A redundant server is mostly used to assure the reliability of an end point’s service when it loses connectivity with the primary server.
Configuring a redundant server is recommended for medium and large VoIP deployment installations.
Users can then keep using the service on their end points when the main server cannot be reached, service is down or when administrators need to do maintenance tasks on it.
This guide will outline the use and configuration of redundant SIP server on Grandstream GXP IP Phones.
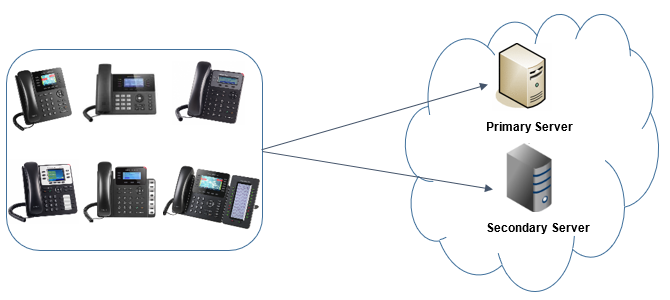
SIP SERVER REDUNDANCY
Grandstream GXP IP phones will send REGISTER requests and SUBSCRIBE messages (except for message waiting) to both primary and secondary SIP servers for the same account, when both primary and secondary SIP servers are configured.
When making a call, the phone will use the registered primary SIP server first. If not available, the secondary SIP server will be used instead.
Requirements
- A SIP end point supporting primary and secondary SIP server configuration options under its SIP account(s)/Profile(s).
- Two SIP servers having the same extension’s credentials.
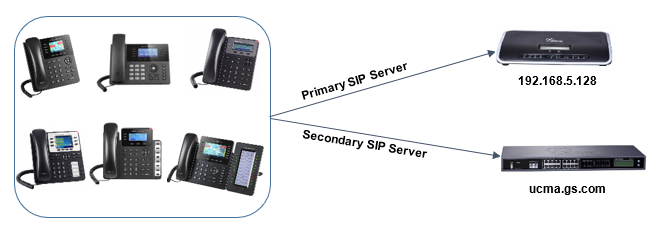
Configuration on GXP phones
The following shows usage and configuration of primary and secondary SIP server using a GXP2130 web interface as example:
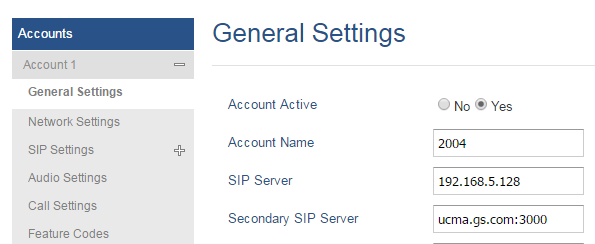
- Access web interface and go to Accounts 🡪 Account X 🡪 General Settings.
- Enter the “IP Address: Port” or “FQDN: Port” of your primary SIP server in SIP Server field.
- Enter the “IP Address: Port” or “FQDN: Port” of your secondary SIP server in Secondary SIP Server field.
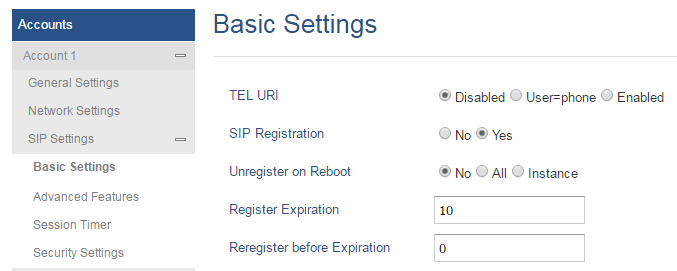
- (Optional) Administrator can also change Register Expiration and Reregister before Expiration values so the end point can check and refresh its registration accordingly with set values (in minutes for Register Expirations and in seconds for Reregister before Expiration).
In the below figure Register Expiration is set to 10 minutes, while Reregister before Expiration will not be used (set to 0 second).
Phone Behavior against Servers Availability
In above example, GXP2130 will send two SIP REGISTER requests to the IP/FQDN configured in SIP Server and Secondary SIP server fields.
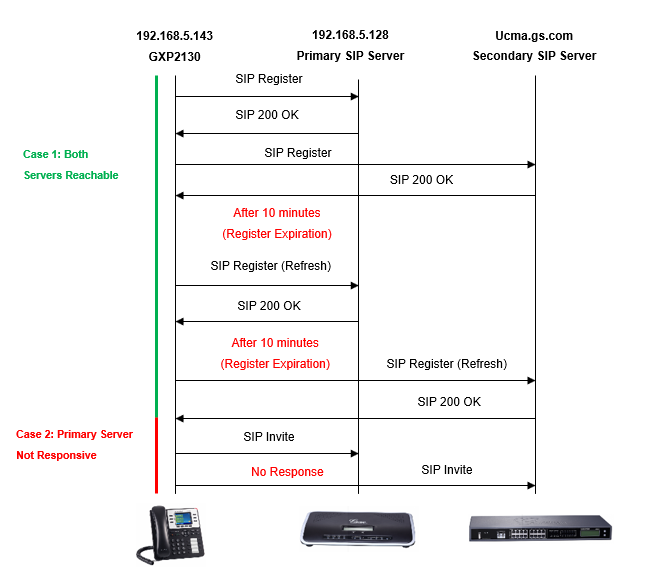
Case 1: Both Servers Reachable
If both SIP Server and Secondary SIP Server are reachable, the phone will register on both servers.
The phone will always use the primary server for calls, and refresh its registration each Register Expiration period (10 minutes in above example) to ensure that both servers are still reachable.
Case 2: Primary Server Not Responsive
If primary SIP Server is not responsive, the phone will use Secondary SIP Server for phone services instead (including making/receiving calls).
Flow Examples
The following figure shows SIP flow example between Grandstream IP phone (GXP2130 in this example) and primary/secondary SIP Servers. The flow shows successful registration on both primary and secondary SIP servers (case 1: both servers reachable) and also when the primary SIP server becomes unresponsive (case 2: primary SIP server not responsive) to the SIP INVITE.
SUPPORTED DEVICES
| Model | Supported | Firmware |
|---|---|---|
GXP16xx Series | Yes | 1.0.4.6 or higher |
GXP17xx Series | Yes | 1.0.0.37 or higher |
GXP21xx Series | Yes | 1.0.7.25 or higher |