OVERVIEW
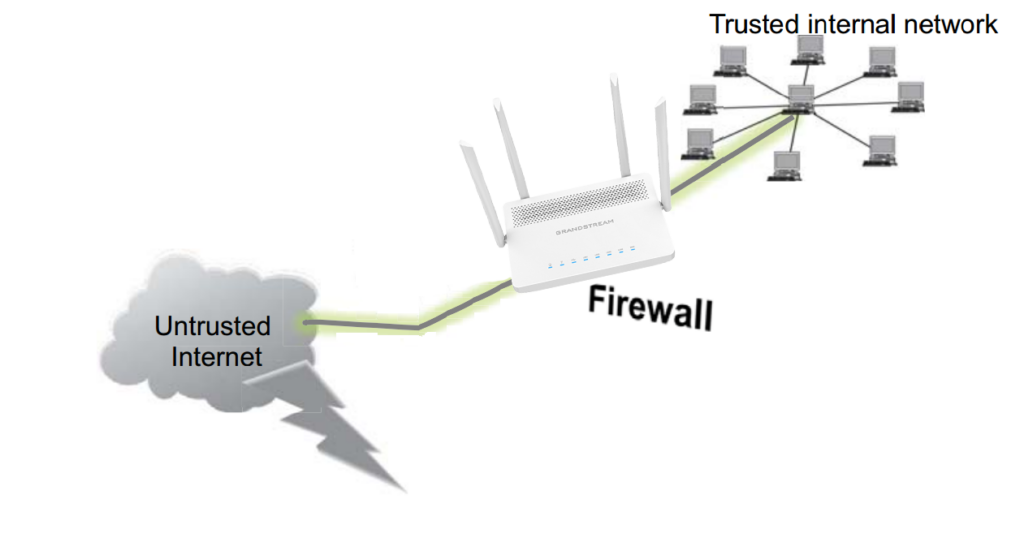
A firewall is a system of security measures intended to prevent unauthorized access to a networked computer system. Like walls in building construction, their purpose is to create a barrier between different “networks” or “compartments.” By utilizing predefined firewall policies, a firewall can filter incoming or outgoing traffic to safeguard private networks and individual machines from Internet threats.
The GWN7052(F)/GWN7062 Firewall offers Basic Settings to:
- Flush Connection Reload
- Establish Protection against Simple DoS Attacks,
- Manage Rules and Policies such as MSS Clamping and IP Masquerading.
This guide offers an overview and instructions for configuring the GWN7052(F)/GWN7062’s basic firewall features, which are accessible via the “Firewall → Basic” menu.
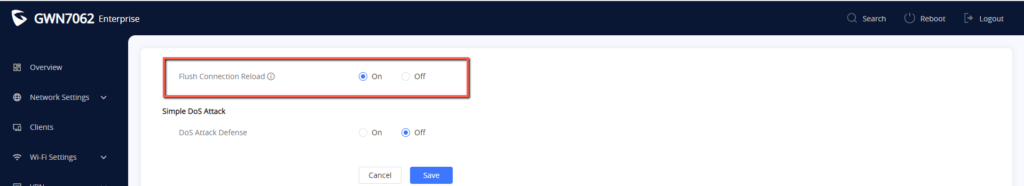
Flush Connection Reload
Overview
The “Flush Connection Reload” option results in the termination of existing connections that were authorized by the previous firewall rules when a firewall configuration change is made. The rationale behind this is to prevent reconnection in cases where the new firewall rules do not authorize a connection that had been previously established. If the option is disabled, existing connections are allowed to persist until they expire, regardless of whether the new rules would prohibit the connection’s establishment.
Configuration
To activate this option simply access the Basic Settings under Firewall and enable the “Flush Connection Reload” feature, it is enabled by default
Simple DoS Attack
Overview
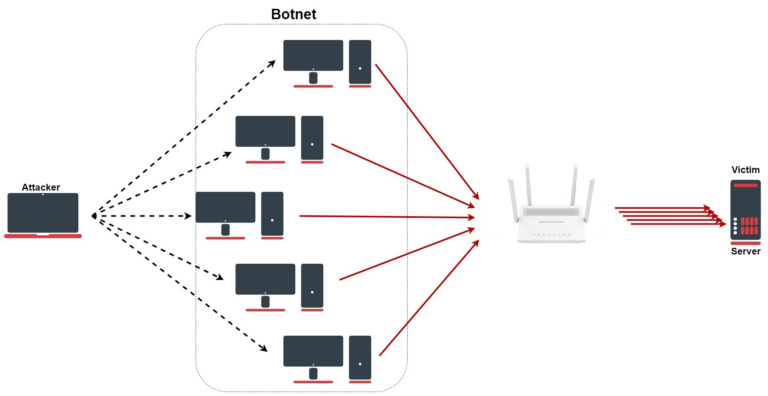
A Simple DoS (Denial of Service) attack is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker attempts to disrupt the normal functioning of a website, server, or network by overwhelming it with traffic or other requests. The goal of this attack is to make the targeted system unavailable to its users.
In a Simple DoS attack, the attacker typically sends a large number of requests to the target system or floods it with traffic, causing it to crash or become unresponsive. This can be accomplished using a variety of techniques, including sending large numbers of connection requests, flooding the network with data packets, or overwhelming the target with requests for processing power or memory.
Simple DoS attacks are relatively easy to execute, and they can be carried out with relatively simple tools and techniques. They are often used by cybercriminals to extort money from businesses by threatening to take down their websites or networks. They can also be used by political activists or hacktivists to disrupt the operations of organizations or governments.
To protect against Simple DoS attacks, organizations can implement various security measures, such as firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, among these measures.
We will explore the DoS Attack Defense options available on the GWN7052(F)/GWN7062 routers.
Configuration
We will go through the recommended configurations to establish a DoS Attack Defense.
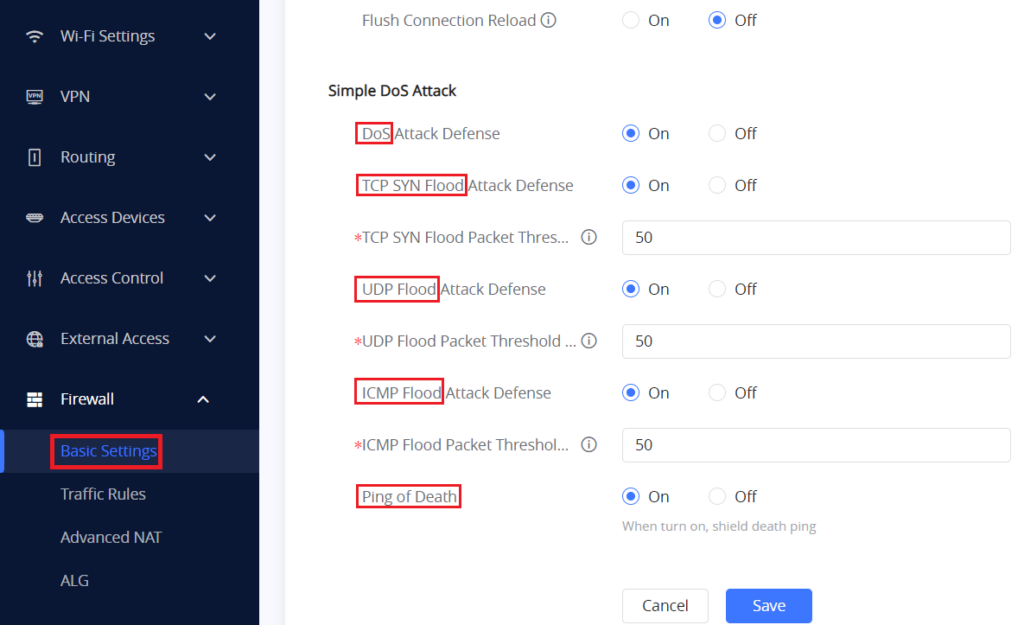
DoS Attack Defense includes:
- TCP SYN Flood Attack Defense.
- UDP Flood Attack Defense.
- ICMP Flood Attack Defense.
- Ping of Death.
TCP SYN Flood Attack Defense
TCP SYN flood (a.k.a. SYN flood) is a type of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack that exploits part of the normal TCP three-way handshake to consume resources on the targeted server and makes it unresponsive.
Essentially, with SYN flood DDoS, the offender sends TCP connection requests faster than the targeted machine can process them, causing network saturation.
- TCP SYN Flood Packet Threshold (Packets/s)
This option sets the threshold for the number of incomplete connection attempts per second before the device drops the packets.
The Default value in the GWN7052(F)/GWN7062 is 50 packets per second, and the valid range is 1-10000.
UDP Flood Attack Defense
“UDP flood” is a type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack in which the attacker overwhelms random ports on the targeted host with IP packets containing UDP datagrams.
The receiving host checks for applications associated with these datagrams and—finding none—sends back a “Destination Unreachable” packet. As more and more UDP packets are received and answered, the system becomes overwhelmed and unresponsive to other clients.
- UDP Flood Packet Threshold (packets/s)
This option defines that the defense attack immediately starts after the UDP package reaches the threshold.
The default value is 50 packets per second and the valid range is 1-10000.
ICMP Flood Attack Defense
An Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) flood attack is a commonly distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack where malicious actors try to overwhelm a server or network device with ICMP pings or echo-request packets. Typically, ICMP pings are used to determine the health of a device and its connection to it.
By overwhelming a targeted device with ICMP flood DDoS attacks, a device loses its ability to respond with an equal number of reply packets, consuming too many resources and rendering the device unable to function properly.
- ICMP Flood Packet Threshold (packets/s)
This parameter will specify a threshold for inbound ICMP packets. If the number of inbound ICMP packets destined for one single IP address per second exceeds the threshold, the system will identify the traffic as an ICMP flood and take the specified action.
The default value is 50 packets per second, Valid range is 1-10000.
Ping of Death
Ping of Death (a.k.a. PoD) is a type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack in which an attacker attempts to crash, destabilize, or freeze the targeted computer or service by sending malformed or oversized packets using a simple ping command.
While PoD attacks exploit legacy weaknesses that may have been patched in target systems. However, in an unpatched system, the attack is still relevant and dangerous. Recently, a new type of PoD attack has become popular. In this attack, commonly known as a Ping flood, the targeted system is hit with ICMP packets sent rapidly via ping without waiting for replies.
Rules Policy
Overview
In GWN7052(F)/GWN7062, a list of rules policies can be defined for inbound and Outbound policies and as well as the IP Masquerading, MSS Clamping, Log Drop / Reject Traffic, and Traffic limit.
Configuration
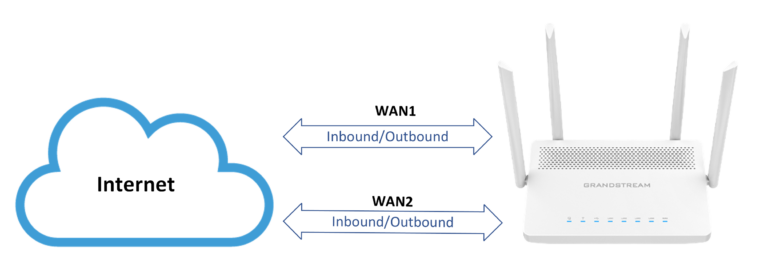
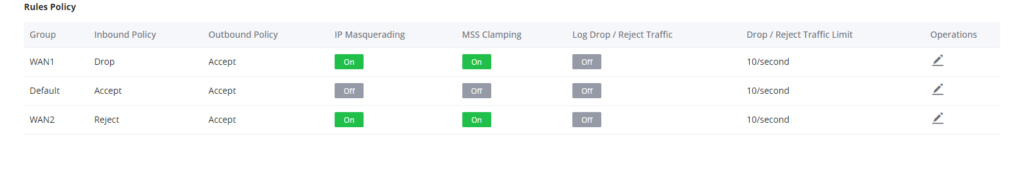
By default, there will be Rules and Policies created for the Default VLAN interface and for each WAN interface in the router separately.
In the example below we have the default rules policies added in a GWN7062 router that has dual band activated (WAN1 and LAN/WAN2), in addition to the Default LAN.
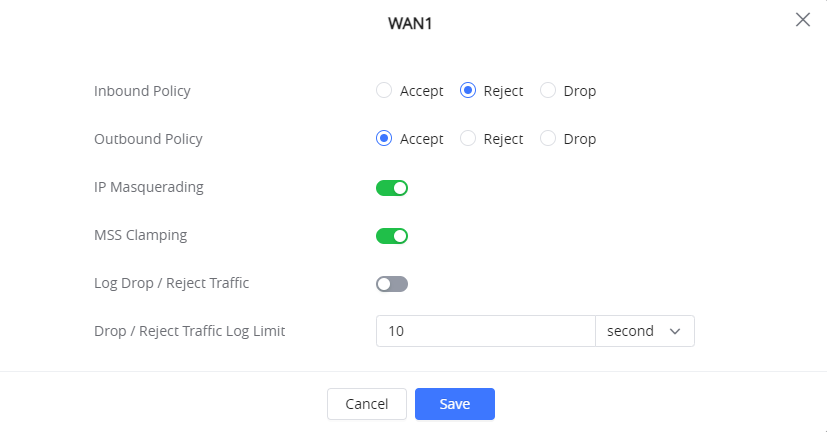
To configure the available parameters manually, click the icon and the following window will pop up :
For each Group Policy, the following can be defined :
- Inbound Policy: this option chooses whether to accept, Reject or Drop the Inbound Traffic coming onto the Router.
- Outbound policy: Outbound firewall policies on the other hand protect against outgoing traffic, originating inside a network.
- IP Masquerading: IP masquerading is a technique used to allow devices on a private network to communicate with devices on the public internet by translating the private IP addresses into a single public IP address. This is achieved by modifying the source IP address of outgoing network traffic with the IP address of the masquerading host. In other words, IP masquerading disguises the true identity of a device on a private network by making it appear as though it is communicating from a different IP address, thereby allowing it to communicate with devices on the internet while keeping its private IP address hidden. This technique is commonly used in network address translation (NAT) and firewall systems.
- MSS Clamping: When packets are transferred over a network with a smaller maximum transmission unit (MTU) size, MSS Clamping is a technique used to modify the maximum segment size (MSS) value in TCP packets. The MSS, which is the maximum amount of data that can be sent across a single TCP segment, is normally agreed upon by two endpoints during the initial handshake. A TCP segment must be divided into smaller pieces when it is greater than the network’s MTU size, which can affect performance and raise the possibility of packet loss or corruption, To make the segment size less than the network’s MTU size, MSS Clamping modifies the MSS value in the TCP header to a lower value than what is agreed upon during the handshake phase. This improves performance and lowers the chance of packet loss or corruption by enabling the TCP segment to be transmitted without fragmentation. Devices used in networks, like routers and firewalls, frequently employ MSS clamping.
- Log Drop / Reject Traffic: Drop/Reject Log The term “traffic” refers to network communication that a firewall or other network device discards or blocks and records in a log file for analysis or troubleshooting. A device like a firewall receives network traffic, which is then inspected in accordance with a set of rules and policies. The device will discard the communication and prevent it from reaching its intended destination if it complies with any criteria that specify that it should be dropped or rejected. The device will also keep track of the dropped or rejected traffic’s source and destination addresses as well as the reason why in a log file at the same time, The log file can then be used to look into security incidents or troubleshoot network problems. For example, if a particular IP address is consistently being dropped or rejected by the firewall, it could indicate that the IP address is part of a known malicious network or that there is an issue with the configuration of the firewall. Network administrators can take appropriate actions to address security concerns or optimize network performance by analyzing log files.
- Drop / Reject Traffic Log Limit: Drop/Reject Traffic Log Limit refers to the maximum number of log entries that a network device, such as a firewall, can record when traffic is dropped or rejected. When a network device drops or rejects traffic, it logs the information in a log file, the GWN7052(F)/GWN7062 has this configuration setting to restrict the amount of traffic that can be logged when it is dropped or rejected in order to avoid these problems. This limit is typically specified as a maximum number of log entries or a maximum size for the log file.