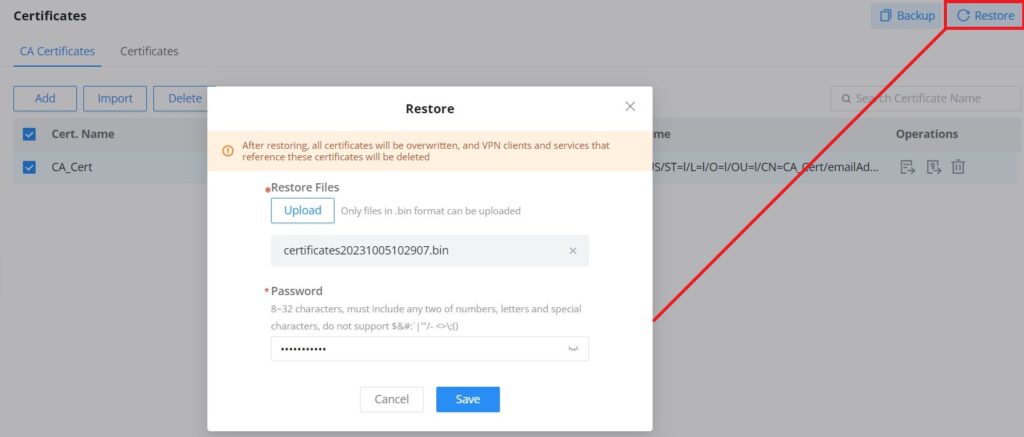
Certificates Backup and Restore
To back up the created certificates, first select all the desired certificates, then click on the “Backup” button and enter a password to protect it as shown below:
To restore a certificate, click on the “Restore” button, then upload the file and enter the password.
File Sharing
The GCC601X(W) devices have a USB port that can be used for file sharing, either using a USB flash drive or a Hard Drive, enabling clients with Windows, Mac, or Linux to access files easily on the local network. There is also an option to enable a password for security reasons.
Navigate to System Settings → File Sharing.
RADIUS
RADIUS is a distributed, client /server information exchange protocol that can protect the network from unauthorized access. It is often used in various network environments that require high security and allow remote users to access it. This protocol defines the UDP-based RADIUS packet format and its transmission mechanism and specifies destination UDP ports 1812 and 1813 as the default authentication and accounting port numbers, respectively.
Radius provides access services through authentication and authorization and collects and records the use of network resources by users through accounting. The main features of RADIUS protocol are client/server mode, secure message exchange mechanism, and good expansibility.
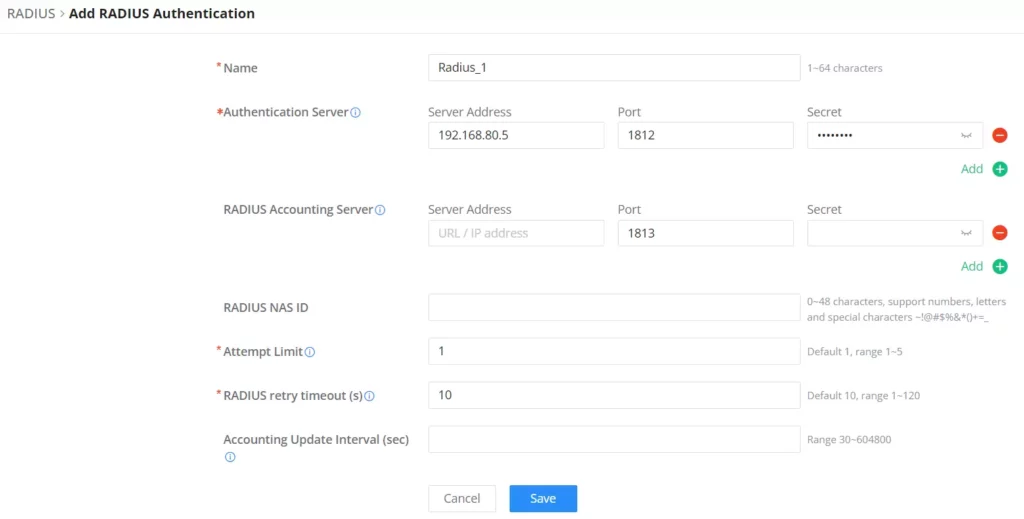
To add a RADIUS to the GCC Networking module, navigate to Networking → System Settings → RADIUS, then click on the “Add” button to add a new RADIUS.
Name | Defines the name of the RADIUS Server |
Authentication Server | The "Authentication server" in RADIUS sets the server responsible for verifying user credentials during network access attempts.The authentication server(s) will be used in the displayed order (top to bottom), and RADIUS servers will be used after these authentication servers, you can define the server address , port number and secret key in the authentification server, you can define up to two authentification servers. |
RADIUS Accounting Server | The RADIUS accounting server specifies the server responsible for logging and tracking user network usage data. you can define up to two RADIUS Accounting Servers |
RADIUS NAS ID | Configure the RADIUS NAS ID with up to 48 characters. Supports alphanumeric characters, special characters "~! @ # ¥%&* () -+=_" and spaces |
Attempt Limit | Sets the max number of packet sending attempts to the RADIUS server |
RADIUS retry timeout (s) | Sets the max time to wait for RADIUS server response before resending RADIUS packets |
Accounting Update Interval (sec) | Sets the frequency for sending accounting updates to the RADIUS server, measured in seconds. Enter a number from 30 to 604800. If the external splash page has also configured this, that other value will take priority. |
Add RADIUS