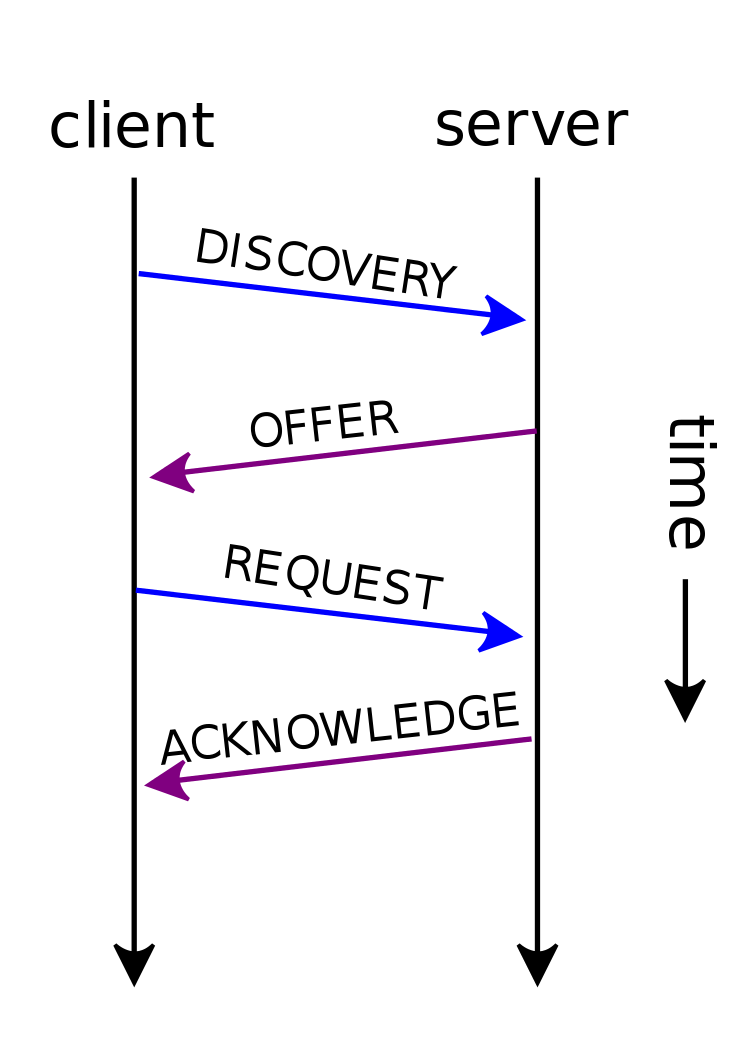
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a standardized network protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for dynamically distributing network configuration parameters, such as IP addresses for interfaces and services. With DHCP, network devices request IP addresses and networking parameters automatically from a DHCP server, reducing the need for a network administrator or a user to configure these settings manually.
DHCP servers can be configured to provide optional data that fully configures TCP/IP on a client. Some of the most common DHCP option types configured and distributed by the DHCP server during leases include default gateway, router, DNS, and WINS parameters.
This guide describes advanced DHCP options supported on Grandstream products. Administrators can use these DHCP options for easy setup, to provide specific configuration per device model, synchronize time with NTP servers, configure ACS server URL on devices and more…
ENVIRONMENT SETUP
This chapter provides steps to setup a minimal test environment to run DHCP options described in this guide. In this guide, we will use isc-dhcp-server on an Ubuntu 12 machine with static IP 192.168.1.11.
Administrators can use other Windows or Linux based DHCP servers at their convenience.
Step 1: Install DHCP Server
- Launch a Linux terminal.
- Login as root by typing sudo su
- Download and install DHCP server using following command: apt-get install isc-dhcp-server

Step 2: DHCP Server Basic Configuration
There are two main files to be configured:
/etc/default/isc-dhcp-server (specify network interface to use for DHCP server)
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf (all DHCP Options in this guide can be defined in dhcpd.conf file)
- Enter nano /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server to edit isc-dhcp-server file
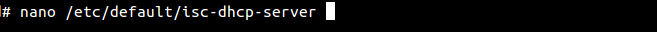
- Replace eth0 with the network interface to use for DHCP server.
- Save and exit the file using Ctrl+X
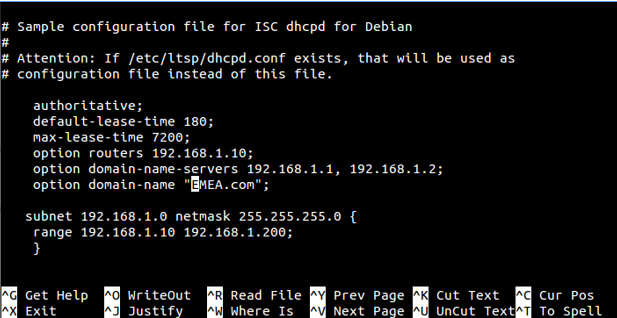
- Enter nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf to edit dhcpd.conf file

- Configure DHCP server with basic options including subnet¸ netmask¸ range…
Screenshot below shows an example of configuration; in this example DHCP server will provide clients IP addresses from range 192.168.1.10 to 192.168.1.200. The server will lease an IP address for 180 seconds if no specific time frame requested by the client; otherwise, maximum (allowed) lease is 7200 seconds. DHCP server will also advise clients to use 255.255.255.0 as subnet mask, 192.168.1.10 as router/gateway, 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.2 as DNS servers.
- Restart DHCP server
Start and Stop DHCP service

DHCP OPTIONS
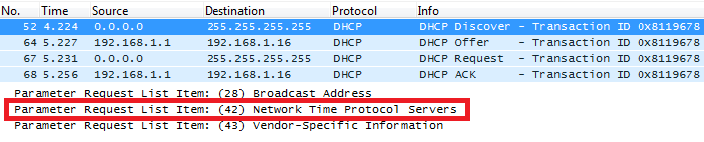
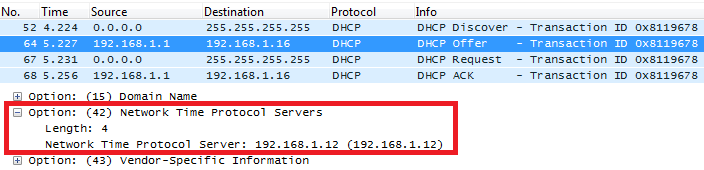
DHCP Option 42 (NTP Server)
Description
DHCP option 42 specifies a list of NTP servers available to the client by IP address.
Please refer to RFC2132 for more details.
Example

Screenshots
Below screenshots of DHCP Discover/Offer for Option 42.
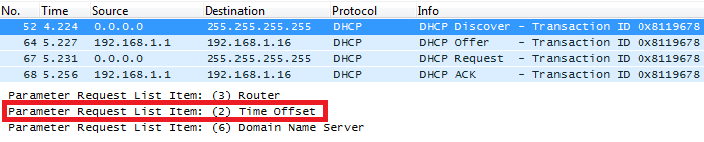
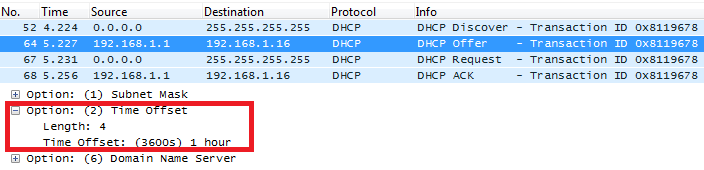
DHCP Option 2 (Time Offset)
Description
DHCP option 2 informs the client about the time zone offset (in seconds).
A positive offset indicates a location east of the zero meridian and a negative offset indicates a location west of the zero meridian.
Please refer to RFC2132 for more details.
Example

In above example, GMT+1 was set as an offset value
(One hour * 60 minutes/hour * 60 seconds/minute) = 3600.
To set Pacific Standard Time (GMT-8). This field would be filled with “-28800”.
(Eight hours * 60 minutes/hour * 60 seconds/minute).
Screenshots
Below screenshots of DHCP Discover/Offer for Option 2
DHCP Option 66 (TFTP Server Name)
Description
DHCP option 66 provides the IP address or the hostname of a single provisioning server where devices will be redirected to get their configuration files. Without this DHCP option, a manual configuration is requested on each phone the first time it boots.
Please refer to RFC2132/RFC5859 for more details.
Example

If http:// is not specified, default TFTP protocol is used for configured server.
Screenshots
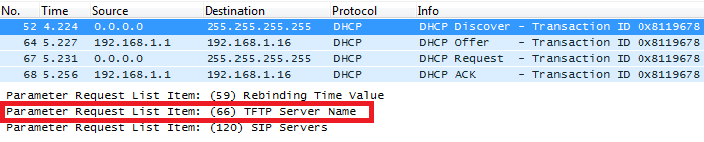
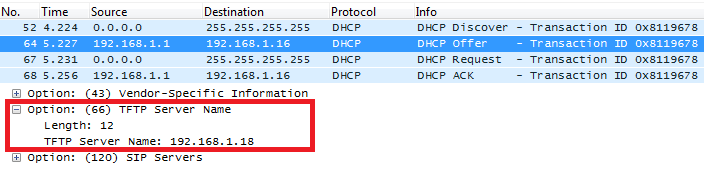
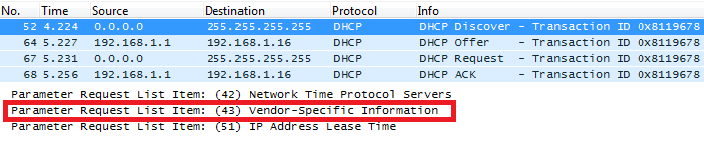
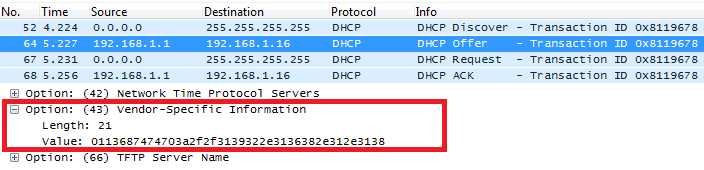
DHCP Option 43 (Vendor Specific Information)
Description
This option is used by clients and servers to exchange vendor-specific information.
DHCP server can send one or more vendor specific parameters to clients, encoded in the form option_code/value_length/value in hexadecimal format.
Please refer to RFC2132 for more details.
Example
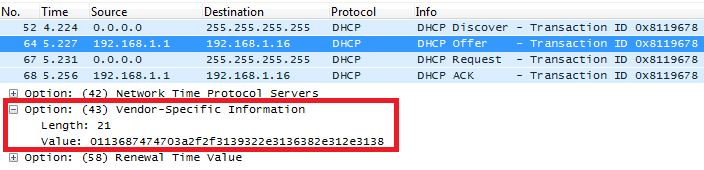
In following example, DHCP server is configured to send CWMP information (ACS URL http://192.168.1.18) encapsulated in option 43.

Above DHCP option 43 contains the following:
0x01 (CWMP option for ACS URL)
0x13 (hex of decimal 19 = length of the URL)
19 bytes forming the URL in hexadecimal format (http://192.168.1.18)
Screenshots
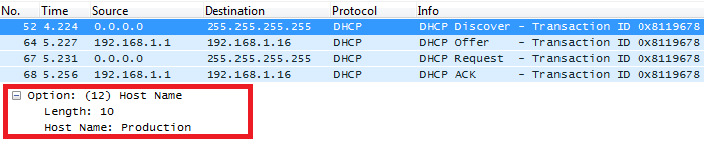
DHCP Option 12 (Host Name)
Description
This option specifies the name of the client.
Option 12 is used to identify the client’s name against the DHCP server in order to make special configuration from the server side, this is similar to option 60 and 125.
Please refer to RFC1533/RFC2132 for more details
Screenshots
Below screenshot is taken from GXP2170, the value of Option 12 can be modified from the WebGUI under Network Settings > Basic Settings.
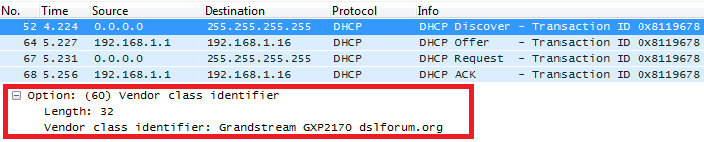
DHCP Option 60 (Vendor Class Identifier)
Description
Option 60 is used by clients to optionally identify the vendor type and configuration of a DHCP client.
When using multiple devices from different vendors, DHCP server can provide specific configuration for each client based on received Option 60.
Please refer to RFC1533/RFC2132 for more details.
Example
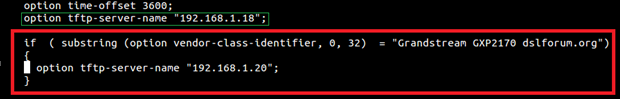
In following example, option 60 is configured to identify GXP2170 with its value “Grandstream GXP2170 dslforum.org”.
If option 60 received matches the one configured, GXP2170 phones will get option 66 (tftp-server-name) with value 192.168.1.20. For all other clients, they will get option 66 with value 192.168.1.18
Screenshots
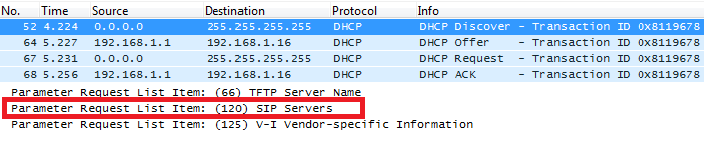
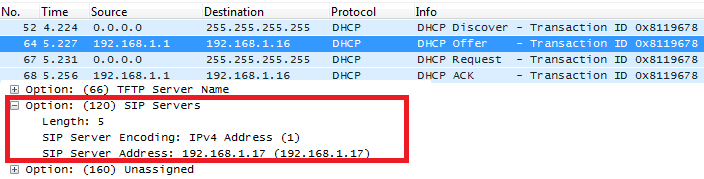
DHCP Option 120 (SIP Server)
Description
The option is used to provide SIP server IP address or FQDN to SIP clients.
Please refer to RFC3361 for more details.
Example

Screenshots
DHCP Option 125 (Vendor-Identifying Vendor Options)
Description
DHCP clients may use this option to identify the vendor that manufactured the hardware on which the client is running the software in use in a unique way.
Option 125 is similar to option 12 & 60 but advertising more parameters of a device:
- DeviceManufacturerOUI
- DeviceSerialNumber (Grandstream products set DeviceSerialNumber with MAC address)
- DeviceProductClass
Please refer to RFC3925 for more details.
Screenshots
During DHCP initiation, DHCP Discover/DHCP Request including option 125 are sent from client, the server checks V-I Vendor-specific information, if matching configured values, specific configuration will be provided to client, otherwise, common configuration is provided to client.
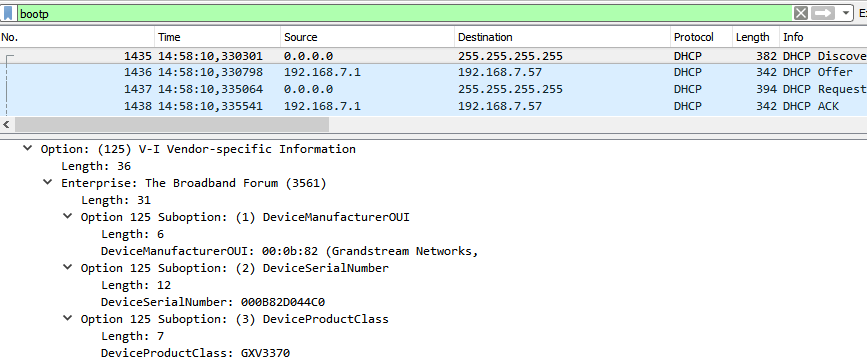
Advertised information in above option 125 are:
- DeviceManufacturerOUI = 000b82
- DeviceSerialNumber = DeviceMACaddress = 000b82XXXXXX
- DeviceProductClass = GXV3370
DHCP Option 132 (Vlan ID)
Description
This option allows to assign a VLAN ID tag to devices during booting stage/DHCP renewal.
Please refer to RFC4578 / IEEE_802.1Q for more details.
Example

Screenshots
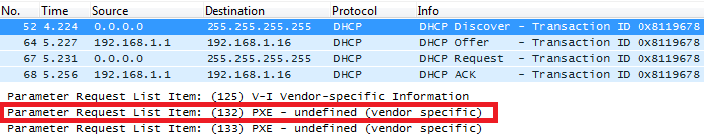
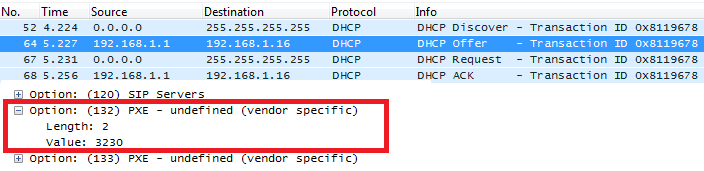
In above screenshot, value 3230 is 20 (vlan-id) converted from text to hexadecimal.
DHCP Option 133 (QoS priority level)
Description
This option assigns the priority within an Ethernet frame header when using VLAN tag, it specifies a priority value between 0 and 7 to differentiate the traffic priority.
Please refer to RFC4578 / IEEE_P802.1p for more details
Example

Screenshots
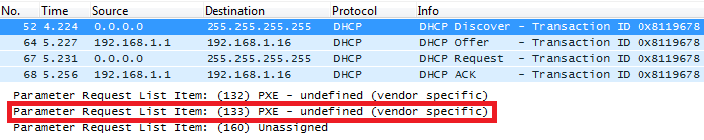
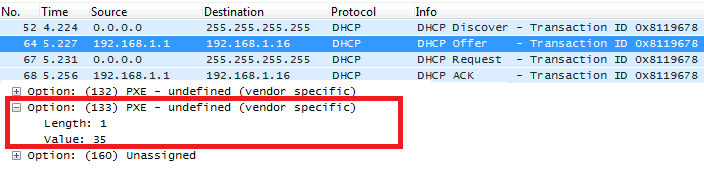
In above screenshot, value 35 is 5 (priority level) converted from text to hexadecimal.
DHCP Option 150 (TFTP Servers List)
Description
DHCP option 150 provides one or more IP addresses of TFTP server(s) where devices will be redirected to download their configuration files. Without this DHCP option, a manual configuration is requested on each phone the first time it boots.
Please refer to RFC5859 for more details.
Example

Screenshots
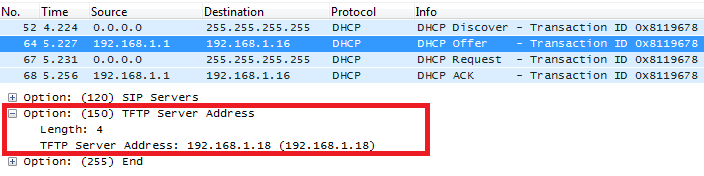
DHCP Option 160 (Configuration Server Address)
Description
Similar to option 66, DHCP option 160 can provide one or more configuration server(s) to clients to get automatically provisioned. Without this DHCP option, a manual configuration is requested on each phone the first time it boots.
Example

Screenshots
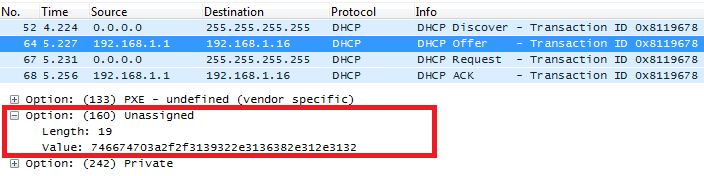
In above screenshot, the value of the TFTP server was converted to hexadecimal. The phone contacts this IP address to get provisioned after receiving TFTP server value.
DHCP Option 242 (Avaya IP Phones)
Description
Once this option enabled, the phone will use configuration info issued by DHCP sever.
Option 242 can include following parameters:
- MC IP address
- VLAN configuration
- HTTP server, Proxy
- Transport Protocol
Example

Screenshots
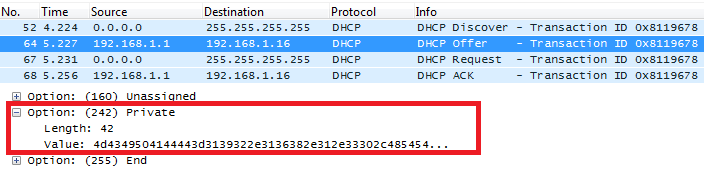
In above screenshot, MCIPADD and HTTPSRVR are converted to hexadecimal.
SUPPORTED DEVICES
Following table shows Grandstream products supporting DHCP Options:
DHCP Options | Grandstream Models | ||||||||||
GXP16XX | GXP17XX | GXP21XX | GRP261X | GRP260X | GVC320X | GAC2500 | GXV33XX | GXW42XX | HT8XX | DP75X | |
Option 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 12 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 42 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 43 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 60 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 66 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 120 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 125 | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 132 | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
Option 133 | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
Option 150 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
Option 160 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
Option 242 | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |