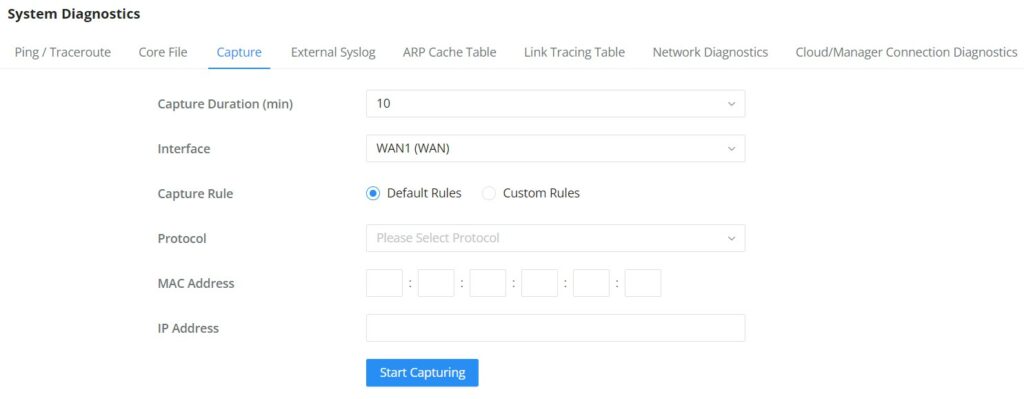
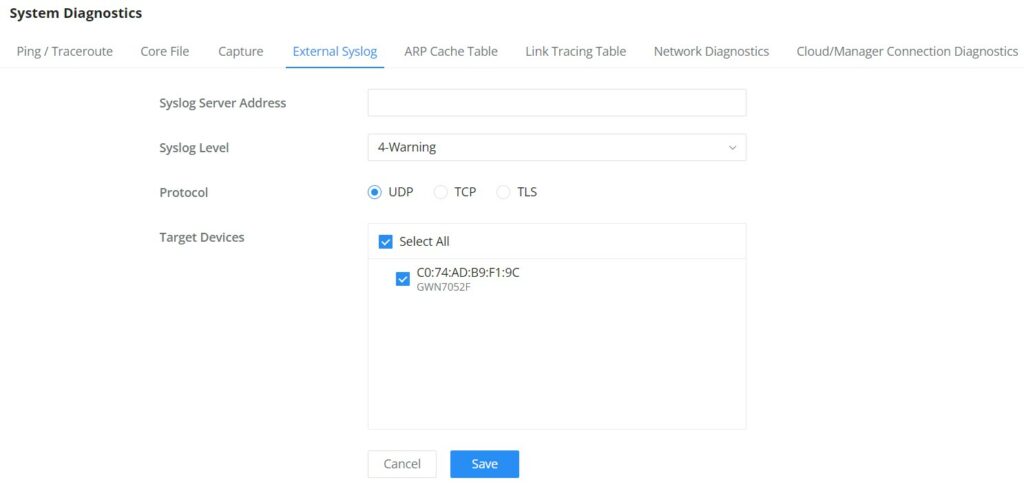
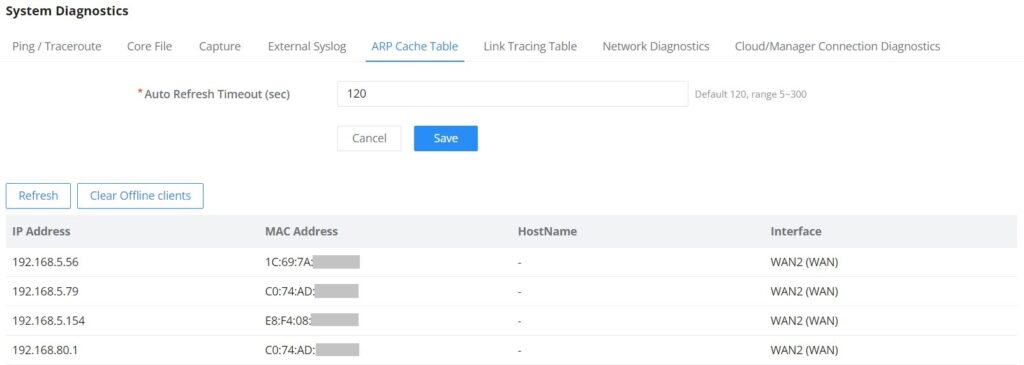
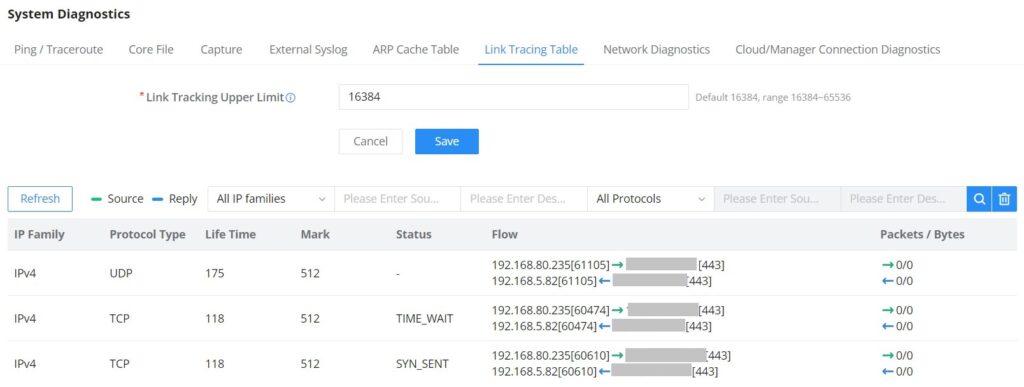
Grandstream GWN70x2 offers secure routers ideal for small offices, home offices, and remote workers, the GWN7052/GWN7052F are dual-band Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) routers providing Wi-Fi speeds of up to 1.266 Gbps and up to 100 wireless devices, while the GWN7062 is a dual-band Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) router with DL/UL OFDMA technology. It features a powerful 64-bit 1.2GHz quad-core processor to provide blazing fast Wi-Fi speeds up to 1.77 Gbps with 4 times increased data capacity to 256 wireless devices. The GWN70x2 routers can power smart offices, and allow smooth 4K Ultra HD streaming, web meetings, video conferences, and more. They support enterprise-grade security features to ensure secure Wi-Fi and VPN access, they also include a built-in controller embedded within the product’s web user interface. By combining accelerated Wi-Fi speeds, mesh networking, and wired AP connections with advanced features including VPN and advanced QoS, Grandstream GWN70x2 are the ideal routers for a growing home and business network.
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Technical Specifications
○ GWN7052/GWN7052F
GWN7052 | GWN7052F | |
Memory and NAT Sessions |
|
|
NAT Routing & IPSec VPN Performance |
| |
Wi-Fi Standards | IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac | |
Antennas | 4 individual external antennas, 2 per band
| |
Wi-Fi Data Rates | 5G: | |
Frequency Bands |
*Not all frequency bands can be used in all regions | |
Channel Bandwidth |
| |
Wi-Fi and System Security | WPA/WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2 Enterprise (TKIP/AES); WPA3, anti-hacking secure boot and critical data/control lockdown via digital signatures, unique security certificate and random default password per device | |
MIMO |
| |
Maximum TX Power |
*Maximum power varies by country, frequency band and MCS rate | |
Receiver Sensitivity | 2.4G
5G
| |
SSIDs | 16 SSIDs total *8 per radio (2.4ghz and 5ghz) | |
Concurrent Clients | Up to 100 concurrent clients | |
Network Interfaces |
|
|
Number of VLANs Supported | Create up to 8 VLANs | |
Auxiliary Ports |
| |
Mounting |
| |
LEDs |
| |
Network Protocols | IPv4, IPv6, 802.1Q, 802.1p, 802.1x, 802.11e/WMM | |
QoS | 802.11e/WMM, VLAN, TOS | |
Firewall | DDNS, Port Forwarding, DMZ, UPnP, Anti-DoS, traffic rules, NAT, ALG | |
VPN |
| |
Network Management | GWN7052 embedded controller can manage itself | GWN7052F embedded controller can manage itself |
Power & Green Energy Efficiency | Universal power adaptor included: | |
Environmental | Operation: 0°Cto 50°C | |
Physical |
| |
Package Content |
| |
GWN7052/GWN7052F Technical Specifications
○ GWN7062
Wi-Fi Standards | IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax |
Antennas | 4 individual internal antennas, 2 per band
|
Wi-Fi Data Rates | 5G:
2.4G:
*Actual throughput may vary depending on many factors including environmental conditions, distance between devices, radio interference in the operating environment and mix of devices in the network |
Frequency Bands |
(2412-2472MHz are channel central frequency range; 2400-2483.5MHz is Frequency band)
*Not all frequency bands can be used in all regions |
Channel Bandwidth |
|
Wi-Fi and System Security | WPA/WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2 Enterprise (TKIP/AES); WPA3, anti-hacking secure boot and critical data/control lockdown via digital signatures, unique security certificate and random default password per device |
MIMO |
|
Coverage Range | Up to 175 meters |
Maximum TX Power |
*Maximum power varies by country, frequency band and MCS rate |
Receiver Sensitivity | 2.4G
5G
|
SSIDs | 32 SSIDs total *16 per radio (2.4GHz & 5GHz) |
Concurrent Wireless Clients | Up to 256 wireless clients |
Network Interfaces |
|
Number of VLANs Supported | Create up to 16 VLANs |
Auxiliary Ports |
|
Mounting | Desktop |
LEDs |
|
Network Protocols | IPv4, IPv6, 802.1Q, 802.1p, 802.1x, 802.11e/WMM |
QoS | 802.11e/WMM, VLAN, TOS |
Firewall | DDNS, Port Forwarding, DMZ, UPnP, Anti-DoS, traffic rules, NAT, ALG |
VPN |
|
Network Management | GWN7062 embedded controller can manage it self and up to 50 GWN Aps |
Power and Green Energy Efficiency | Universal power adaptor included: |
Environmental | Operation: 0°Cto 50°C |
Physical |
|
Package Content |
|
Compliance | FCC, CE, RCM, IC, UKCA |
GWN7062 Technical Specifications
INSTALLATION
Before deploying and configuring the GWN70x2 router, the device needs to be properly powered up and connected to the network. This section describes detailed information on the installation, connection, and warranty policy of the GWN70x2 router.
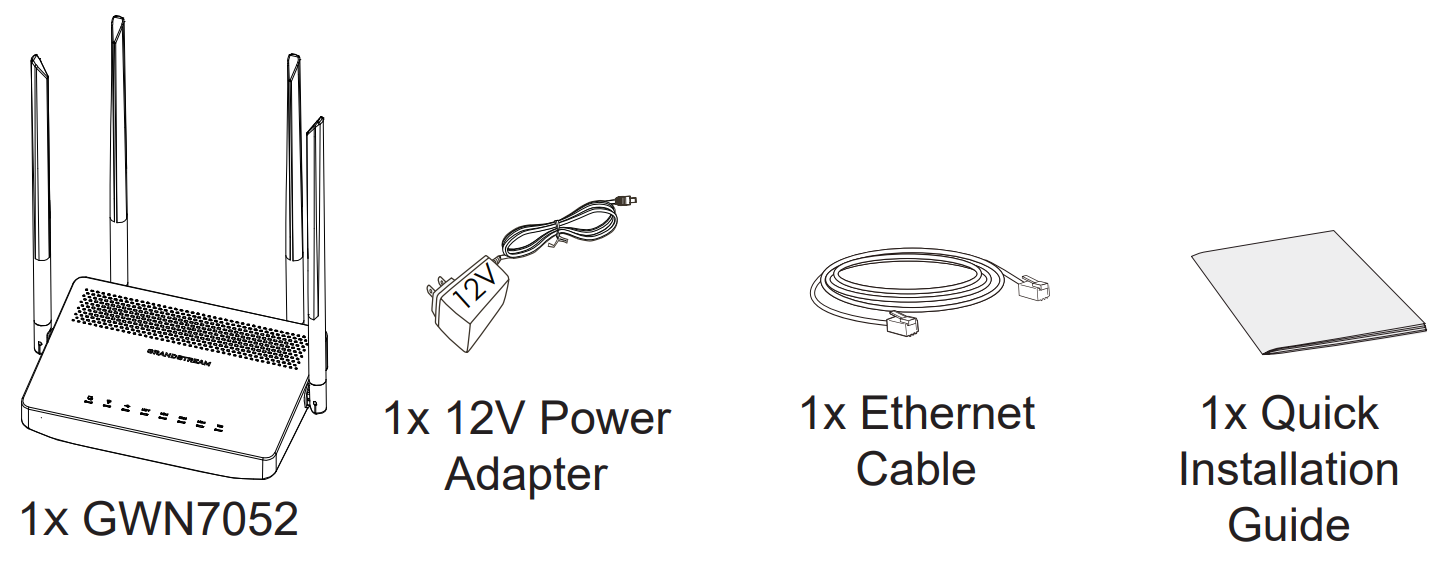
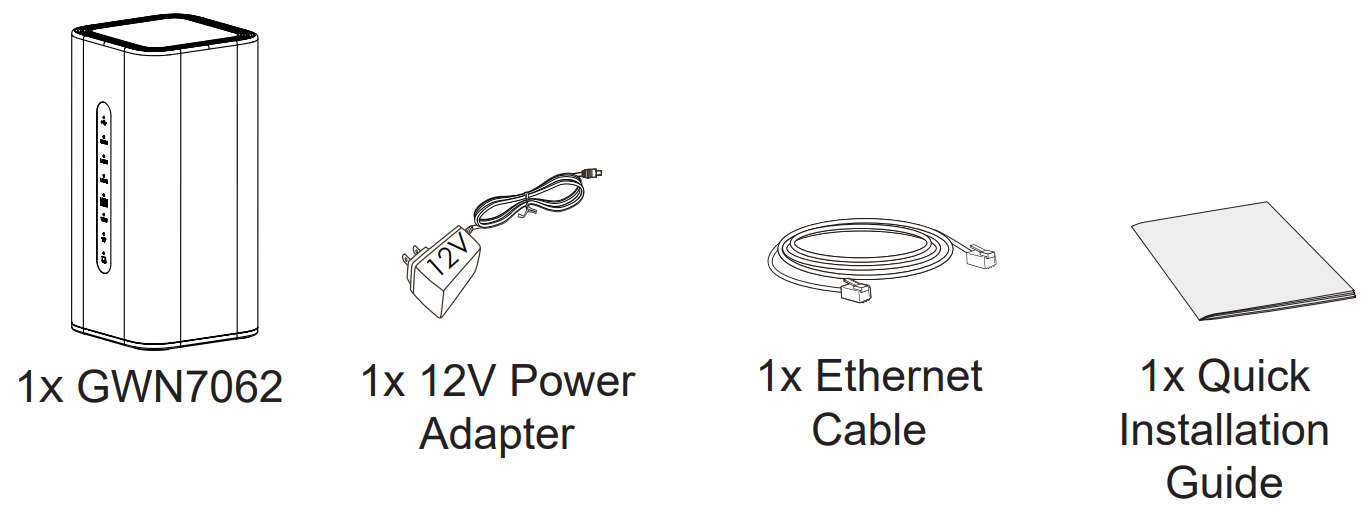
Package Contents
○ GWN7052/GWN7052F
○ GWN7062
GWN70x2 Ports
○ GWN7052
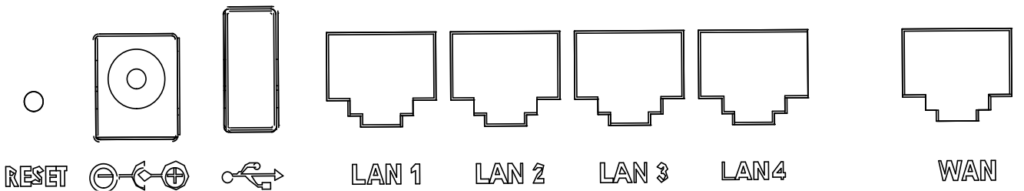
○ GWN7052F
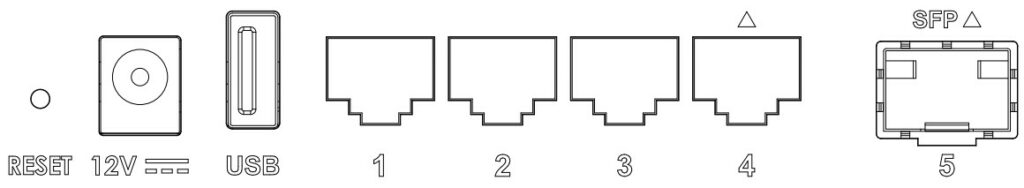
○ GWN7062
Powering and Connecting GWN70x2
○ GWN7052/GWN7052F
1. Power the GWN7052/GWN7052F
GWN7052/GWN7052F can be powered on using the right PSU (DC 12V, 1A).
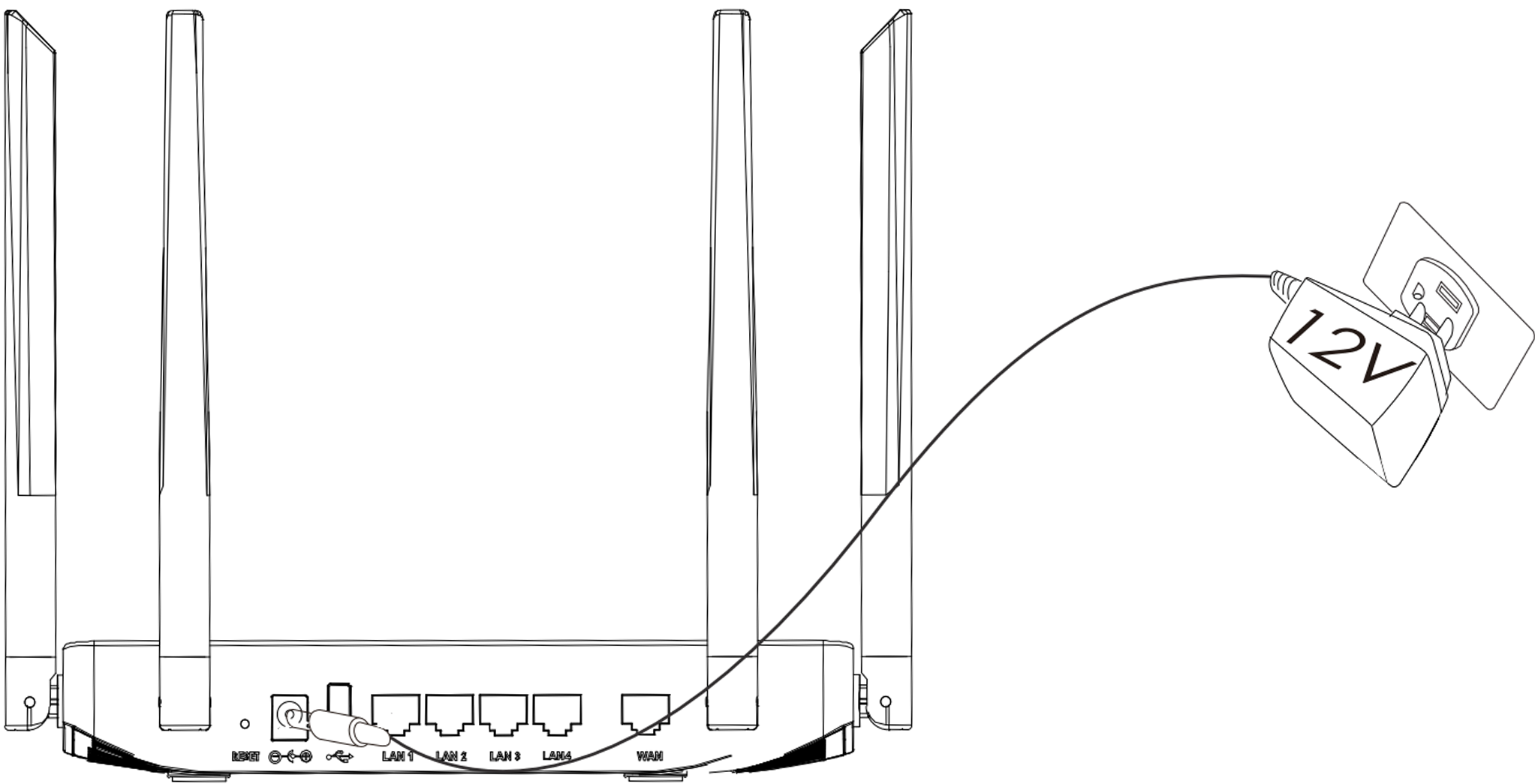
2. Connect to the Internet
Connect the WAN port to an optical fiber broadband modem (or connect using SFP module for GWN7052F), ADSL broadband modem, or community broadband interface.
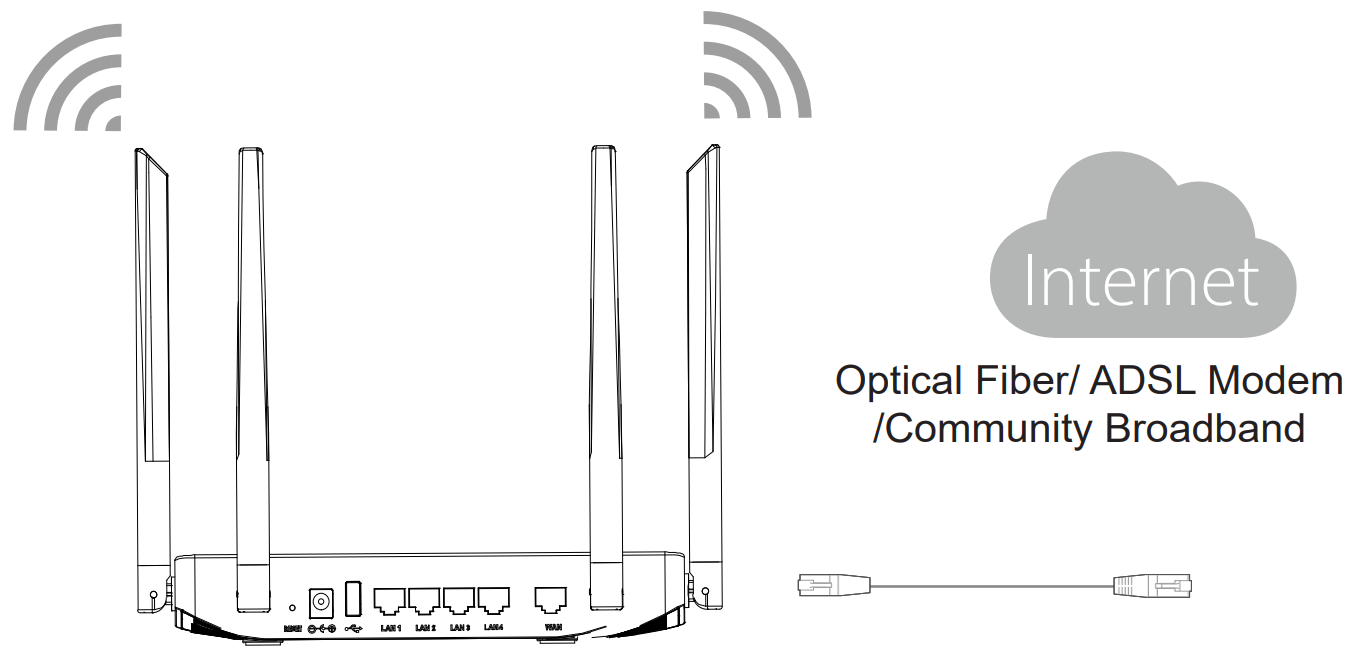
3. Connect to the Default Network
○ GWN7062
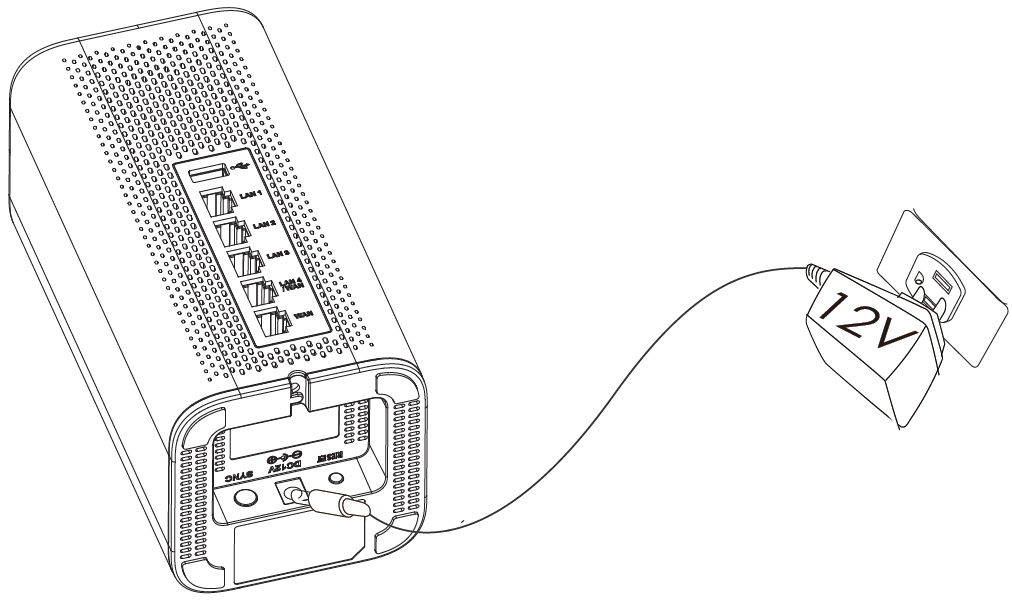
1. Power the GWN7062
GWN7062 can be powered on using the right PSU (DC 12V, 1.5A).
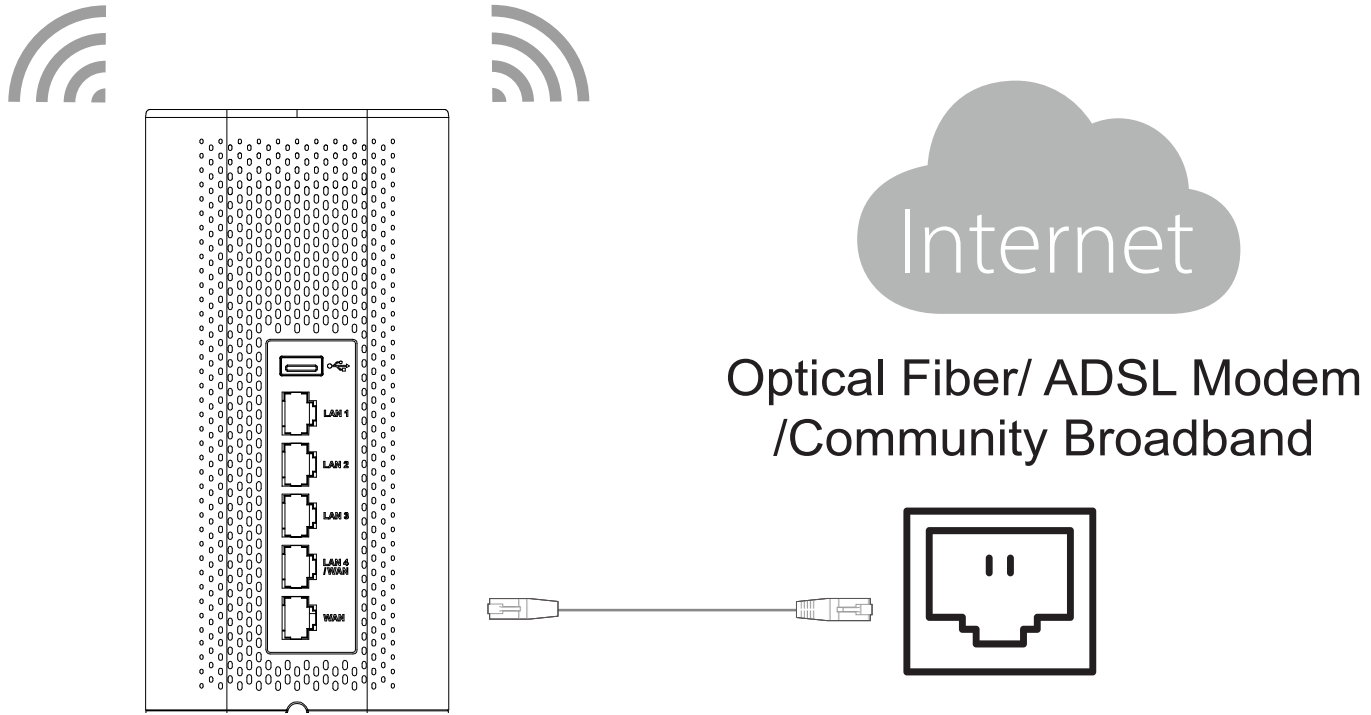
2. Connect to the Internet
Connect the WAN port to an optical fiber broadband modem, ADSL broadband modem, or community broadband interface.
3. Connect to GWN7062 Default Network
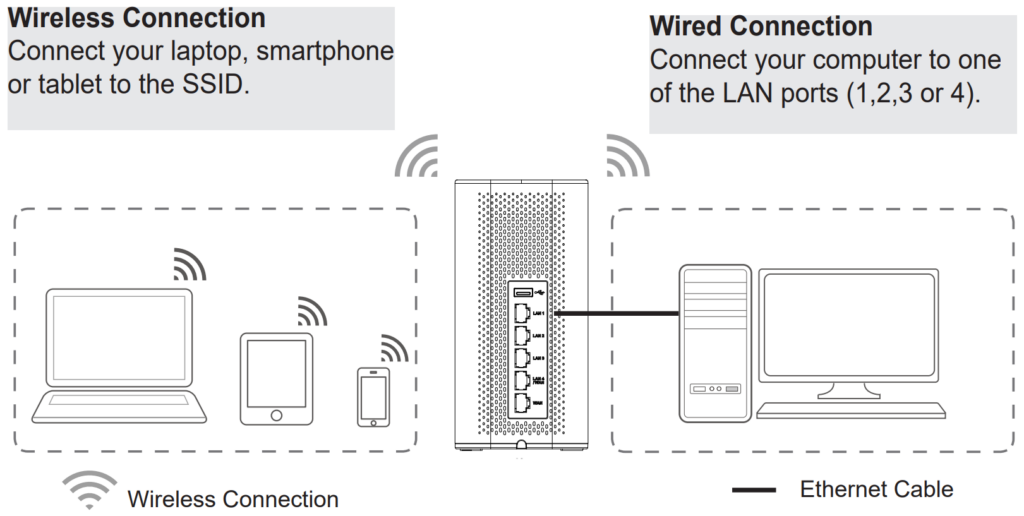
GETTING STARTED
The GWN70x2 Dual-Band Wi-Fi Routers provide an intuitive web GUI configuration interface for easy management to give users access to all the configurations and options for the GWN70x2’s setup.
This section provides step-by-step instructions on how to read LED indicators and use the Web GUI interface of the GWN70x2.
LED Indicators
The front panel of the GWN70x2 has LED indicators for power and interface activities, the table below describes the LED indicators’ status.
LED | Status | Indication |
Power/Provision | Flashing Red | Resetting |
Solid Red | Upgrade failed | |
Pink | No Web login after reset | |
Green | Powering | |
Blue | Normal use | |
Wi-Fi | Solid Blue | Wi-Fi enabled |
Off | Wi-Fi disabled | |
WAN | Flashing Blue | Connected as a client to another network and data is transferring |
Off | No network, cable is disconnected | |
LAN | Flashing Blue | Connected to the corresponding LAN port and data is transferring |
Off | No network, cable is disconnected | |
USB | Solid Blue | Connected to USB device |
Off | No USB device is connected |
LED Indicators
Use the WEB GUI
Access WEB GUI
The GWN70x2 embedded Web server responds to HTTPS GET/POST requests. Embedded HTML pages allow users to configure the device through a Web browser such as Microsoft IE, Mozilla Firefox, or Google Chrome.
To access the Web GUI:
- Connect a computer to a LAN port of the GWN70x2.
- Ensure the device is properly powered up, and the Power and LAN port LEDs light up in green.
- Open a Web browser on the computer and enter the web GUI URL in the following format:
https://192.168.80.1 (Default IP address). - Enter the administrator’s login and password to access the Web Configuration Menu. The default administrator’s username is “admin” and the default password is printed on the MAC tag of the unit.
At first boot or after factory reset, users will be asked to change the default administrator and user passwords before accessing the GWN70x2 web interface. The password field is case-sensitive with a maximum length of 32 characters. Using strong passwords including letters, digits, and special characters is recommended for security purposes.
Once the user enters the password, this is the initial page that will be shown. This page contains general information and the status of the router.
Search
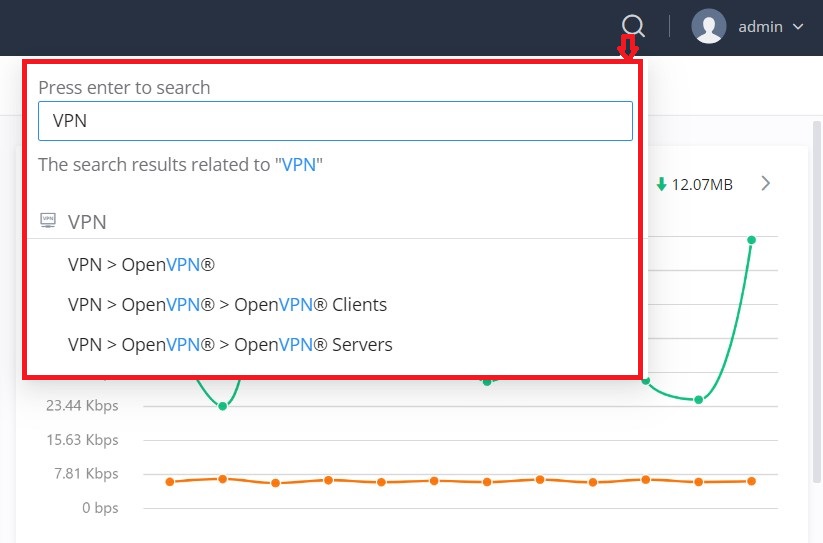
To make it easier for the user to find a particular option quickly, the GWN70x2 web UI has a search feature that can be accessed by clicking on the magnifier icon on the top right corner of the screen and typing the option name.
Setup Wizard and Feedback
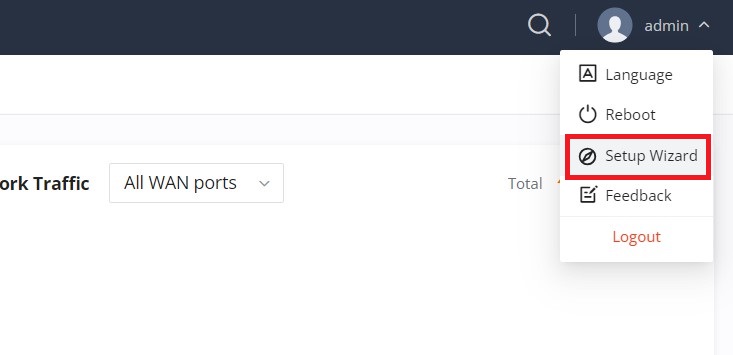
Setup Wizard
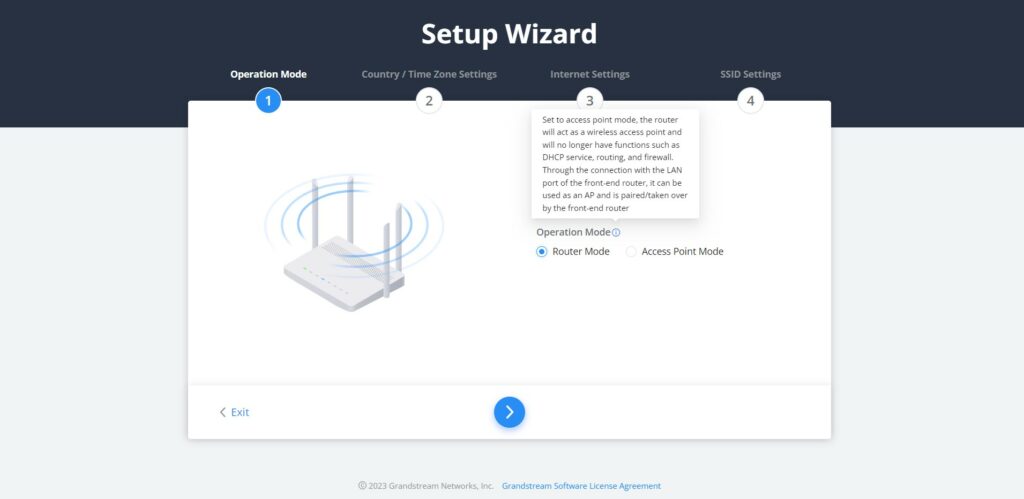
If the user missed the Setup Wizard at the first boot of GWN70x2. It’s accessible all the time at the top of the page and it contains the necessary settings that the user must configure in 4 steps, first Operation Mode, Country/Time zone settings, Internet settings, and finally SSID settings.
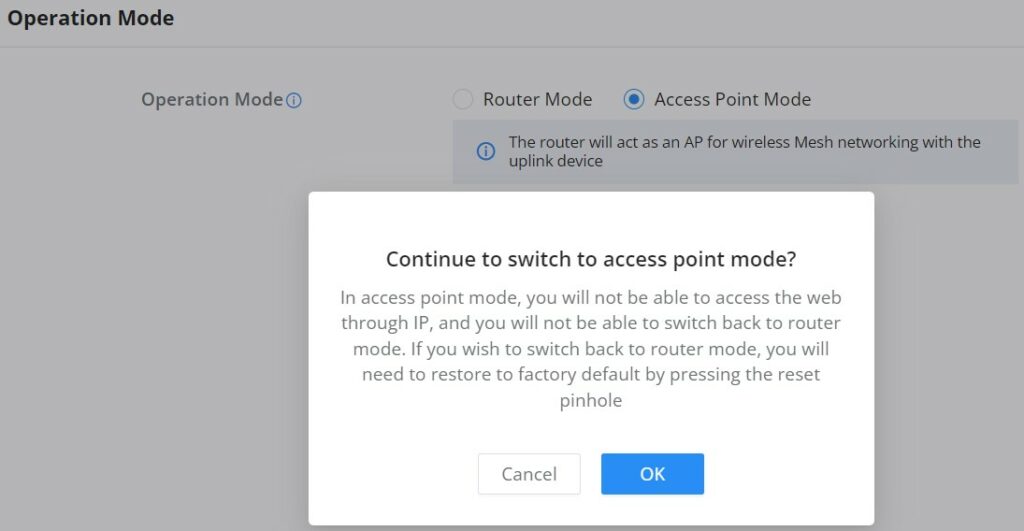
- Operation Mode
In the first step, the user has the option to either select the Router or Access Point Mode, if the Access Point mode is selected the router will act as a wireless access point and will no longer have functions such as DHCP service, routing, and firewall. Through the connection with the LAN port of the front-end router, it can be used as an AP and is paired/taken over by the front-end router, and this mode also supports wireless mesh networking with the uplink device.
If the Router Mode is selected, click on
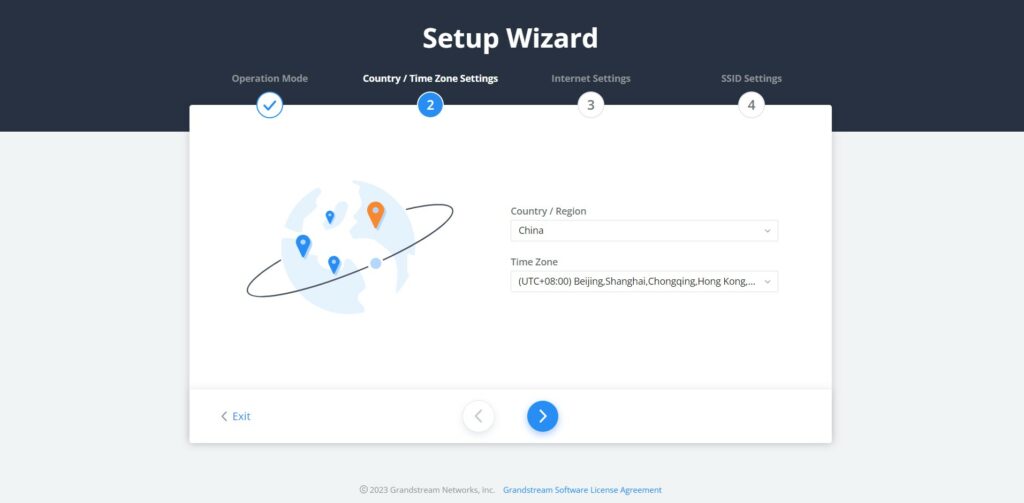
- Country/Time Zone Settings
In the second step, the user can specify the country/Region and Time Zone.
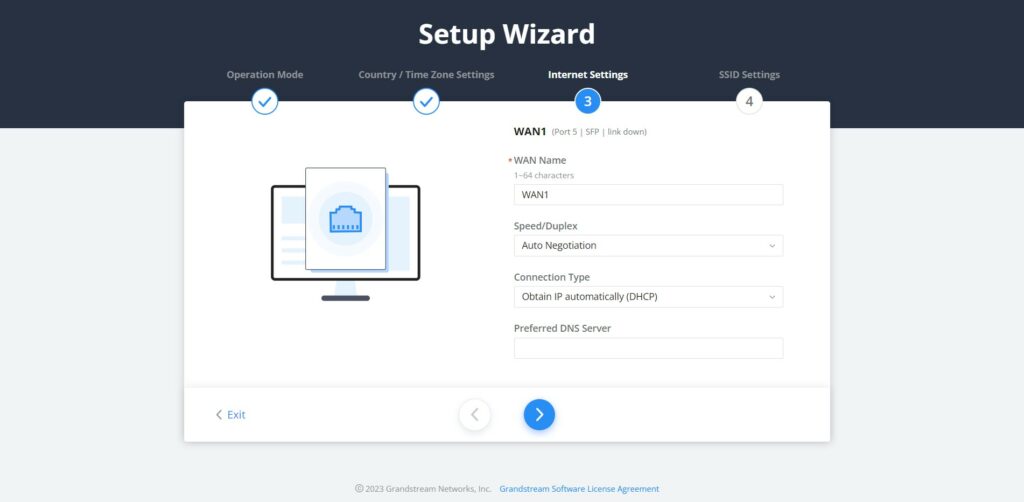
- Internet Settings
The third step is about configuring the WAN ports’ basic settings by specifying the WAN name, Speed/Duplex, Connection (DHCP, static IP, etc), and the preferred DNS Server.
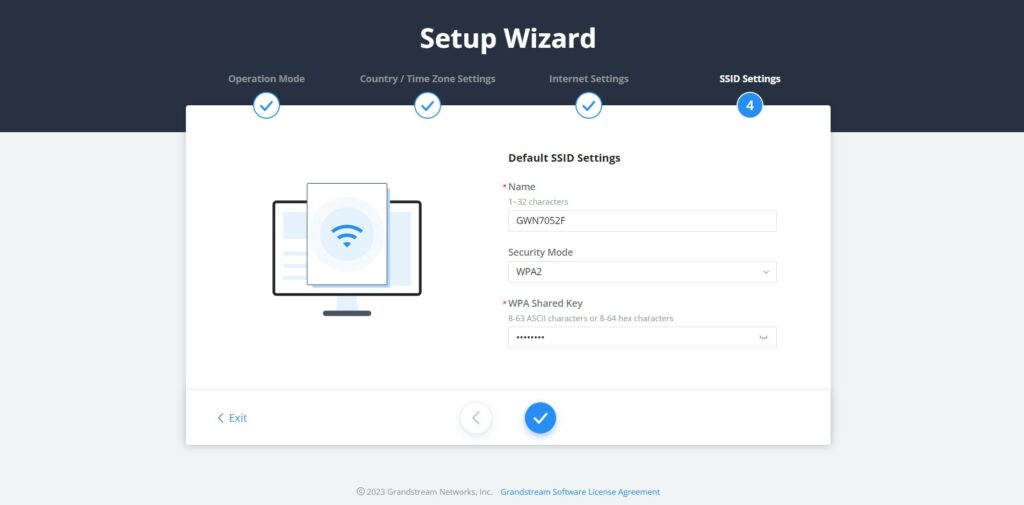
- SSID Settings
The last step is where the user can configure the initial SSID by specifying a name and the security mode.
Feedback
If the user has a question or a suggestion to make the GWN70x2 product even better or has an issue, he can always send feedback, in case of a problem it’s better to include Syslog as it may help solve the problem faster.
OVERVIEW
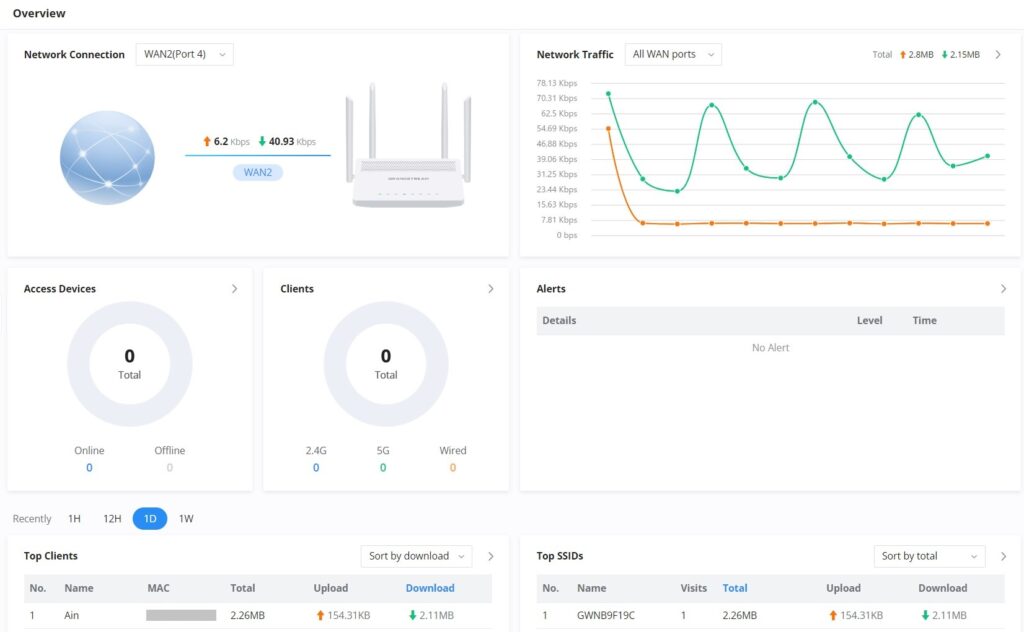
Overview Page
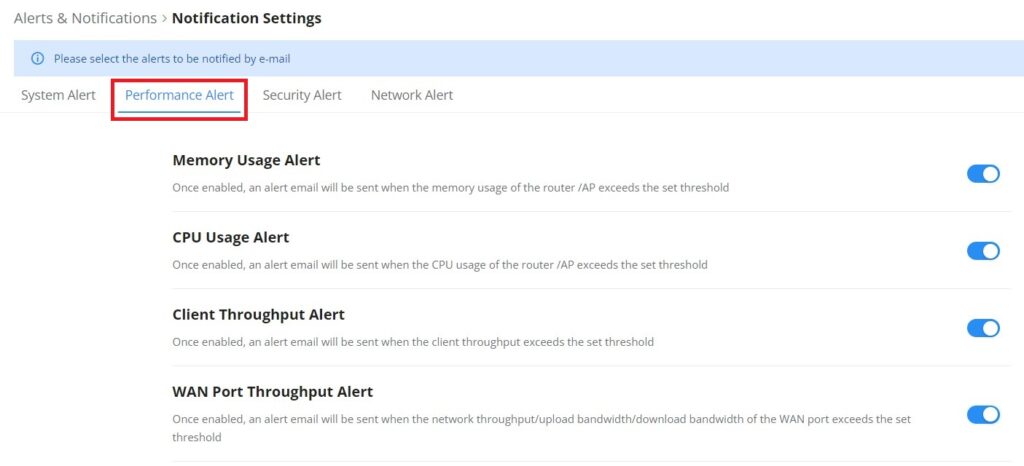
Overview is the first page shown after successful login to the GWN70x2’s Web Interface. It provides an overall view of the GWN70x2’s information presented in a Dashboard style for easy monitoring. Please refer to the figure and table below:
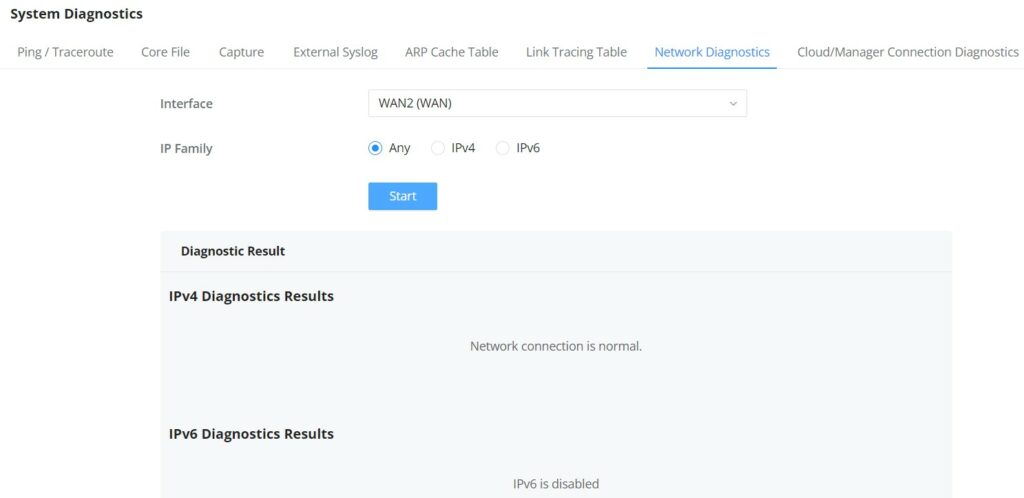
Network Connection | Displays the current state of the network connection for the selected WAN port and shows the current upload and download speed. Note: the user can select the WAN port from the drop-down list. |
Network Traffic | Shows network traffic in real time. Note: the user can select the WAN port from the drop-down list or select All WAN ports. |
Access Devices | shows the total number of Access Devices online and offline. |
Clients | Shows the total number of clients connected either wirelessly (2.4G and 5G) and also wired connections. |
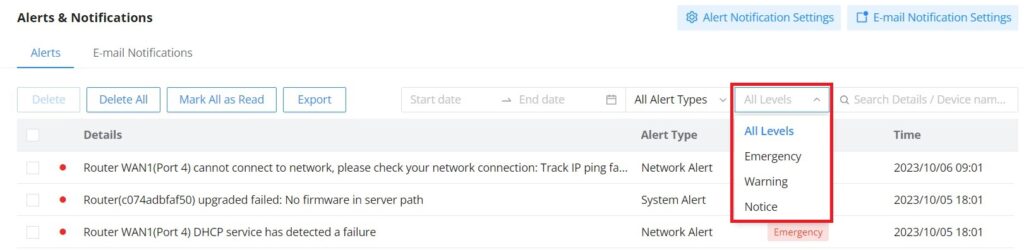
Alerts | Shows Alerts General, Important or Emergency with details and time. |
Clients Speed | Displays Clients speed based on time (1H, 12H, 1D or 1W) |
Top Clients | Shows the Top Clients list, users may assort the list of clients by their upload or download. Users may click on to go to Clients page for more options. |
Top SSIDs | Shows the Top SSIDs list, users may assort the list by number of clients connected to each SSID or data usage combining upload and download. Users may click on to go to SSID page for more options. |
Top Access Devices | Shows the Top Access Devices list, assort the list by the number of clients connected to each access device or data usage combining upload and download. Click on the arrow to go to the access point page for basic and advanced configuration options. |
Overview page
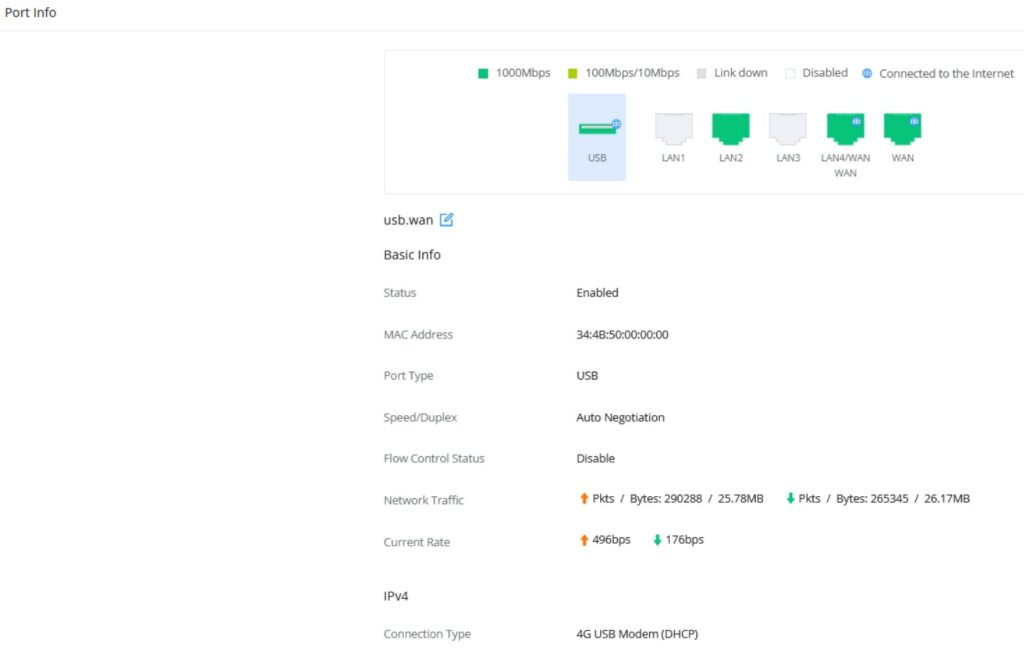
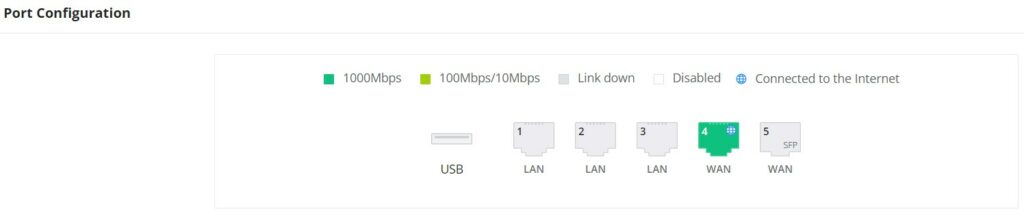
Port Info
The Port Info page displays an overview of all ports’ status including the USB Port, Gigabits ports, and SFP ports, indicating the links up with green color and links down with grey color, furthermore, the user can click on the port icon to get more info about the select link, refer to the figure below:
Navigate to Web UI → Overview → Port Info:
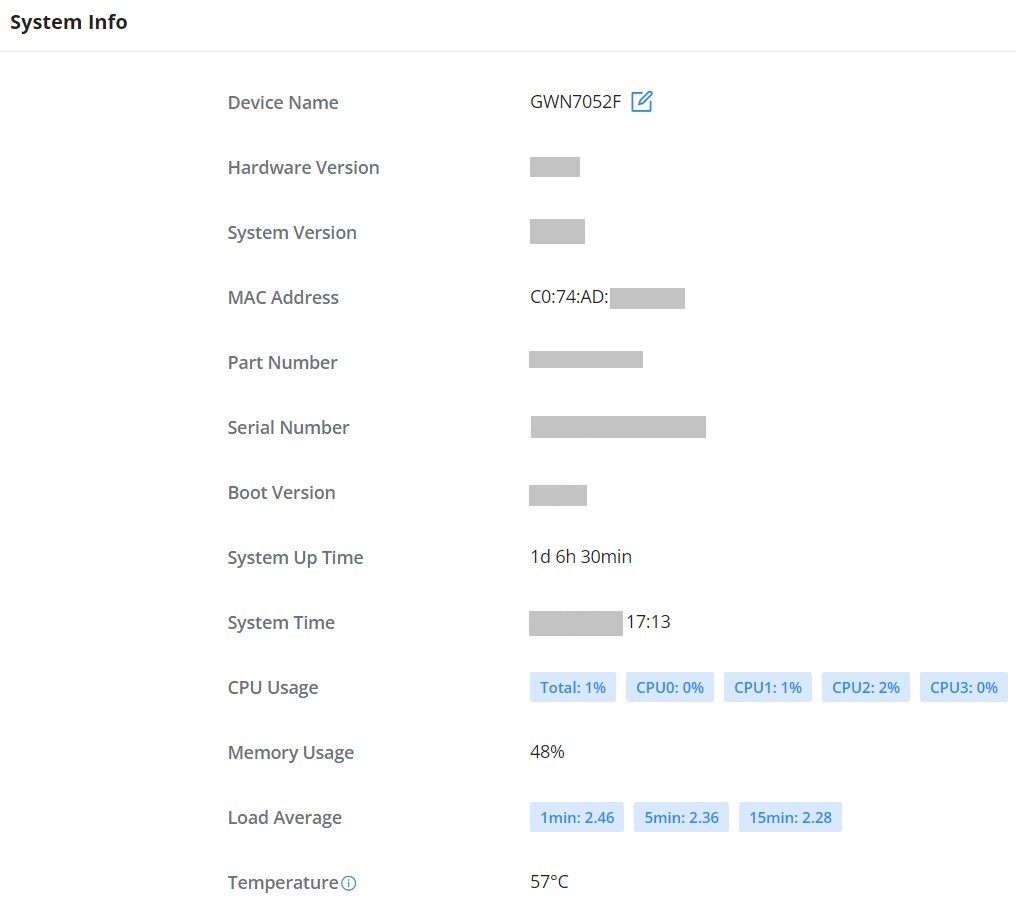
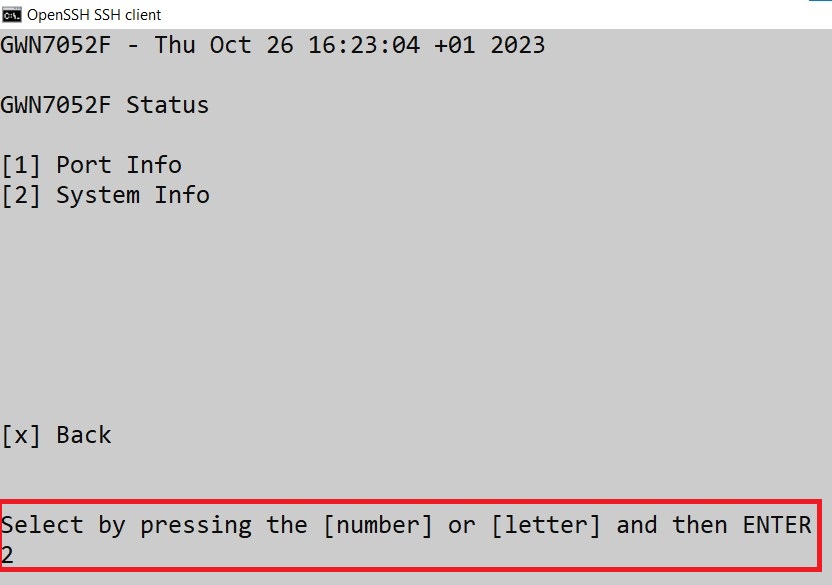
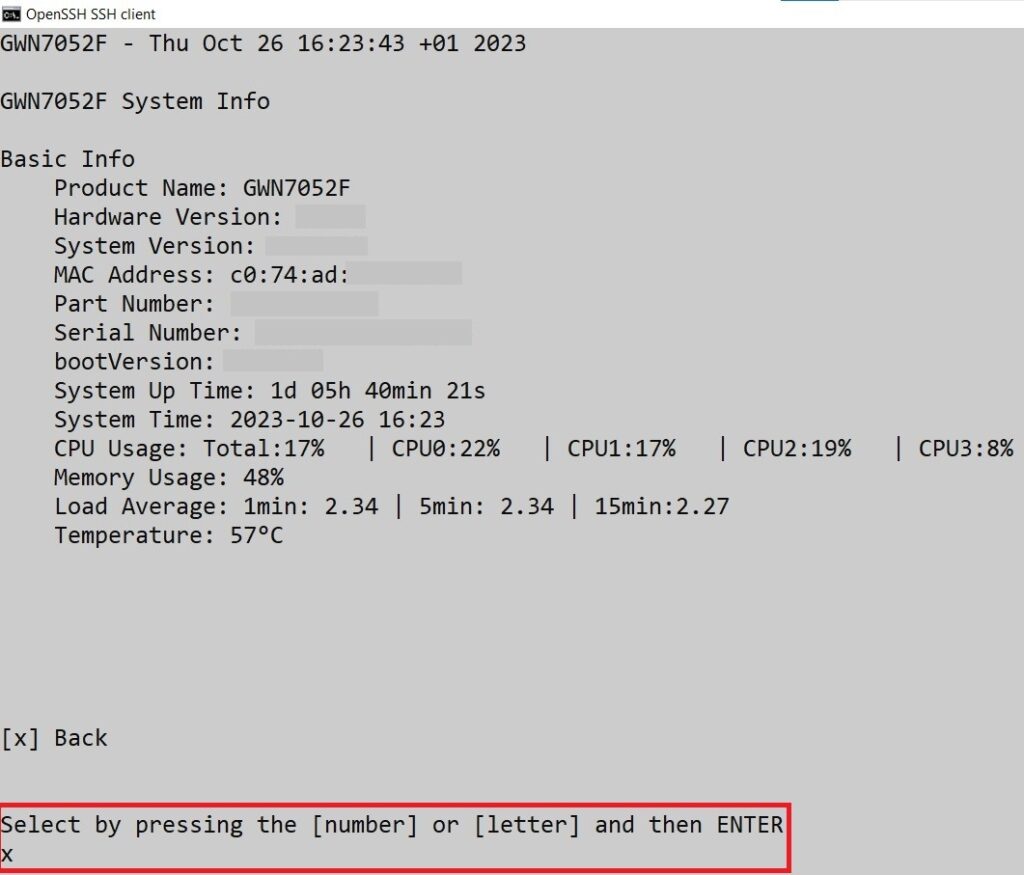
System Info
The System Info page shows much info related to GWN70x2 routers like device name, system version, MAC address, system uptime, CPU and memory usage, temperature, etc.
The router’s System Info can be accessed from the Web GUI → Overview → System Info Tab.
NETWORK SETTINGS
Port Configuration
To access port configuration, please access the user interface of the GWN70x2 router and then navigate to Network Settings → Port Configuration.
- Port Status
On the top, you can find the status of all the ports of the router.
- Green color: port speed is 1Gbps.
- Light green color: port speed is 100Mbps/10Mbps.
- Grey color: link down.
- White color: port disabled.
- Internet icon: port connected to the internet (for WAN ports).
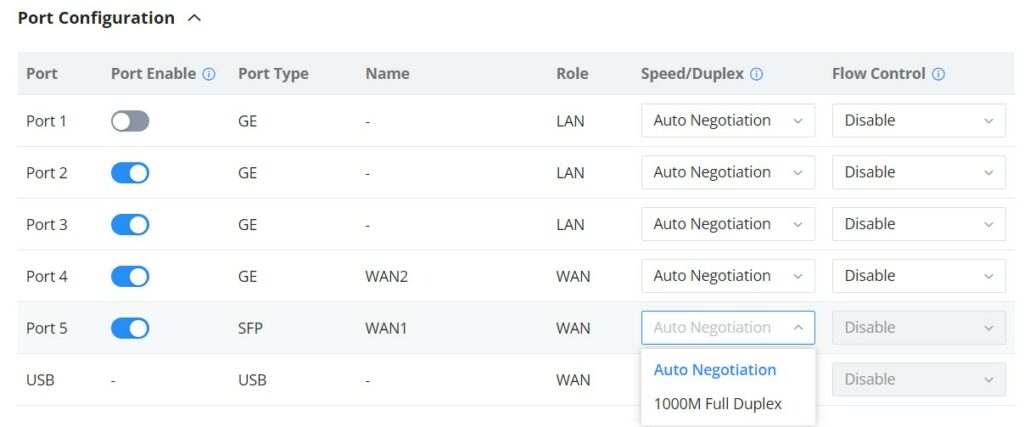
- Port Configuration
The Port configuration page allows the user to configure the settings related to all the ports of the router; this includes the gigabit Ethernet ports as well as the SFP ports. The settings that can be edited include flow control, speed, and duplex mode.
Port | This field indicates the port number. |
Port enabled | Toggle ON or OFF the port. Note: When set to disabled, this physical port is disabled and all port-based configurations do not take effect. |
Port Type | This field indicates the port type.
|
Name | This indicates the port name. |
Role | This indicates the port role.
|
Speed/Duplex | In this setting, the user can configure the duplex mode as well as the speed of the port. When the mode is set to Auto Negotiation, the router will determine based on the settings negotiated with the device connected. |
Flow Control | The user can enable or disable flow control using this option. Note: When the setting is set to Auto Negotiation, the router will determine based on the settings negotiated with the device connected. |
Port configuration – part 2
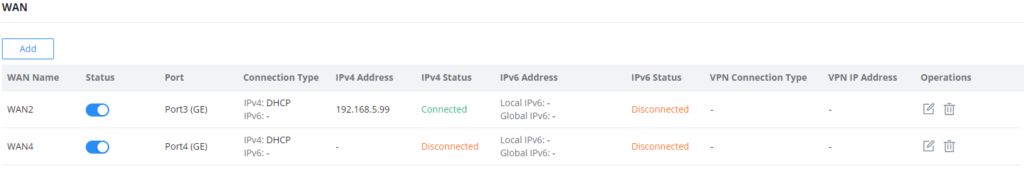
WAN
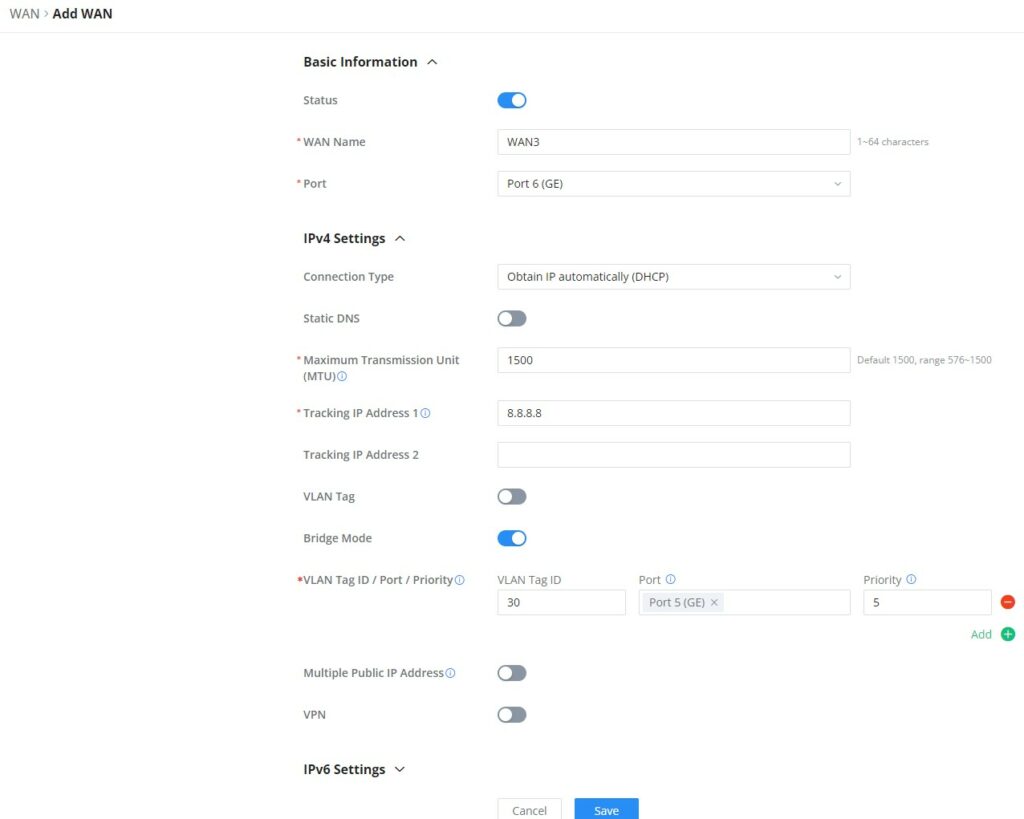
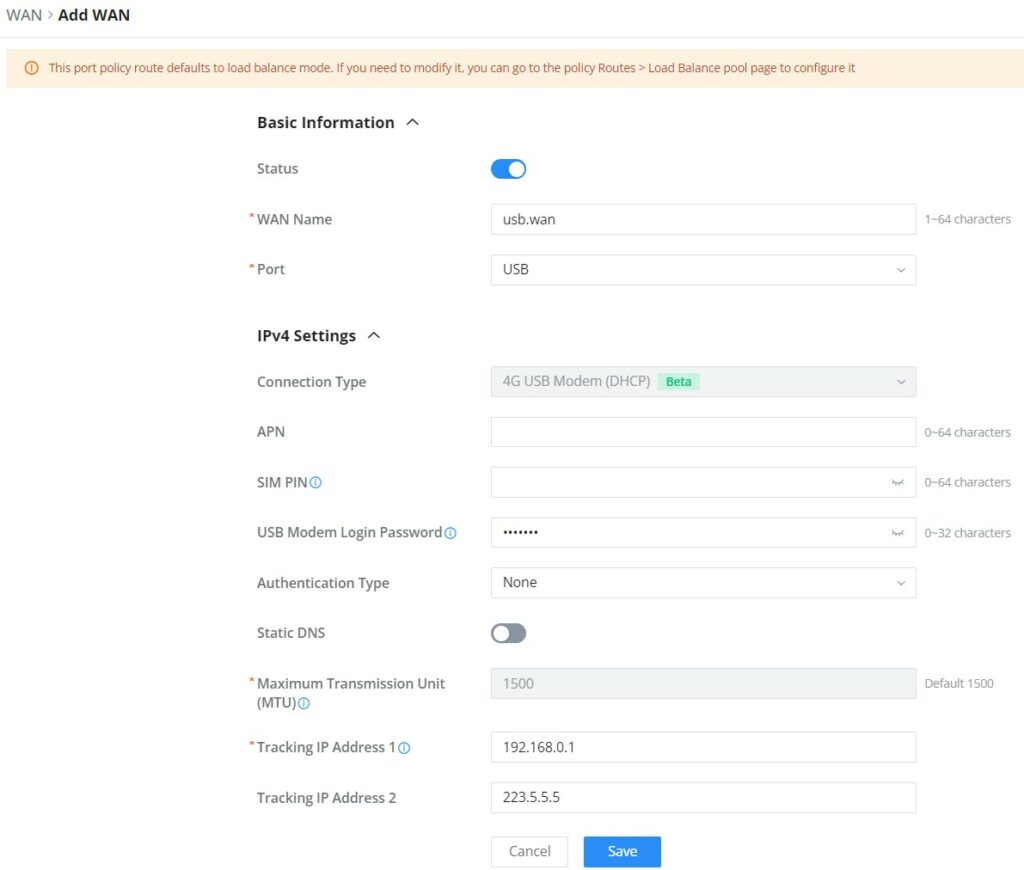
The WAN ports can be connected to a DSL modem or a router. WAN port support also sets up static IPv4/IPv6 addresses and configures PPPoE. It’s also possible to use the USB port with a USB 4G dongle, by default the port policy route will be in load balance mode, it also can be configured to run in Backup (Failover) mode under Routing → Policy Routes → Load Balance Pool. With a USB 4G dongle (GWN7062 only), the user can adapt to many scenarios like remote places with no wired WAN or constantly moving or as a failover (Backup) WAN to ensure redundancy, also it can adapt to various modems.
On this page, the user can modify the setting for each WAN port and also can delete or even add another WAN, Adding a WAN port will reduce the LAN port number. In the case where there is more than one WAN port, load balancing or backup (Failover) can be configured.
If a GWN router is added to either GWN.Cloud or GWN Manager, the WAN Speed Test feature will be available to users. Please for more details check GWN Management Platforms – User Guide (WAN Speed Test).
Click on to add another WAN port or click on the “edit icon” to edit the previously created ones.
Please refer to the following table for network configuration parameters on the WAN port.
Basic Information | |
Status | Click to enable or disable the WAN |
WAN Name | Enter a name for the WAN port |
Port | Select from the drop-down list the port to be used as a WAN |
IPv4 Settings | |
Connection Type |
The default setting is “Obtain IP automatically (DHCP)”. |
Static DNS | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable static DNS |
Preferred DNS Server | Enter the preferred DNS Server, ex: 8.8.8.8 |
Alternative DNS Server | Enter the altenative DNS Server, ex: 1.1.1.1 |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | Configures the maximum transmission unit allowed on the wan port.
|
Tracking IP Address 1 | Configures tracking IP address of WAN port to determine whether the WAN port network is normal. |
Tracking IP Address 2 | Add another alternative address for Tracking IP Address |
VLAN Tag | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable VLAN Tag |
VLAN Tag ID | Enter the VLAN Tag ID with the priority Note: priority is 0~7 with 7 being the highest priority. Default is 0. |
Multiple Public IP Address | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable Multiple Public IP Address Note: Please use with Port Forward function, so that you can access to router via public IP address. |
Public IP Address | Enter a public IP address Note: Click on "Plus" or "minus" icons to add or delete public IP addresses. |
VPN | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable VPN |
VPN Connection Type |
|
Username | Enter the username to authenticate into the VPN server. |
Password | Enter the password to authenticate into the VPN server. |
Server Address | Enter the IP address or the FQDN of the VPN server. |
MPEE Encryption (if PPTP is selected) | When PPTP is chosen as the VPN Connection Type, the user can choose to toggle on or off the MPEE Encryption. |
IP Type |
|
VPN Static DNS | Enable this option to use the statically assigned DNS server addresses. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This configures the value of the maximum transmit unit. The valid range for this value is 576 - 1460. Note: Please do not change this value unless it's necessary. |
IPv6 Settings | |
IPv6 | Enable this option to use IPv6 on this specific WAN port. |
Connection Type |
|
IPv6 Address | When the Connection Type is set to Static IP, the user can can enter the static IP address in this field. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Prefix Length | Enter the prefix length. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Default Gateway | Enter the IP address of the default gateway Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Preferred DNS Server | Enter the IP address of the preferred DNS server. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Alternative DNS Server | Enter the IP address of the alternative DNS server Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to Static IPv6. |
Static DNS | Enable this option to enter statically assigned DNS. Note: This option appears only when the Connection Type is set to DHCPv6. |
IPv6 Relay to VLAN | Once enabled, relay IPv6 addresses to clients on the LAN side. Note: This function will take effect only "IPv6 Relay from WAN" is enabled on VLAN. |
WAN Settings
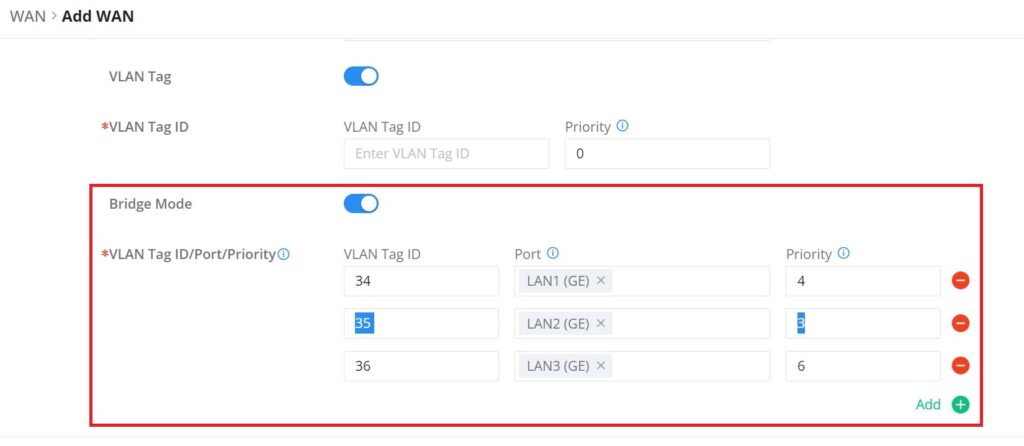
Triple Play
Triple Play allows the user to benefit from a multi-service plan (depending on ISP provider), and with a single WAN connection each service e.g: Internet, Voice (VoIP), and IPTV can be separated using VLANs and a specific port.
Navigate to Network Settings → WAN → Edit/Add WAN, then scroll down and search for Bridge Mode, please refer to the figure below:
LAN
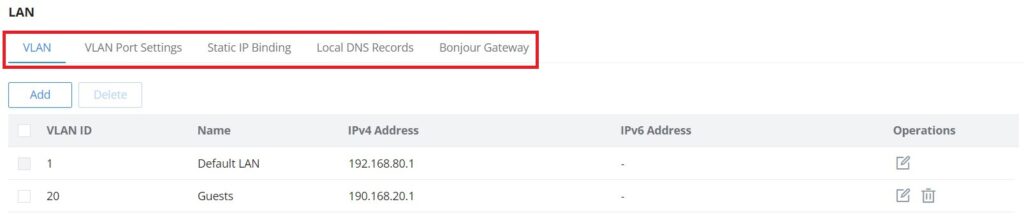
To access the LAN configuration page, log in to the GWN70x2 WebGUI and go to Network Settings → LAN. VLAN configuration such as adding VLANs or setting up a VLAN port can be found here on this page, as well as the ability to add Static IP Bindings, local DNS Records, and Bonjour Gateway.
VLAN
GWN70x2 router integrates VLAN to enhance security and add more functionalities and features. VLAN tags can be used with SSIDs to separate them from the rest, also the user can allow these VLANs only on specific LANs for more control and isolation and they can be used as well with policy routing.
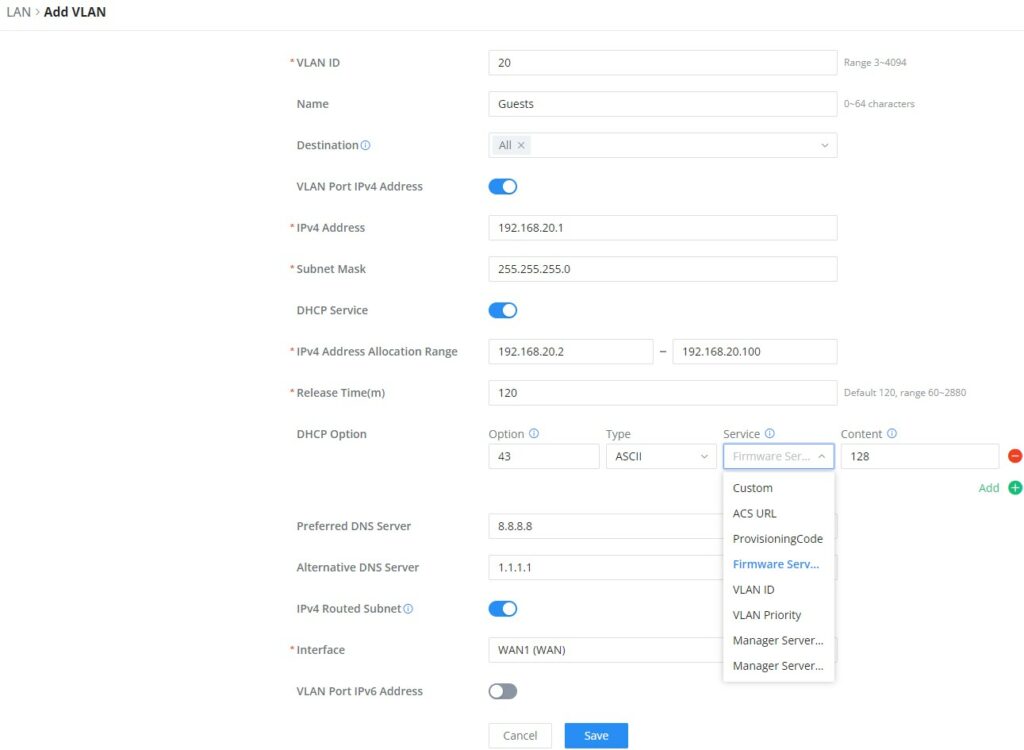
- Add or Edit VLAN
To Add or Edit a VLAN, Navigate to Router Interface → Network Settings → LAN. Click on button or click on
Edit button.
VLAN ID | Enter a VLAN ID Note: VLAN ID range is from 3 to 4094. |
Name | Enter the VLAN name |
Destination | To fast configure the VLAN's single-way data communication with WANs, other VLANs and VPNs. The option selected by default will be based on "Policy Routing" option to keep the default route accessible. |
VLAN Port IPv4 Address | |
IPv4 address | Enter IPv4 Address |
Subnet Mask | Enter Subnet Mask |
DHCP Server | By default it's "Off", choose "On" to specifiy the IPv4 address Allocation Range |
IPv4 Address Allocation Range | Enter the start and the end of the IPv4 address Allocation Range. |
Release Time(m) | The default value is 120, and the valid range is 60~2880. |
DHCP Option | Select the option, type, service and content for each DHCP option. Click on "Plus" or "Minus" icons to add or delete an entry.
|
Preferred DNS Server | Enter the Preferred DNS Server |
Alternative DNS Server | Enter the Alternative DNS Server |
IPv4 Routed Subnet | Once enabled, clients under the VLAN will be allowed to access the Internet using their real IP addresses. |
Interface | Select the WAN interface from the drop-down list |
VLAN Port IPv6 Address | |
IPv6 Address Source | Select from the drop-down list the WAN port |
Interface ID | Toggle ON or OFF the interface ID |
Customize Interface ID | Enter the interface ID |
IPv6 Preferred DNS Server | Enter the IPv6 Preferred DNS Server |
IPv6 Alternative DNS Server | Enter the IPv6 Alternative DNS Server |
IPv6 Relay form WAN | Once enabled, clients will get IPv6 addresses directly from the WAN side. Note: This function will take effect only "IPv6 Relay to VLAN" is enabled on the WAN side. |
IPv6 Address Assignment | Select from the drop-down list the IPv6 address assignment
|
Add/edit VLAN
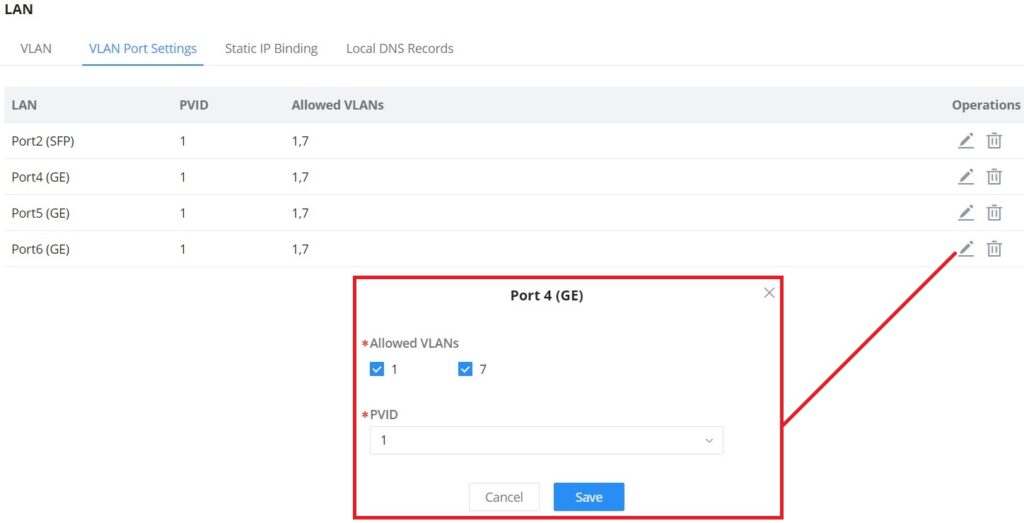
VLAN Port Settings
The user can use LAN ports to allow only specific VLANs on each LAN port and in case there are more than one VLAN then there is an option to choose one VLAN as the default VLAN ID (PVID or Port VLAN Identifier). Click on to edit the VLAN Port Settings or click on
to delete that configuration and bring back the default settings which is by default VLAN 1.
| Allowed VLANs | Choose the VLANS to be allowed on this port. |
| PVID | Select the Port VLAN Identifier or the default VLAN ID |
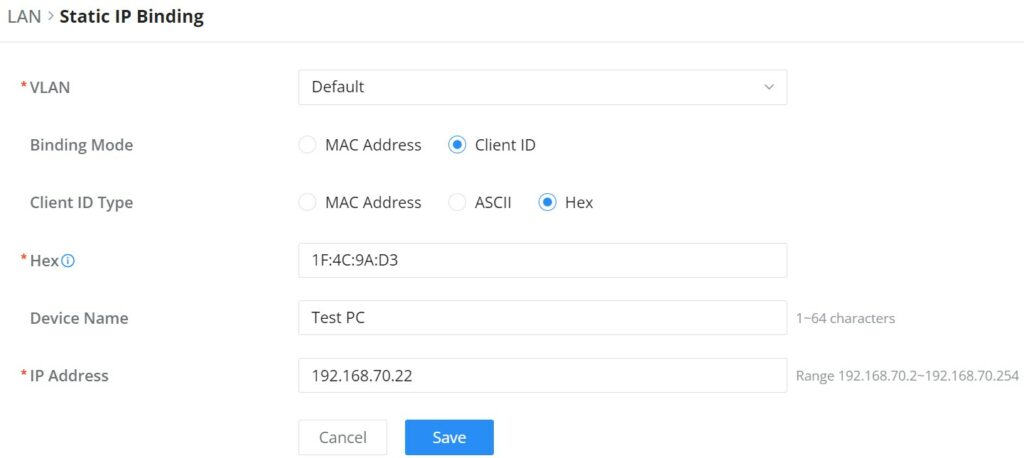
Static IP Binding
The user can set IP static binding to devices in which the IP address will be bound to the MAC address. Any traffic that is received by the router that does not have the corresponding IP address and MAC address combination will not be forwarded.
To configure Static IP Binding, please navigate to Network Settings → LAN → Static IP Binding, refer to the figure and table below:
VLAN | Select the VLAN from the drop-down list. |
Binding Mode | select the binding mode, either using the client MAC address or Client ID. |
Binding Devices | Select the device MAC address from connected devices list. Note: only available bindind mode is set to MAC Address. |
Client ID Type | Select the client ID type, either based on:
Note: only available bindind mode is set to Client ID. |
MAC Address | Enter the MAC Address Note: only available bindind mode or Client ID Type is set to MAC Address |
ASCII | Enter the ASCII Note: only available Client ID Type is set to ASCII |
Hex | Please enter XX:XX:XX:XX format or a valid even-digit hexadecimal number string, the first two digits need to enter the type value. Note: only available Client ID Type is set to Hex |
Device Name | Enter a name for the device |
IP Address | Enter the static IP address based on the VLAN selected previously. |
Static IP Binding
Local DNS Records
Local DNS Records is a feature that allows the user to a DNS records into the router which can be used to map the domain name to an IP address. This feature can be used when the user needs to access a specific server using a domain name instead of an IP address when they do not want to include the entry in public DNS servers. To add a local DNS record, please navigate to Network Settings → LAN → Local DNS Records, then click “Add”
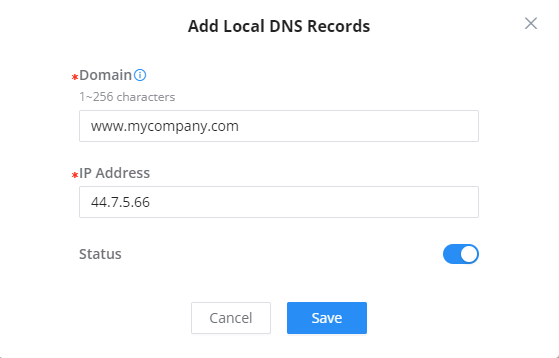
- Enter the domain name in “Domain“
- Then, enter the IP address to which the domain name will be mapped.
- Toggle on the “Status” for the mapping to take effect.
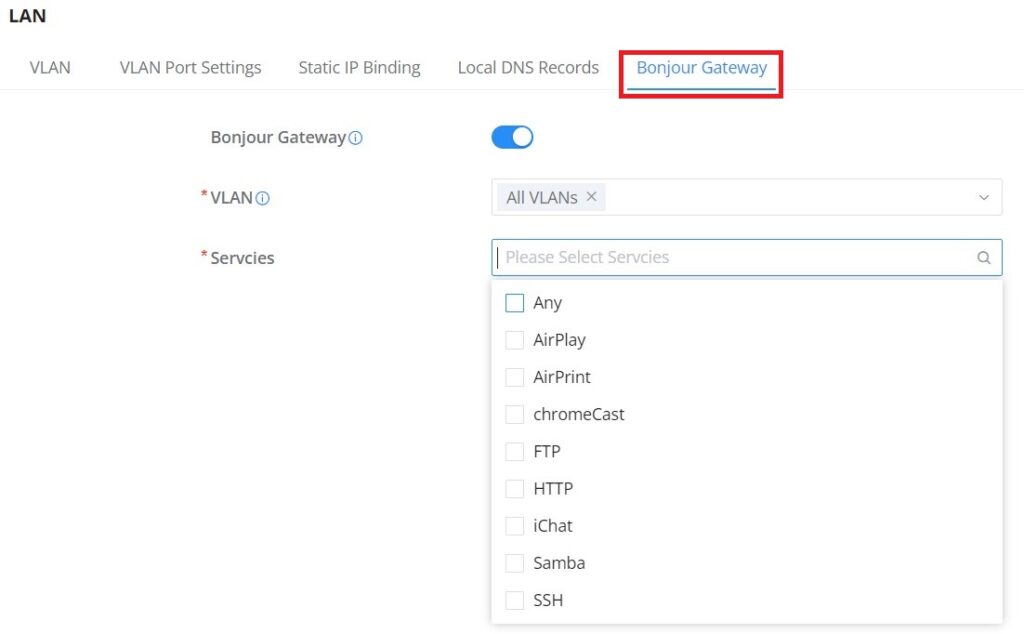
Bonjour Gateway
The Bonjour service is a zero-configuration network that enables the automatic discovery of devices and services on a local network. For example: it can be used on a local network to share printers with Windows® and Apple® devices.
Once enabled, Bonjour services (such as Samba) can be provided to Bonjour supporting clients under multiple VLANs. Once enabled, configure the services of the VLANs and proxies that need to intercommunicate.
To start using Bonjour Gateway, Toggle ON or OFF the service first, then select the VLAN and the services as shown below:
IGMP
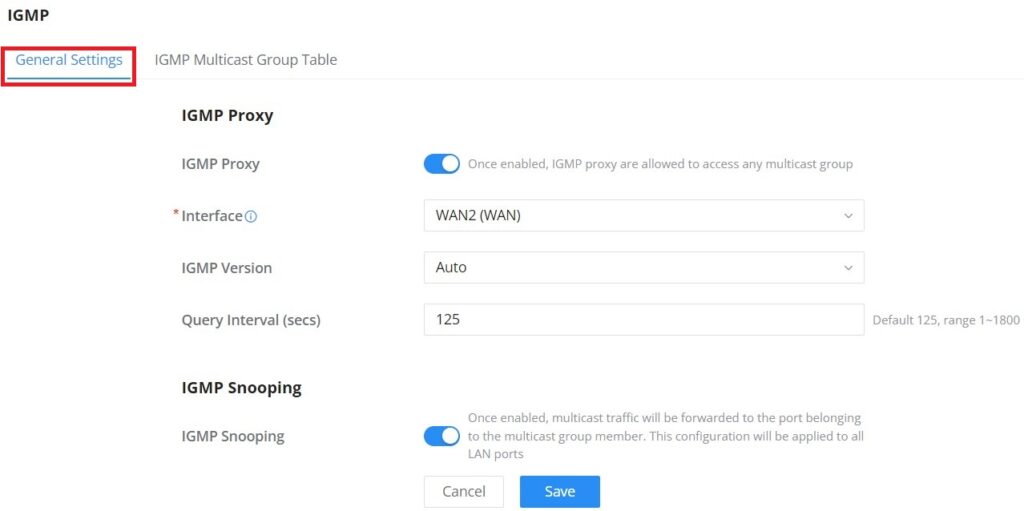
When IGMP Proxy is enabled, the GWN router can issue IGMP messages on behalf of the clients behind it, then the GWN router will be able to access any multicast group.
To start using IGMP Proxy:
- Toggle ON IGMP Proxy first.
- Select the WAN interface to be used from the drop-down list (Note: IGMP proxy cannot be enabled on a WAN port with bridge mode enabled)
- Select the version, be default is Auto.
The user can also enable IGMP Snooping. Once enabled, multicast traffic will be forwarded to the port belonging to the multicast group member. This configuration will be applied to all LAN ports.
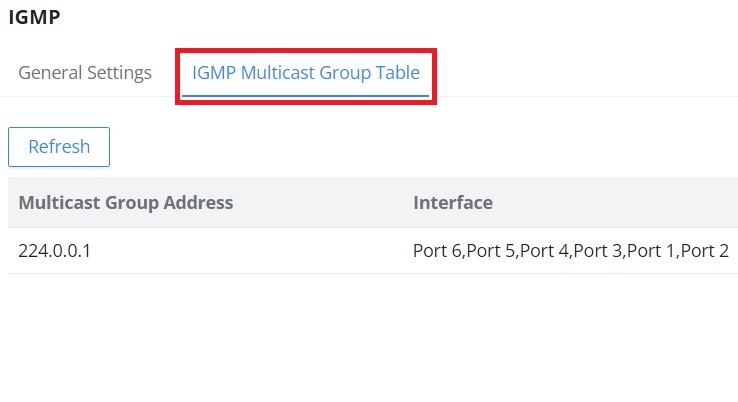
On the IGMP Multicast Group Table, all the active multicast groups will be displayed here.
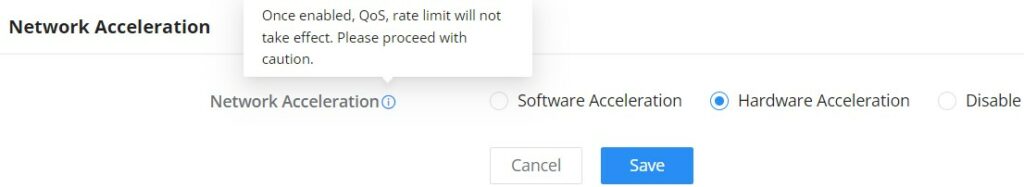
Network Acceleration
Network acceleration allows the router to transfer data at a higher rate when Hardware acceleration is enabled. This ensures a high performance.
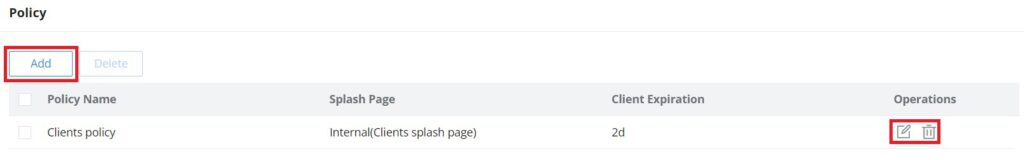
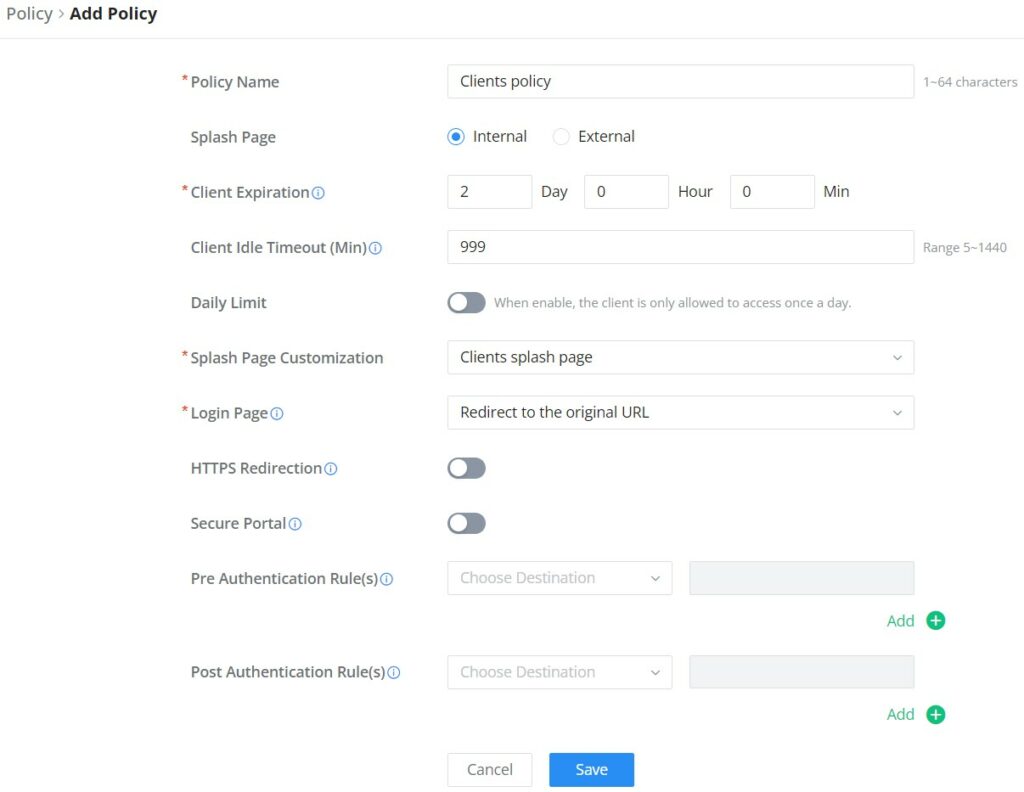
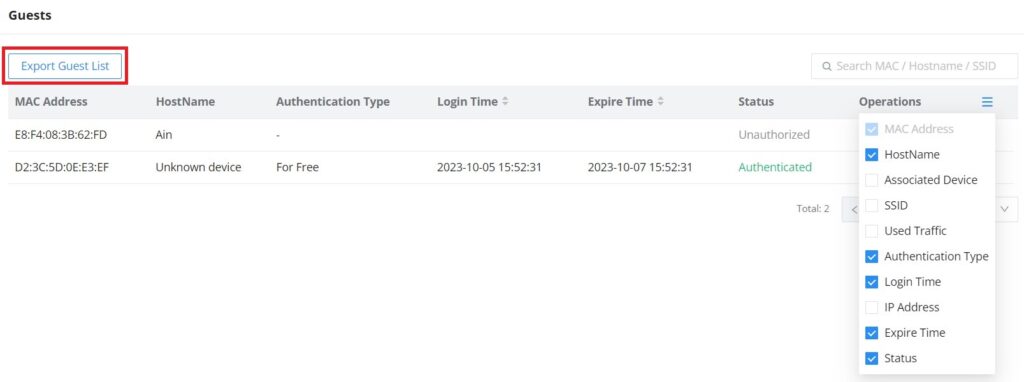
CLIENTS
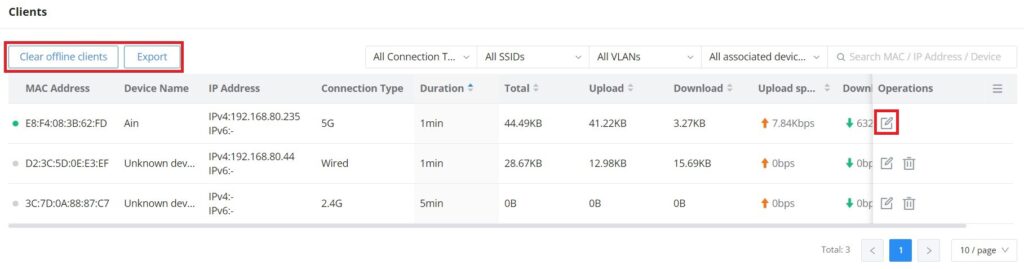
The Clients page keeps a list of all the devices and users connected currently or previously to different LAN subnets with details such as the MAC Address, the IP Address, the duration time, and the upload and download information, etc.
The clients’ list can be accessed from GWN70x2’s Web GUI → Clients to perform different actions for wired and wireless clients.
- Click on “Clear offline clients” to remove clients that are not connected from the list.
- Click on the “Export” button to export the client list to a local device in an EXCEL format.
Please refer to the figure and table below:
MAC Address | This section shows the MAC addresses of all the devices connected to the router. |
Device Name | This section shows the names of all the devices connected to the router. |
VLAN | Displays the VLAN the client connected to. |
IP Address | This section shows the IP addresses of all the devices connected to the router. |
Connection Type | This section shows the medium of connection that the device is using. There are two mediums which can be used to connect:
|
Channel | If device is connected through an access point, the router will retrieve the information of which channel the device is connected to. |
SSID Name | If device is connected through an access point, the router will retrieve the information of which SSID the device is connected to. |
Associated Device | In case of an access point or an access point with the router, this section will show the MAC address of the device used |
Duration | This indicates how long a device has been connected to the router. |
RSSI | RSSI stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator. It indicates the wireless signal strength of the device connected to the AP paired with the router. |
Station Mode | This field indicates the station mode of the access point. |
Total | Total data exchanged between the device and the router. |
Upload | Total uploaded data by the device. |
Download | Total downloaded data by the device. |
Current Rate | The real time WAN bandwidth used by the device. |
Link Rate | This field indicates the total speed that the link can transfer. |
Manufacturer | This field indicates the manufacturer of the device. |
OS | This field indicates the operating system installed on the device. |
Clients Page
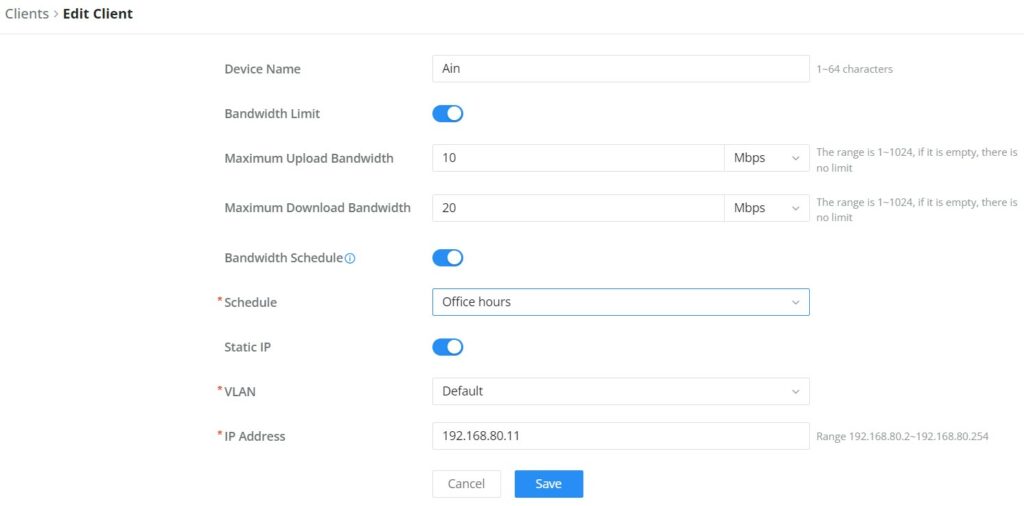
- Edit Device
under the operations column click on the “Edit” icon to set the name of the device, and assign a VLAN ID and static address to the device. It’s also possible to limit bandwidth for this exact device and even assign a schedule to it from the list. Refer to the figure below:
- Delete Device
To delete a device, go to the Operations column and click the button then click “Delete“. Please note that you can only delete the offline devices, the devices online cannot be deleted.
VPN
VPN stands for “Virtual Private Network” and it encrypts data in real-time to establish a protected network connection when using public networks.
VPN allows the GWN70x2 routers to be connected to a remote VPN server using PPTP, IPSec, L2TP, OpenVPN®, and WireGuard® protocols, or configure an OpenVPN® server and generate certificates and keys for clients.
GWN70x2 routers support the following VPN functions:
- PPTP: Client and server
- IPSec: Site-to-site and client-to-site
- OpenVPN®: Client and server
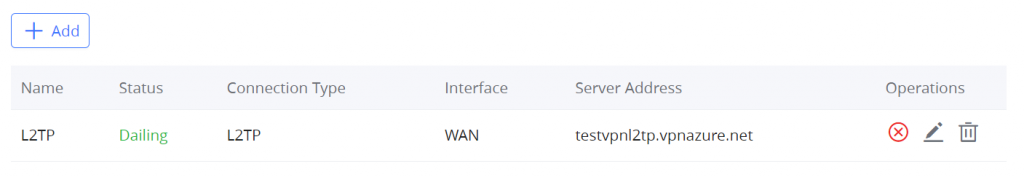
- L2TP: Client
- WireGuard®: Server
VPN page can be accessed from the GWN70x2 Web GUI → VPN.
PPTP
A data-link layer protocol for wide area networks (WANs) based on the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and developed by Microsoft enables network traffic to be encapsulated and routed over an unsecured public network such as the Internet. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) allows the creation of virtual private networks (VPNs), which tunnel TCP/IP traffic through the Internet.
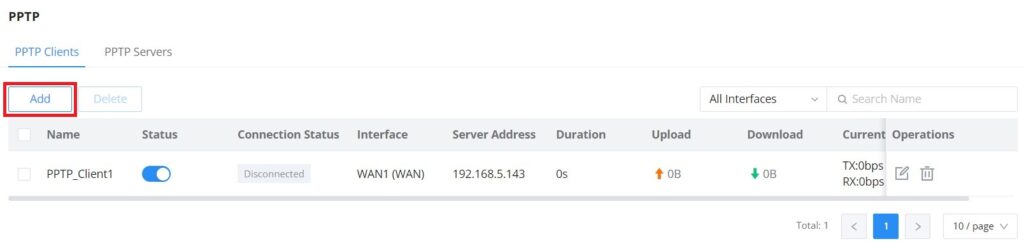
PPTP Clients
To configure the PPTP client on the GWN70x2, navigate under VPN → PPTP → PPTP Clients and set the following:
1. Click on the “Add” button.
The following window will pop up.
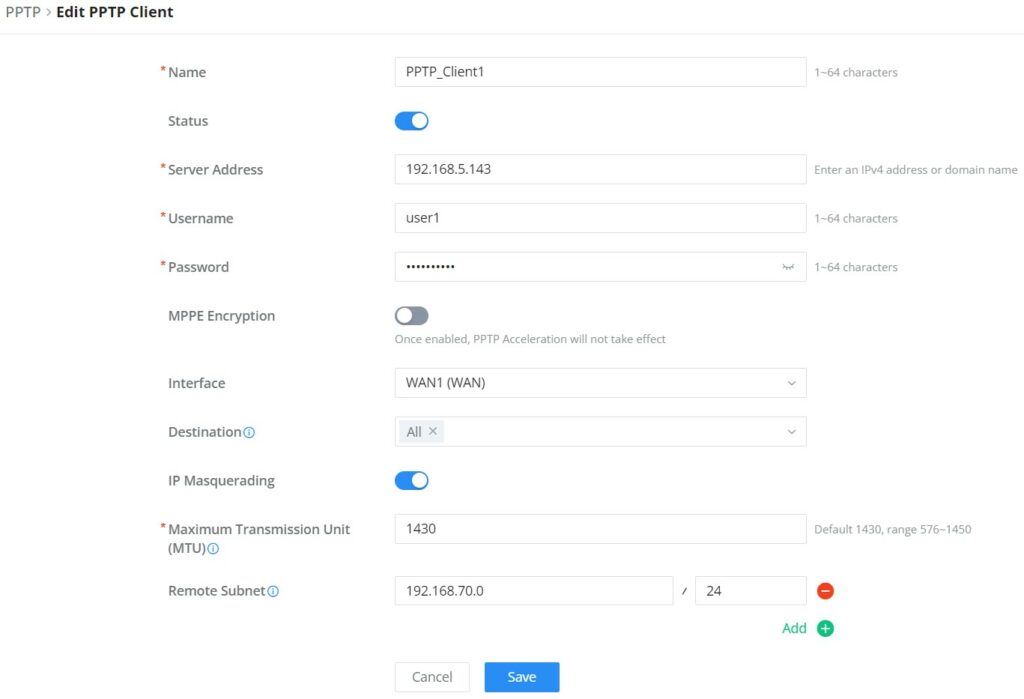
Name | Enter a name for the PPTP client. |
Status | Toggle on/off the VPN client account. |
Server Address | Enter the IP/Domain of the remote PPTP Server. |
Username | Enter the Username for authentication with the VPN Server. |
Password | Enter the Password for authentication with the VPN Server. |
MPPE Encryption | Enable / disable the MPPE for data encryption. By default, it’s disabled. |
Interface | Choose the interfaces. Note: Set forwarding rules in firewall automatically to allow traffic forwarded from VPN to the selected WAN port. If remote device is allowed to access, please set the corresponding forwarding rules in firewall. |
Destination | Choose to which destination group or WAN to allow traffic from the VPN, this will generate automatically a forwarding rule under the menu Firewall → Traffic Rules → Forward. |
IP Masquerading | This feature is a form of network address translation (NAT) which allows internal computers with no known address outside their network, to communicate to the outside. It allows one machine to act on behalf of other machines. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. |
Remote Subnet | Configures the remote subnet for the VPN. The format should be “IP/Mask” where IP could be either IPv4 or IPv6 and mask is a number between 1 and 32. example: 192.168.5.0/24 |
PPTP Client Configuration
PPTP Servers
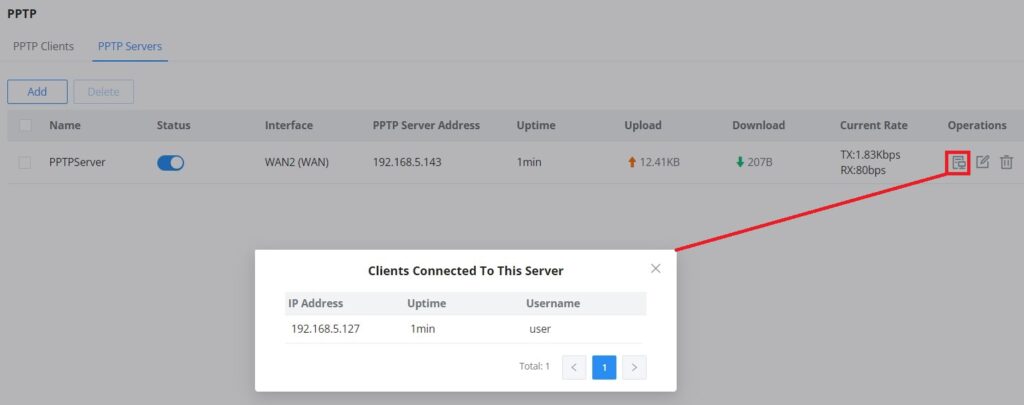
To add a PPTP Server, please navigate to Web UI → VPN → PPTP page → PPTP Servers tab, then click on the “Add” button.
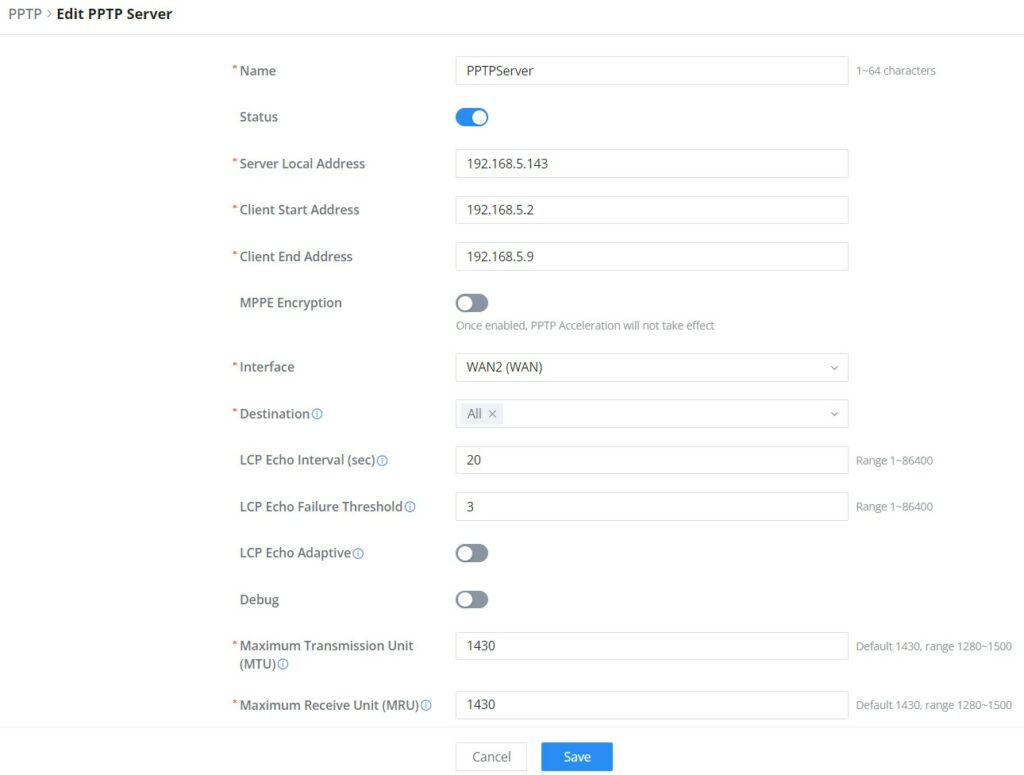
Name | Enter a name for the PPTP Server. |
Status | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable the PPTP Server VPN. |
Server Local Address | Specify the server local address |
Client Start Address | specify client start IP address |
Client End Address | specify client end IP address |
MPPE Encryption | Enable / disable the MPPE for data encryption. By default, it’s disabled. |
Interface | Select from the drop-down list the exact interface (WAN port). |
Destination | Select the Destination from the drop-down list (WAN or VLAN). Note: When selecting "All", subsequent new interfaces will be automatically included. |
LCP Echo Interval (sec) | Configures the LCP echo send interval. |
LCP Echo Failure Threshold | Set the maximum number of Echo transfers. If it is not answered within the set request frames, the PPTP server will consider that the peer is disconnected and the connection will be terminated. |
LCP Echo Adaptive |
|
Debug | Toggle On/Off to enable or disable debug. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. By default is 1450. |
Maximum Receive Unit (MRU) | MRU indicates the size of the received packets. By default is 1450. |
Preferred DNS Server | specify the preferred DNS server. Ex: 8.8.8.8 |
Alternative DNS Server | specify the alternative DNS server. Ex: 1.1.1.1 |
PPTP Server
- Create the remote user credentials:
To create the remote user account which will be required to be entered on the client side and and authenticated on the server side, please refer to the Remote Users section.
To view the clients connected to this server, click on the “Client List” icon as shown below:
IPSec
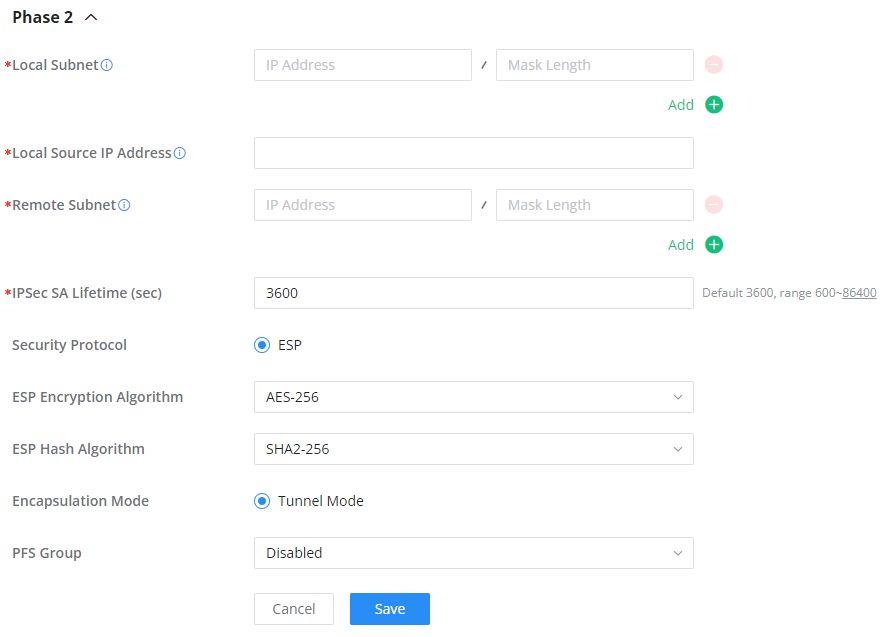
IPSec or Internet Protocol Security is mainly used to authenticate and encrypt packets of data sent over the network layer. To accomplish this, they use two security protocols – ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload) and AH (Authentication Header), the former provides both authentications as well as encryption whereas the latter provides only authentication for the data packets. Since both authentication and encryption are equally desirable, most of the implementations use ESP.
IPSec supports two different encryption modes, they are Tunnel (default) and Transport mode. Tunnel mode is used to encrypt both payloads as well as the header of an IP packet, which is considered to be more secure. Transport mode is used to encrypt only the payload of an IP packet, which is generally used in gateway or host implementations.
IPSec also involves IKE (Internet Key Exchange) protocol which is used to set up the Security Associations (SA). A Security Association establishes a set of shared security parameters between two network entities to provide secure network layer communication. These security parameters may include the cryptographic algorithm and mode, traffic encryption key, and parameters for the network data to be sent over the connection. Currently, there are two IKE versions available – IKEv1 and IKEv2. IKE works in two phases:
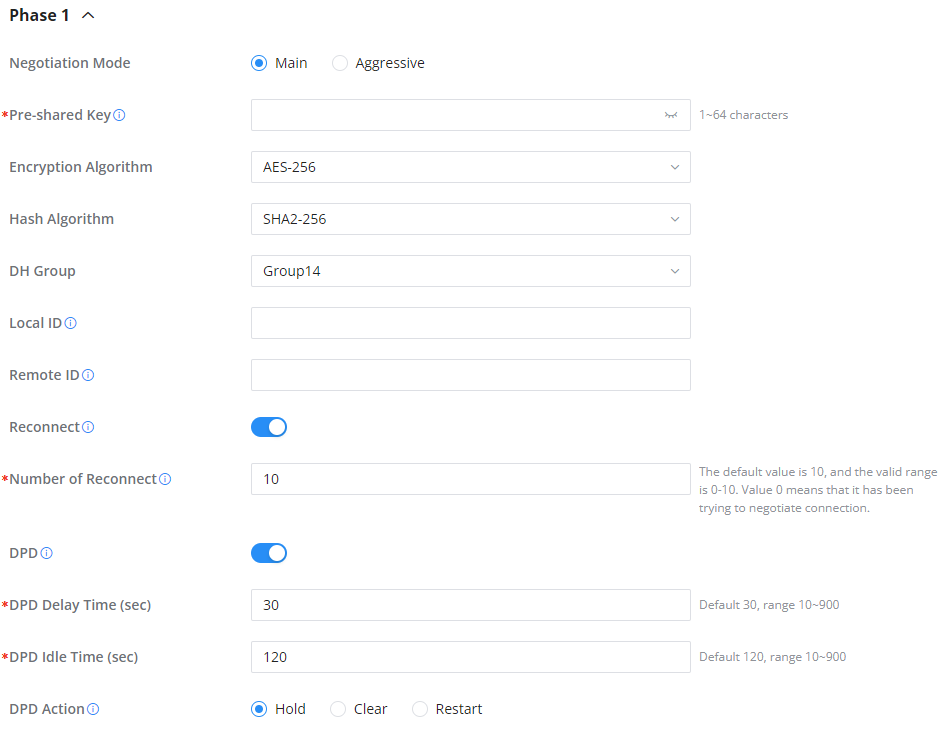
Phase 1: ISAKMP operations will be performed after a secure channel is established between two network entities.
Phase 2: Security Associations will be negotiated between two network entities.
IKE operates in three modes for exchanging key information and establishing security associations – Main, Aggressive, and Quick mode.
• Main mode: is used to establish phase 1 during the key exchange. It uses three two-way exchanges between the initiator and the receiver. In the first exchange, algorithms and hashes are exchanged. In the second exchange, shared keys are generated using the Diffie-Hellman exchange. In the last exchange, verification of each other’s identities takes place.
• Aggressive mode: provides the same service as the main mode, but it uses two exchanges instead of three. It does not provide identity protection, which makes it vulnerable to hackers. The main mode is more secure than this.
• Quick mode: After establishing a secure channel using either the main mode or aggressive mode, the quick mode can be used to negotiate general IPsec security services and generate newly keyed material. They are always encrypted under the secure channel and use the hash payload that is used to authenticate the rest of the packet.
IPSec Site-to-Site
To build an IPSec secure tunnel between two sites located in two distant geographical locations, we can use the sample scenario below:
The branch office router needs to connect to the Headquarters office via an IPSec tunnel, on each side we have a GWN70x2 router. Users can configure the two devices as follows:
The branch office router runs a LAN subnet 192.168.1.0/24 and the HQ router runs a LAN subnet 192.168.3.0, the public IP of the branch office router is 1.1.1.1 and the IP of the HQ router is 2.2.2.2.
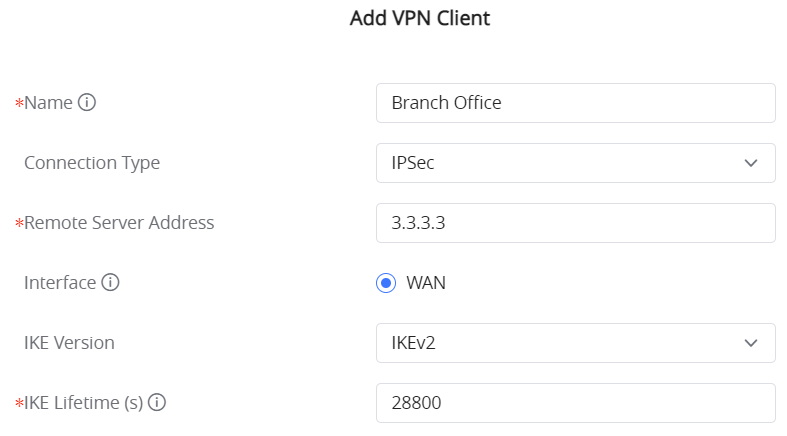
Go under VPN → IPSec → Site-to-Site then click on to add a VPN Client.
○ Phase 1
○ Phase 2
After this is done, press “Save” and do the same for the HQ Router. The two routers will build the tunnel and the necessary routing information to route traffic through the tunnel back and from the branch office to the HQ network.
- Create the remote user credentials:
To create the remote user account which will be required to be entered on the client side and and authenticated on the server side, please refer to the Remote Users section.
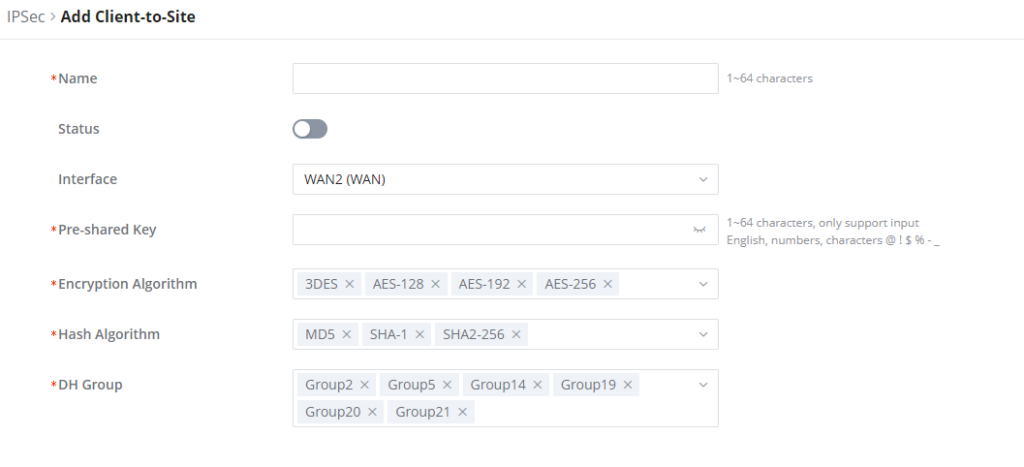
IPSec Client-to-Site
Go under VPN → IPSec → Client-to-Site then fill in the following information:
OpenVPN®
OpenVPN® Client
There are two ways to use the GWN70x2 as an OpenVPN® client:
1. Upload client certificate created from an OpenVPN® server to GWN70x2.
2. Create client/server certificates on GWN70x2 and upload the server certificate to the OpenVPN® server.
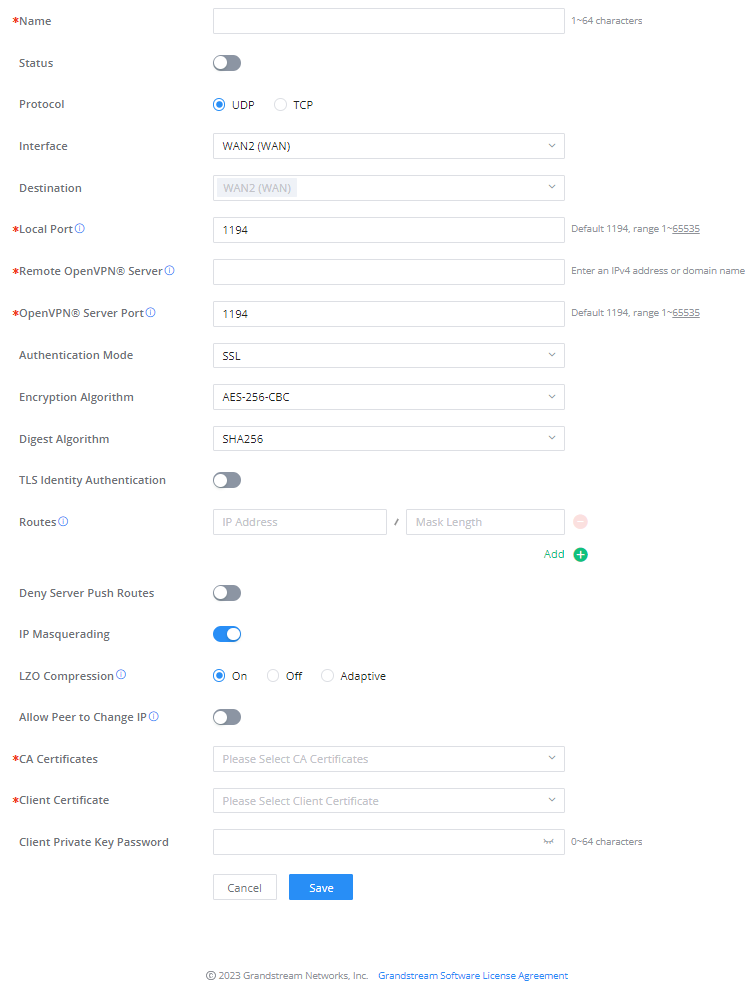
Go to Go to VPN → OpenVPN® → OpenVPN® Clients and follow the steps below:
Click on button. The following window will pop up.
Clickafter completing all the fields.
Name | Enter a name for the OpenVPN® Client. |
Status | Toggle on/off the client account. |
Protocol | Specify the transport protocol used.
Note: The default protocol is UDP. |
Interface | Select the WAN port to be used by the OpenVPN® client. |
Destination | Select the WANs, VLANs and VPNs (clients) destinations that will be used by this OpenVPN® client. |
Local Port | Configures the client port for OpenVPN®.The port between the OpenVPN® client and the client or between the client and the server should not be the same. |
Remote OpenVPN® Server | Configures the remote OpenVPN® server. Both IP address and domain name are supported. |
OpenVPN® Server Port | Configures the remote OpenVPN® server port |
Authentication Mode | Choose the authentication mode.
|
Encryption Algorithm | Choose the encryption algorithm. The encryption algorithms supported are:
|
Digest Algorithm | Select the digest algorithm. The digest algorithms supported are:
|
TLS Identity Authentication | Enable TLS identity authentication direction. |
TLS Identity Authentication Direction | Select the indentity authentication direction.
|
TLS Pre-Shared Key | Enter the TLS pre-shared key. |
Routes | Configures IP address and subnet mask of routes, e.g., 10.10.1.0/24. |
Deny Server Push Routes | If enabled, client will ignore routes pushed by the server. |
IP Masquerading | This feature is a form of network address translation (NAT) which allows internal computers with no known address outside their network, to communicate to the outside. It allows one machine to act on behalf of other machines. |
LZO Compression | Select whether to activate LZO compression or no, if set to “Adaptive”, the server will make the decision whether this option will be enabled or no. |
Allow Peer to Change IP | Allow remote change the IP and/or Port, often applicable to the situation when the remote IP address changes frequently. |
CA Certificates | Click on “Upload” and select the CA certificate |
Client Certificate | Click on “Upload” and select the Client Certificate. |
Client Private Key Password | Enter the client private key password. |
OpenVPN® Client
OpenVPN® Server
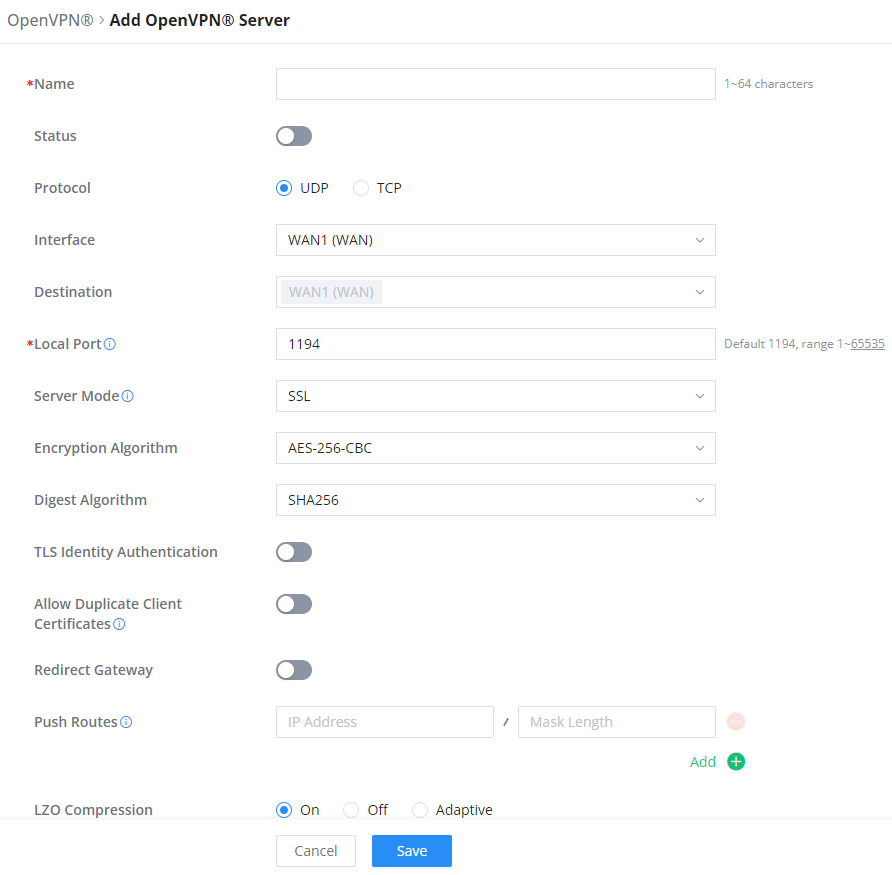
To use the GWN70x2 as an OpenVPN® server, you will need to start creating OpenVPN® certificates and remote users.
To create a new VPN server, navigate under Web UI → VPN → OpenVPN® page → OpenVPN® Servers tab.
Clickafter completing all the fields.
Refer to the table below:
Name | Enter a name for the OpenVPN® server. |
Status | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable the OpenVPN® Server. |
Protocol | Choose the Transport protocol from the dropdown list, either TCP or UDP. The default protocol is UDP. |
Interface | Select from the drop-down list the exact interface (WAN). |
Destination | Select from the drop-down list the destination (WAN or VLAN). |
Local Port | Configure the listening port for OpenVPN® server. The default value is 1194. |
Server Mode | Choose the server mode the OpenVPN® server will operate with. 4 modes are available:
|
Encryption Algorithm | Choose the encryption algorithm from the dropdown list to encrypt data so that the receiver can decrypt it using same algorithm. |
Digest Algorithm | Choose digest algorithm from the dropdown list, which will uniquely identify the data to provide data integrity and ensure that the receiver has an unmodified data from the one sent by the original host. |
TLS Identicy Authentication | This option uses a static Pre-Shared Key (PSK) that must be generated in advance and shared among all peers. This feature adds extra protection to the TLS channel by requiring that incoming packets have a valid signature generated using the PSK key. |
TLS Identity Authentication Direction | Select from the drop-down list the direction of TLS Identity Authentication, three options are available (Server, Client or Both). |
TLS Pre-Shared Key | If TLS Identicy Authentication is enabled, enter the TLS Pre-Shared Key. |
Allow Duplicate Client Certificates | Click on "ON" to allow duplicate Client Certificates |
Redirect Gateway | When redirect-gateway is used, OpenVPN® clients will route DNS queries through the VPN, and the VPN server will need to handle them. |
Push Routes | Specify route(s) to be pushed to all clients. Example: 10.0.0.1/8 |
LZO Compression Algorithm | Select whether to activate LZO compression or no, if set to “Adaptive”, the server will make the decision whether this option will be enabled or no. |
Allow Peer to Change IP | Allow remote change the IP and/or Port, often applicable to the situation when the remote IP address changes frequently. |
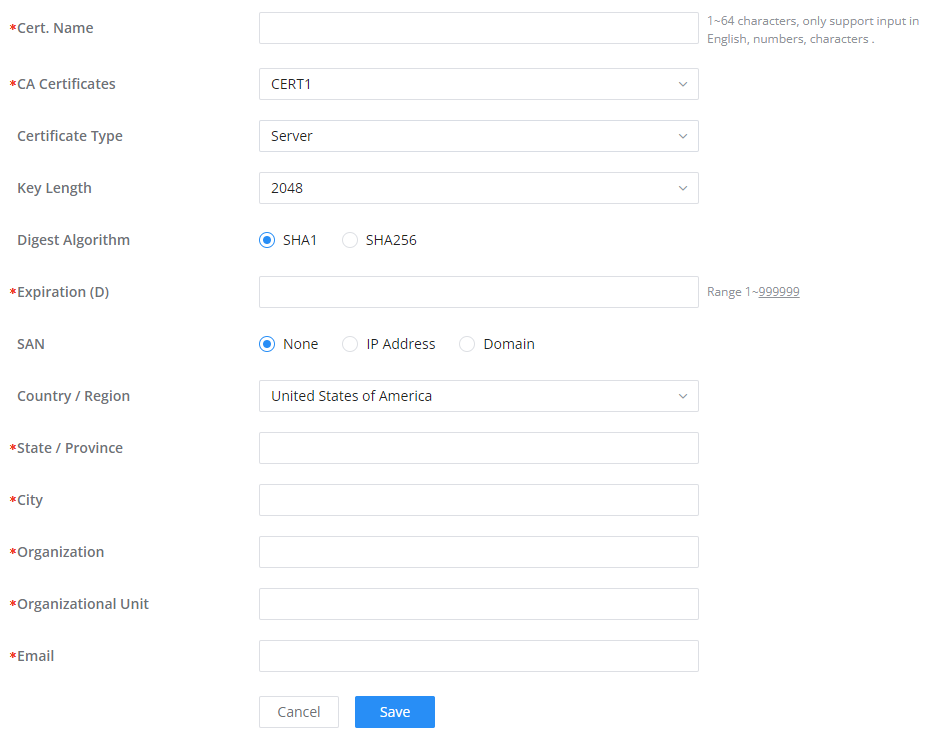
CA Certificate | Select a generated CA from the dropdown list or add one. |
Server Certificate | Select a generated Server Certificate from the dropdown list or add one. |
IPv4 Tunnel Network/Mask Length | Enter the network range that the GWN70xx will be serving from to the OpenVPN® client. Note: The network format should be the following 10.0.10.0/16. The mask should be at least 16 bits. |
Create OpenVPN® Server
- Create the remote user credentials:
To create the remote user account which will be required to be entered on the client side and and authenticated on the server side, please refer to the Remote Users section.
L2TP
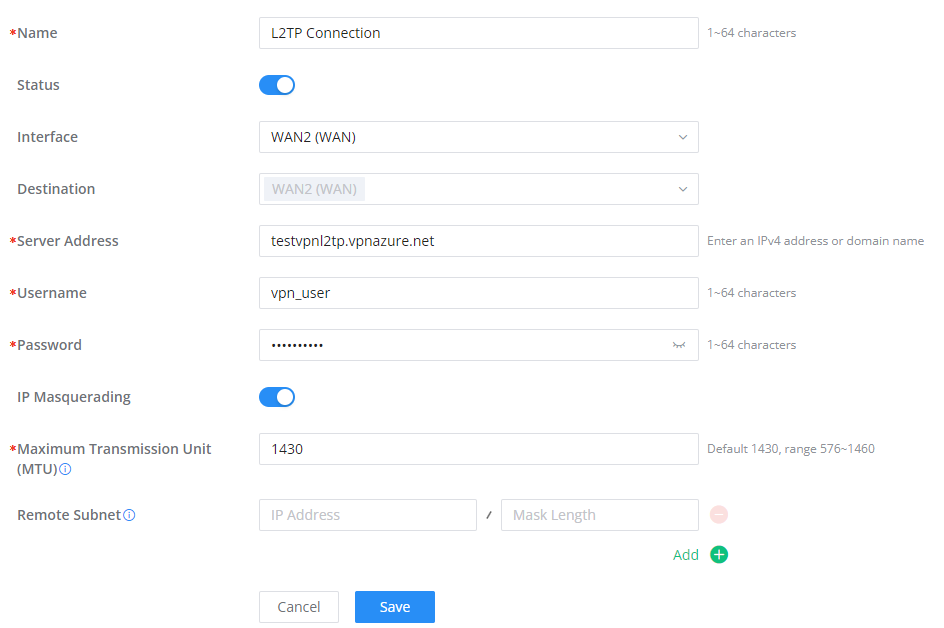
To configure the L2TP client on the GWN70x2 router, navigate under “VPN → VPN Clients” and set the following:
1. Click onbutton and the following window will pop up.
Name | Set a name for this VPN tunnel. |
Status | Toggle on/off this L2TP account. |
Interface | Select the WAN port to be used by VPN. |
Destination | Select the WANs, VLANs destinations that will be using this VPN. |
Server Address | Enter the VPN IP address or FQDN. |
Username | Enter VPN username that has been configured on the server side. |
Password | Enter VPN password that has been configured on the server side. |
IP Masquerading | This feature is a form of network address translation (NAT) which allows internal computers with no known address outside their network, to communicate to the outside. It allows one machine to act on behalf of other machines. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. |
Remote Subnet | Enter the remote Subnet that has been configured on the server side. |
L2TP Client Configuration
Clickafter completing all the fields.
WireGuard®
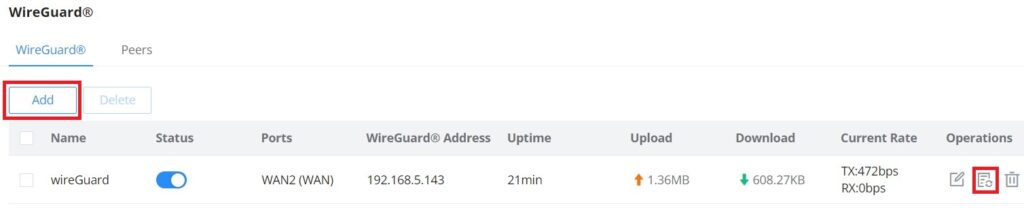
WireGuard® is a free and open-source VPN solution that encrypts virtual private networks, easy to use, high performance, and secure. GWN70x2 routers series support WireGuard® VPN with automatic peer generation and QR code scanning for mobile phones and devices with camera support.
To start using WireGuard® VPN, please navigate to the Web UI → VPN → WireGuard® page. Click on the “Add” button to add a WireGuard® server as shown below:
Please refer to the figure and table below when filling up the fields.
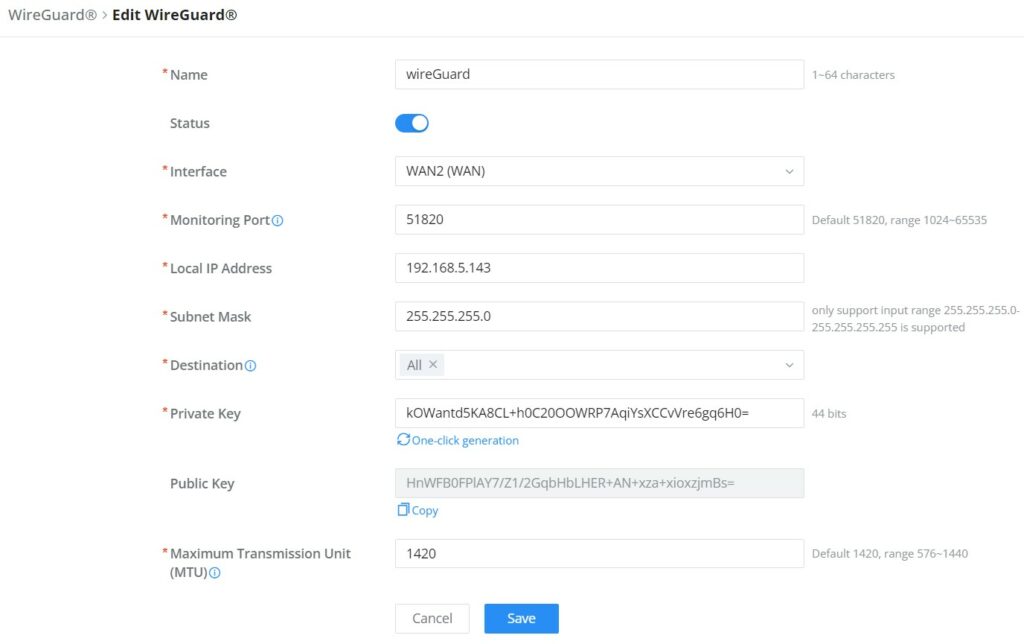
Name | Specify a name for Wireguard® VPN. |
Status | Toggle ON or OFF to enable or disable the Wireguard® VPN. |
Interface | Select from the drop-down list the WAN port. |
Monitoring Port | Set the local listening port when establishing a WireGaurd® tunnel. Default: 51820 |
Local IP Address | Specify the network that WireGuard® clients (Peers) will get IP address from. |
Subnet Mask | Configures the IP address range available to the Peers. |
Destination | Select the Destination(s) from the drop-down list. Note: When selecting "All", subsequent new interfaces will be automatically included. |
Private Key | Click on "One-Click Generation" text to generate a private key. |
Public Key | The public key will be generated according to the private key. Click on "Copy" text to copy the public key. |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) | This indicates the size of the packets sent by the router. Please do not change this value unless necessary. By default is 1450. |
Add/Edit WireGuard®
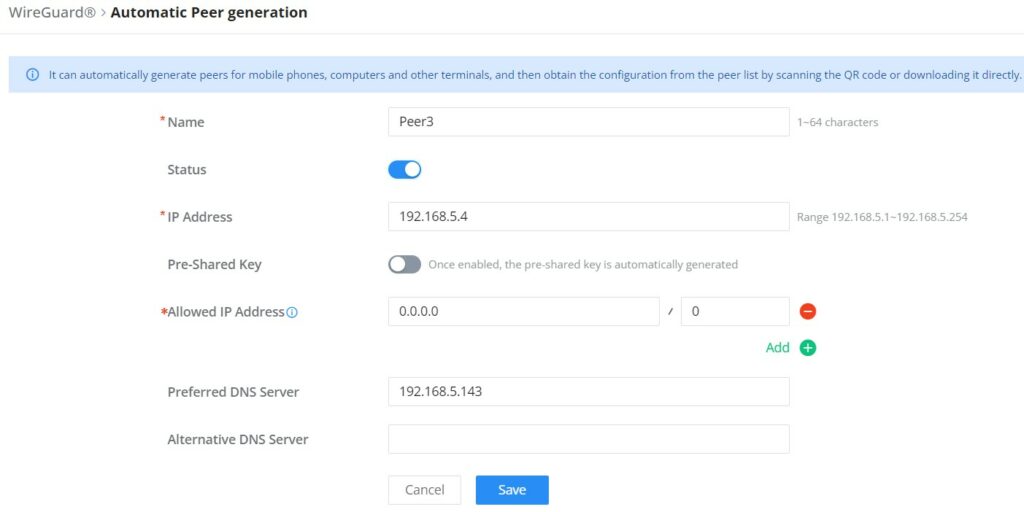
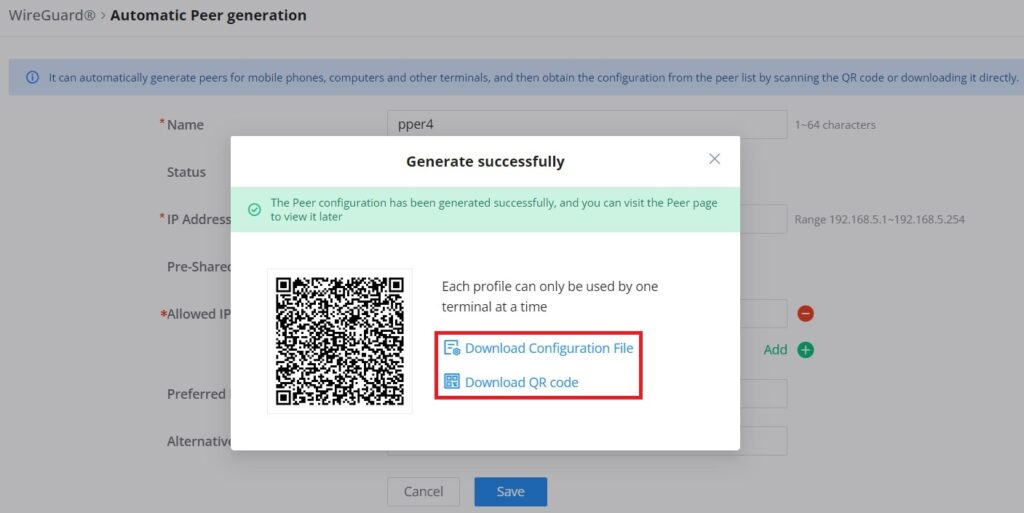
Once finished configuring WireGuard®, click on the “Automatic peer generation” icon to generate peers very quickly and easily as shown in the figures below:
Enter a name and toggle status ON then click on the “Save” button.
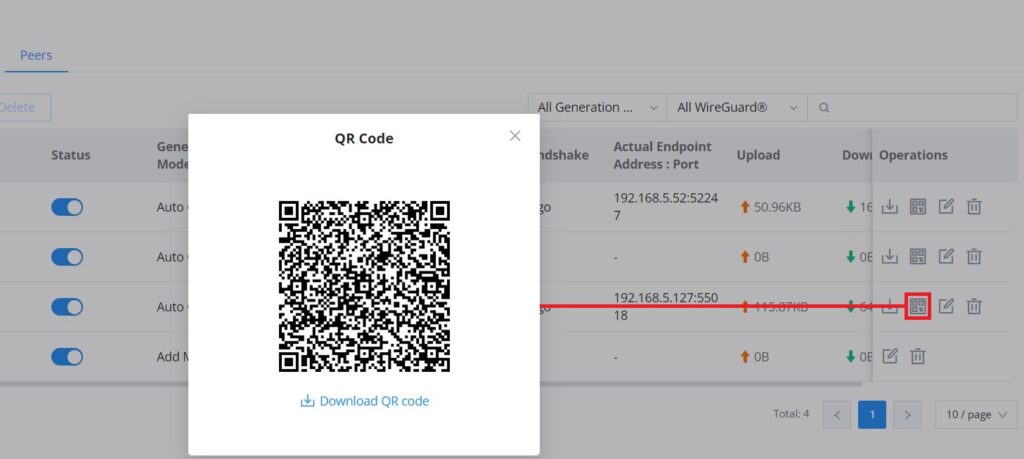
Now, the user can either download the configuration file and share it, or download a QR code for devices like mobile phones to scan.
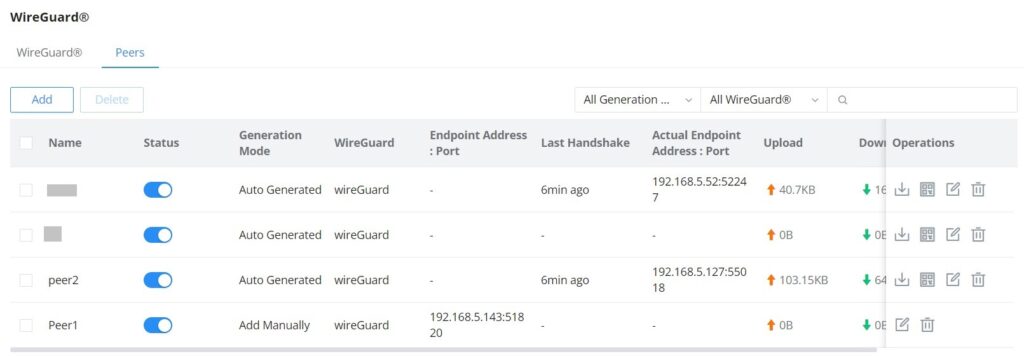
Peers
On the peers’ tab, the user can create peers manually by clicking on the “Add” button.
Please refer to the figure below when filling up the fields.
The user can download the config file after adding the peer.
Or scanning the QR code for devices with camera support.
Remote Users
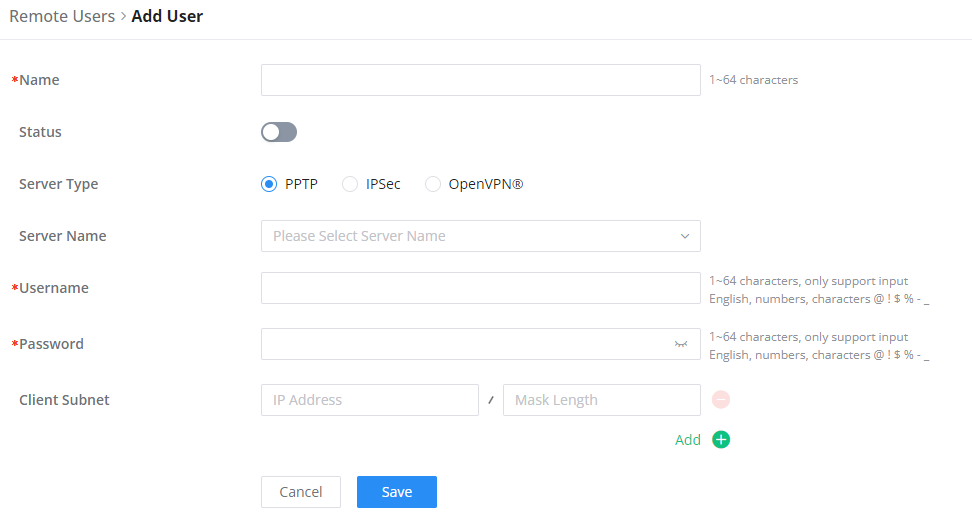
To create the VPN user accounts, please navigate to VPN → Remote Users then click “Add”. The account configured will be used for the client to authenticate into the VPN server. The remote client user that can be created in this section is for PPTP, IPSec, and OpenVPN.
Name | Enter a name for the user. This name will not be used to log in. |
Status | Enable or disable this account. |
Server Type | Choose the type of the server.
|
Server Name | Enter the server's name. |
Username | Enter the username. This username will be used to log in. |
Password | Enter the password. |
Client Subnet | Specify the client subnet. |
Add VPN Remote Users
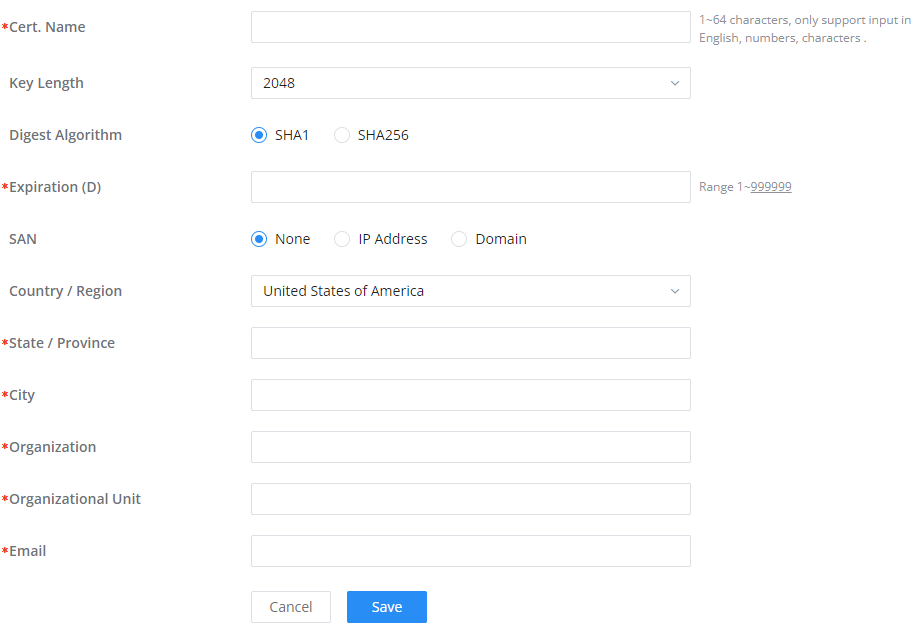
To authenticate a remote user into the VPN server successfully, the username and password are used alongside the client certificate. To create a client certificate please refer to the Certificates section.
To configure the VPN clients for each VPN server type, please refer to the respective VPN client configuration above.
ROUTING
Policy Routes
In this section, the user can create a policy route to either load balance or backup (Failover) between 2 or more WAN ports or VPNs. This feature allows a network administrator to make advanced routing decisions for traffic passing through the router and for high granularity control over policies that dictate what WAN port and even VLAN, traffic should use. Traffic controlled this way can be balanced across multiple VLANs.
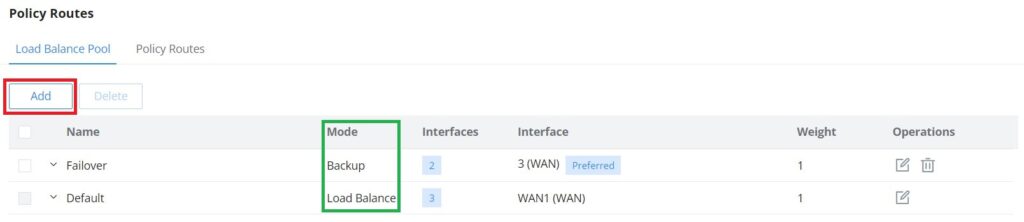
Load Balance Pool
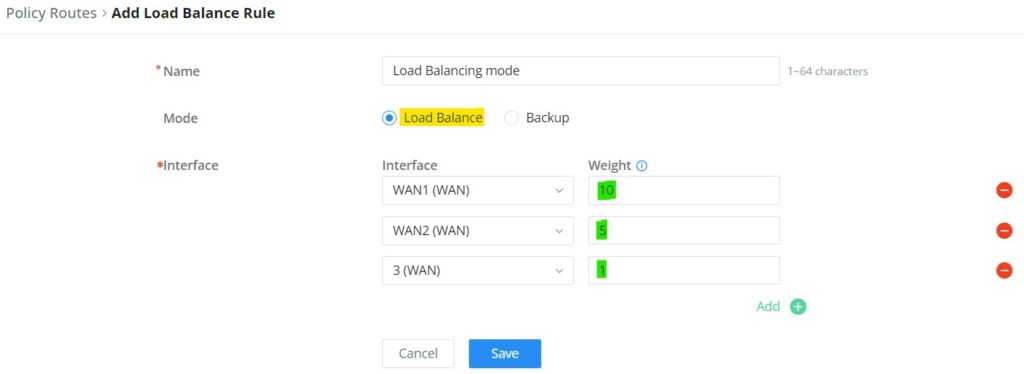
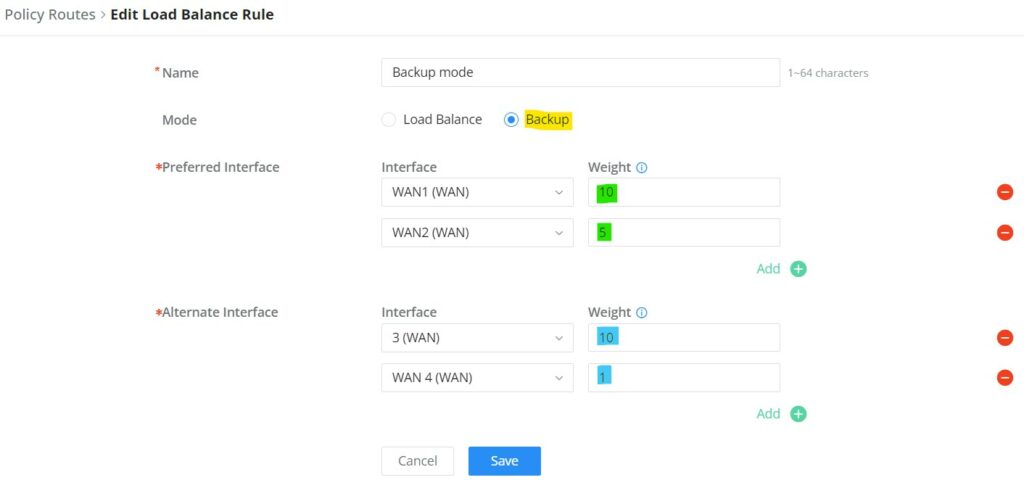
To create a load balance rule, navigate to the Routing → Policy Routes page → Load Balance Pool tab, click on the “Add” button, then select the mode (Load Balance or Backup), after selecting the WAN port or VPN from the drop-down list and specify the Weight for each WAN or VPN added. Please refer to the figures below:
Policy Route
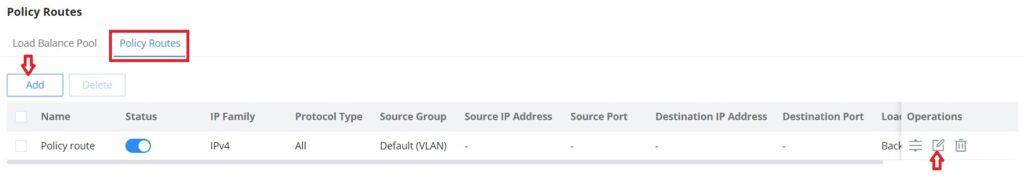
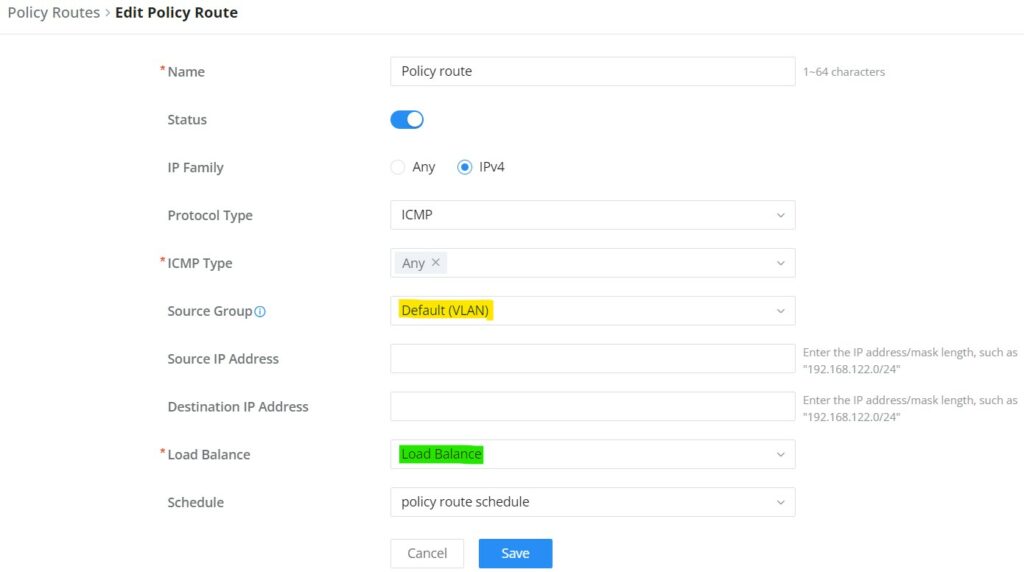
On the second tab (Policy Routes), the user can specify which Networks (VLAN) can use which Load Balance rule (must be created first), also the user can specify the protocol type, source, and destination IP and even assign a schedule for it.
To create a Policy Route, please navigate to Routing → Policy Routes page → Policy Routes tab, then click on the “Add” button as shown below:
Static Routes
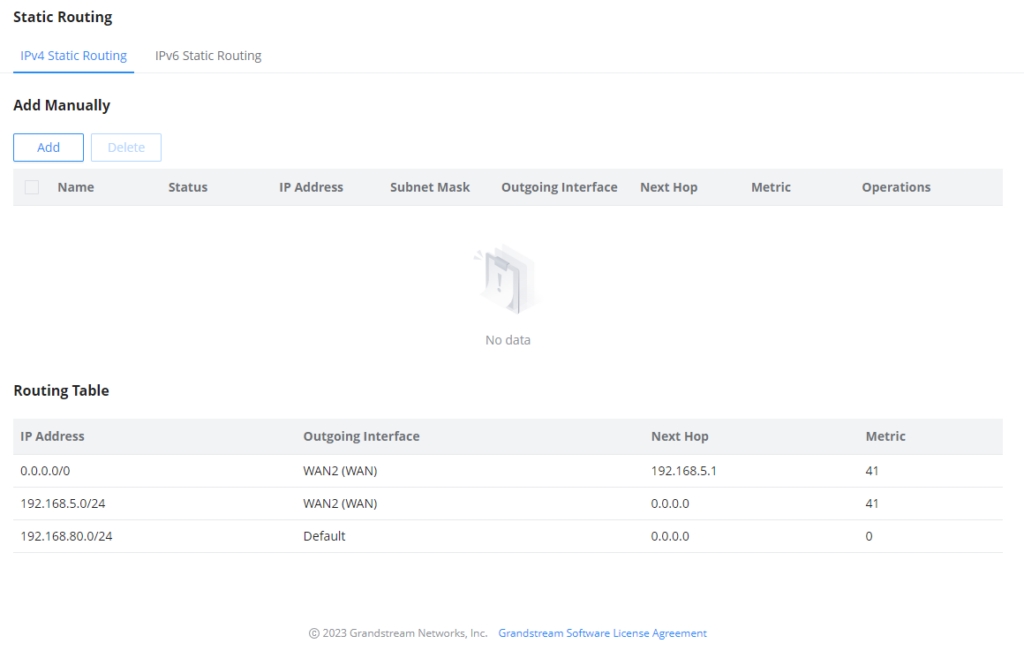
Static routing is a form of routing by manually configuring the routing entries, rather than using a dynamic routing traffic for any service that requires a static address that never changes.
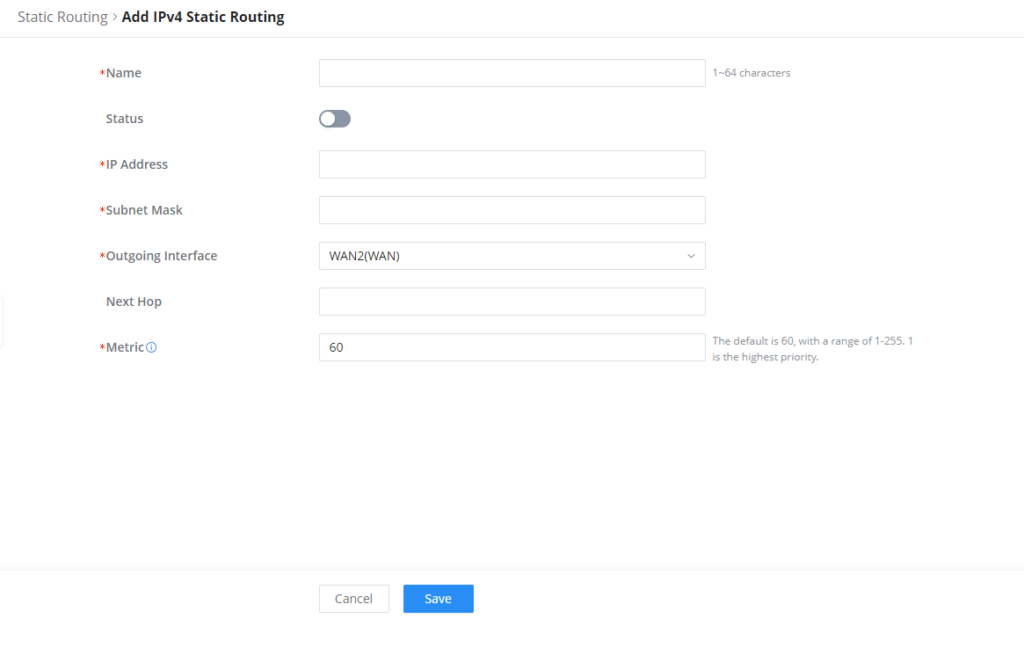
GWN70x2 supports setting manually IPv4 or IPv6 Static Routes which can be accessed from GWN70x2 WebGUI Routing → Static Routing.
To add a new Static Route, the user needs to click on
Name | Specify a name for the Static Routing |
Status | enable or disable the Static Routing |
IP Address | Specify the IP address |
Subnet Mask | Enter the Subnet Mask |
Outgoing Interface | Select the interface |
Next Hop | Specify the next Hop |
Metric | When there are multiple routings in the network that can reach the same destination, the priority of routing rules can be adjusted by setting metric, and the packets will be forwarded according to the path with the smallest metric. |
Add IPv4 Static Routing
TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT
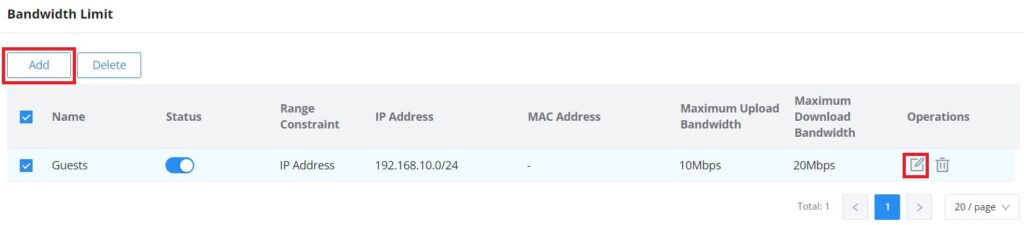
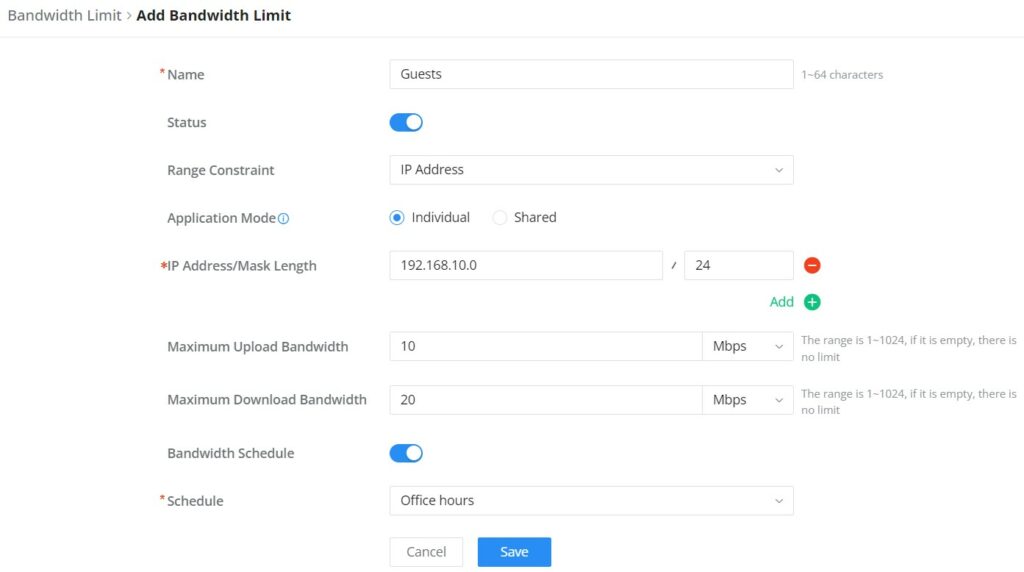
Bandwidth Limit
The Bandwidth limit feature helps to limit bandwidth by specifying the maximum upload and download limit, then this limit can be applied to each IP/MAC address or applied to all IP addresses in the IP address range. Navigate to Web UI → Traffic Management → Bandwidth Limit.
To add a bandwidth rule, please click on the “Add” button or click on the “Edit” icon as shown above.
Please refer to the figure below:
AP MANAGEMENT
GWN70x2 routers come with an embedded controller for the GWN access points. The user can configure all the Wi-Fi-related settings through the controller. When the APs are connected to the router and are paired with it, they will automatically inherit the configuration that has been set on the router’s AP Management section.
Access Points
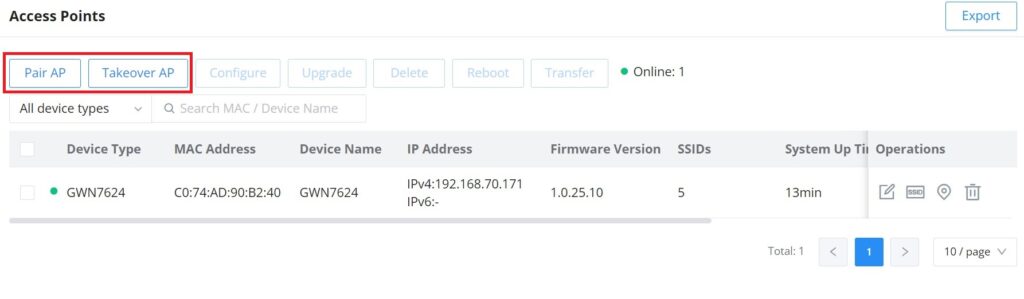
In this section, the user can add the access point which can be controlled using the embedded controller within the router. The user can either pair or takeover an access point to be able to configure it. The configuration performed on the router AP embedded controller will be pushed to the access points; thus, offering a centralized management of the GWN access points.
To add a GWN access point to the GWN router, please navigate to Web UI → AP Management → Access Points.
Pair AP: Use this button when pairing an AP that has not been set as a master.
Takeover AP: Use this button to take over an access point that has formerly been set as a slave to a different master device. To pair the devices successfully, the network administrator must enter the password of the master device.
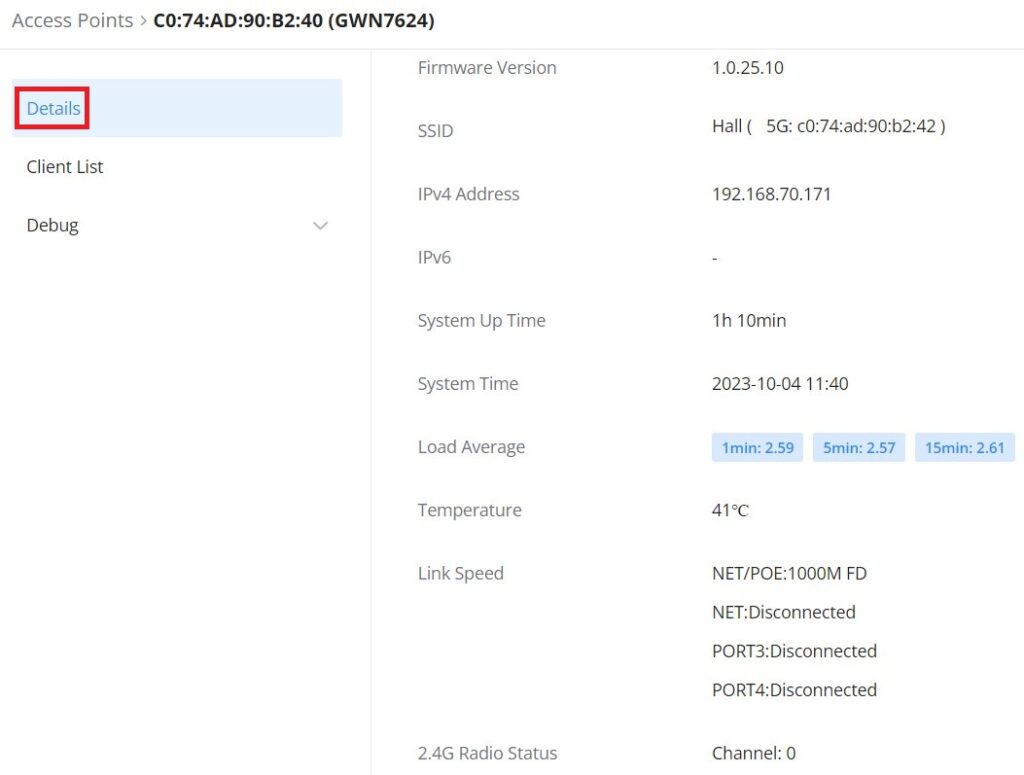
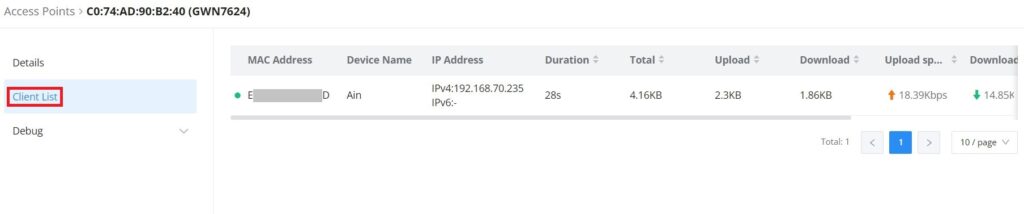
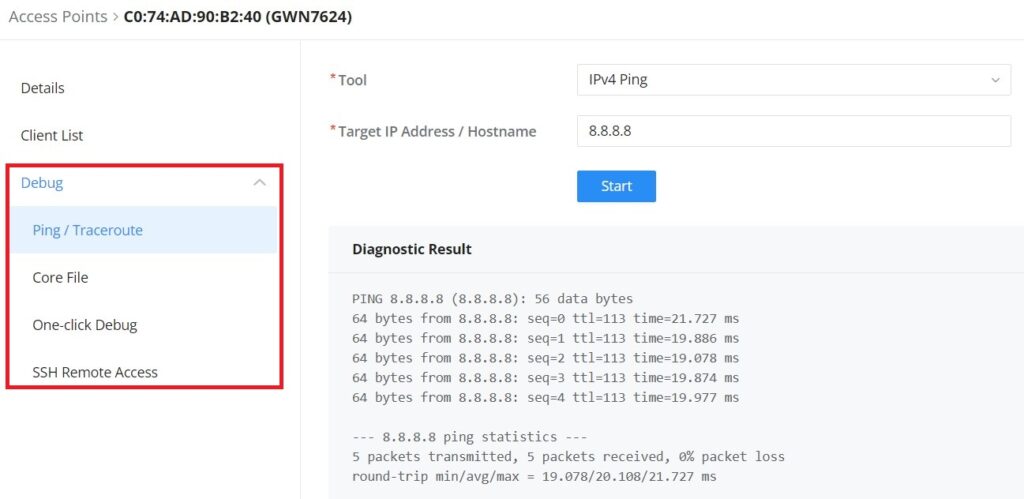
Click on a paired GWN AP to view Details, Client list, and debug tools. Please refer to the figures below:
The Details section contains details about the paired AP like firmware version, SSID, IP address, Temperature, etc.
The Client List section lists all the connected clients through this AP with much info like MAC Address, Device name, IP Address, bandwidth, etc.
The Debug section provides the users with many debug tools to help diagnose any issue like Ping/Traceroute, One-click Debug, and SSH Remote Access.
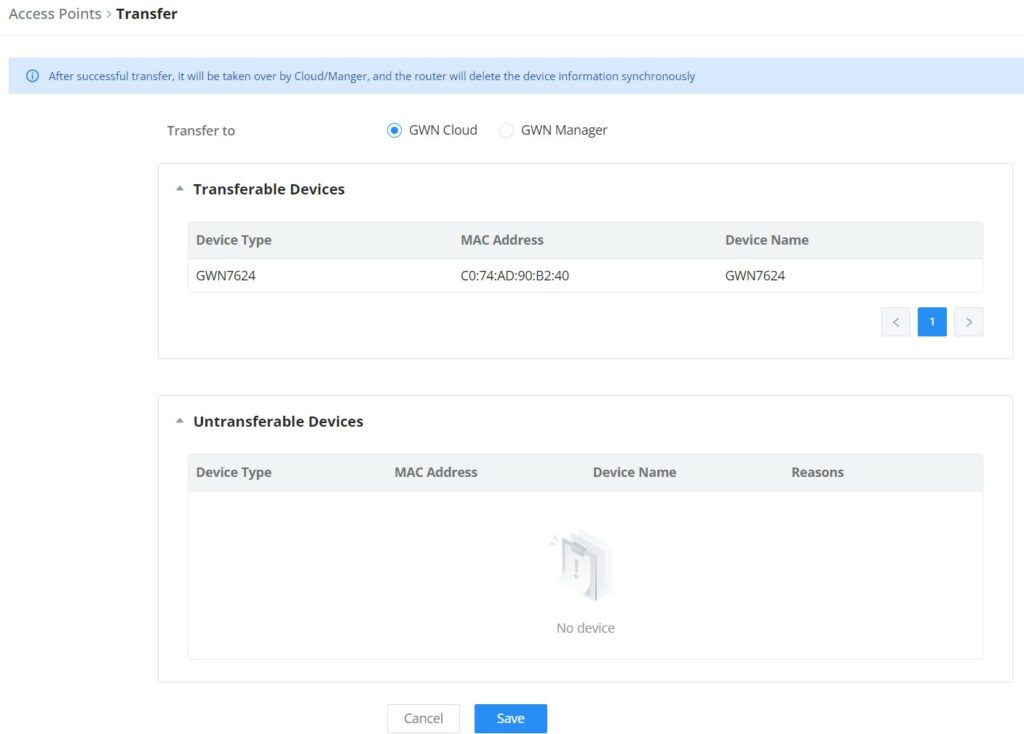
Transfer APs to GWN.Cloud/GWN Manager
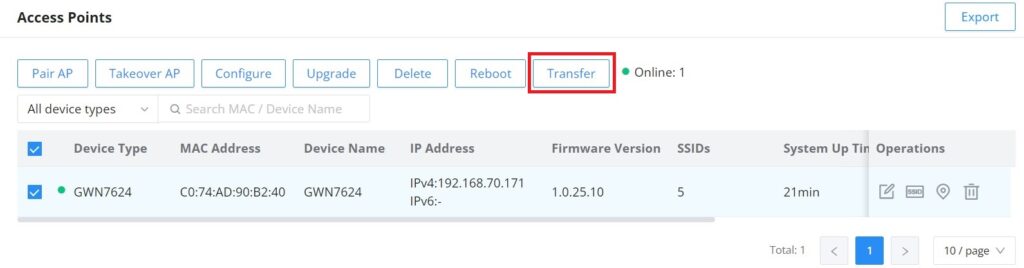
GWN routers also enable users to transfer their paired GWN APs to GWN.Cloud/GWN Manager.
On the AP Management → Access Points page, select the AP or APs then click on the “Transfer” button as shown below:
On the next page, select either GWN Cloud or GWN Manager then click the “Save” button. the user will be forwarded automatically to either GWN Cloud or GWN Manager to log in.
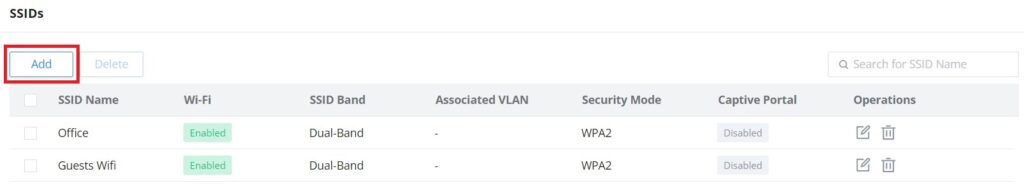
SSIDs
On this page, the user can configure SSID settings. The Wi-Fi SSID will be broadcast by the paired access points. This offers centralized control over the SSIDs created which makes managing many GWN access points easier and more convenient.
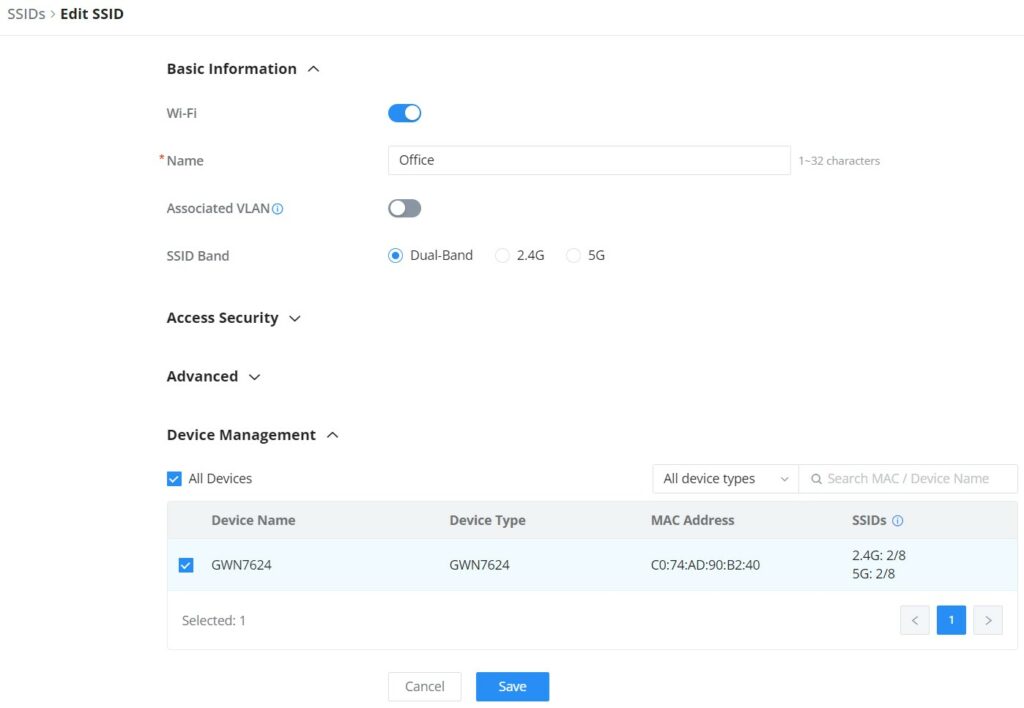
To add an SSID, the user should click on the “Add” button, then the following page will appear:
Basic Information | |
Wi-Fi | Toggle on/off the Wi-Fi SSID. |
Name | Enter the name of the SSID. |
Associated VLAN | Toggle "ON" to enable VLAN, then specify the VLAN from the list or click on "Add VLAN" to add one. |
SSID Band | Choose the Wi-Fi SSID band.
|
Access Security | |
Security Mode | Choose the security mode for the Wi-Fi SSID.
|
WPA Key Mode | Choose the WPA key mode:
|
WPA Encryption Type | Choose the encryption type:
|
WPA Shared Key | Enter the shared key phrase. This key phrase will be required to enter when connecting to the Wi-Fi SSID. |
Enable Captive Portal | Toggle Captive Portal on/off.
|
Blocklist Filtering | Choose a blocklist for the Wi-Fi SSID. |
Client Isolation |
|
802.11w |
|
Advanced | |
SSID Hidden | After enabled, wireless devices will not be able to scan this Wi-Fi, and can only connect by manually adding network. |
DTIM Period | Configure the delivery traffic indication message (DTIM) period in beacons. Clients will check the device for buffered data at every configured DTIM Period. You may set a high value for power saving consideration. Please input an integer between 1 to 10. |
Wireless Client Limit | Configure the limit for wireless client, valid from 1 to 256. If every Radio has an independent SSID, each SSID will have the same limit. Therefore, setting a limit of 256 will limit each SSID to 256 clients independently. |
Client Inactivity Timeout (sec) | Router/AP will remove the client's entry if the client generates no traffic at all for the specified time period. The client inactivity timeout is set to 300 seconds by default. |
Multicast Broadcast Suppression |
|
Convert IP Multicast to Unicast |
|
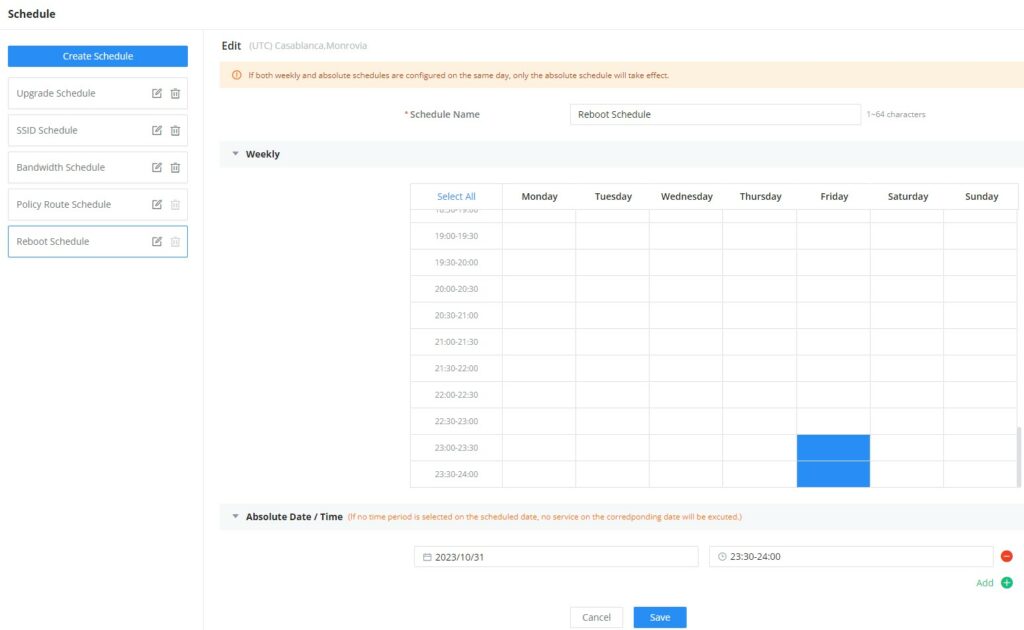
Schedule | Enable then select from the drop-down list or create a time schedule when this SSID can be used. |
Voice Enterprise | Enable voice enterprise. |
802.11r | Enable 802.11r. |
802.11k | Enable 802.11k. |
802.11v | Enable 802.11v. |
ARP Proxy | Once enabled, devices will avoid transferring the ARP messages to stations, while initiatively answer the ARP requests in the LAN. |
U-APSD | Configures whether to enable U-APSD (Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery). |
Bandwidth Limit | Toggle ON/OFF Bandwidth limit Note: If Hardware acceleration is enabled, Bandwidth Limit does not take effect. Please go to Network Settings/Network Acceleration to disable |
Maximum Upload Bandwidth | Limit the upload bandwidth used by this SSID. The range is 1~1024, if it is empty, there is no limit. |
Maximum Download Bandwidth | Limit the download bandwidth used by this SSID. The range is 1~1024, if it is empty, there is no limit |
Bandwidth Schedule | Toggle ON/OFF Bandwidth Schedule; if it's ON, then select a schedule from the drop-down list or click on "Create Schedule". |
Device Management | |
In this section, the user is able to add and remove the GWN access points that can broadcast the Wi-Fi SSID. There is also the option to search the device by MAC address or name. | |
Add SSID
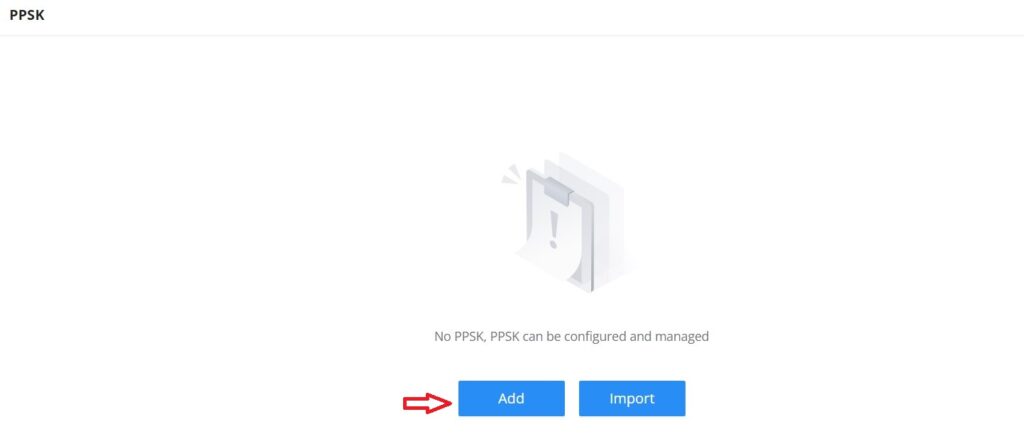
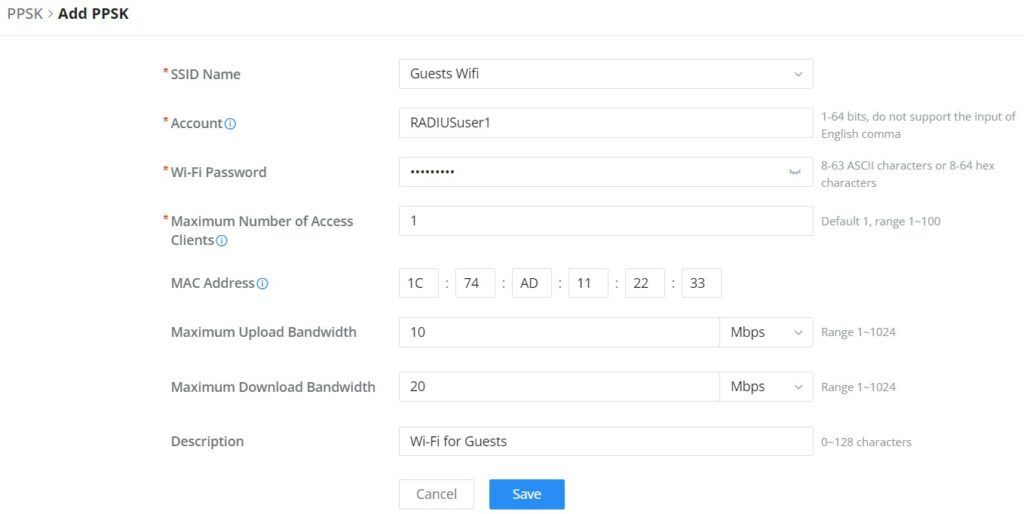
Private Pre-Shared Key (PPSK)
PPSK (Private Pre-Shared Key) is a way of creating Wi-Fi passwords per group of clients instead of using one single password for all clients. When configuring PPSK, the user can specify the Wi-Fi password, maximum number of access clients, and maximum upload and download bandwidth.
To start using PPSK, please follow the steps below:
- First, create an SSID with WPA key mode set to either PPSK without RADIUS or PPSK with RADIUS.
- Navigate to Web UI → AP Management → PPSK page, then click on the “Add” button then fill in the fields as shown below:
SSID Name | Select from the drop-down list the SSID that has been previously configured with WPA Key mode set to PPSK without RADIUS or PPSK with RADIUS. |
Account | If the WPA key mode in the selected SSID is "PPSK with RADIUS", the account is the user account of the RADIUS server. |
Wi-Fi Password | Specify a Wi-Fi password |
Maximum Number of Access Clients | Confgures the maximum number of devices allowed to be online for the same PPSK account. |
MAC Address | Enter a MAC Address Note: this field is only available if the Maximum Number of Access Clients is set to 1. |
Maximum Upload Bandwidth | Specify the maximum upload bandwidth in Mbps or Kbps. |
Maximum Download Bandwidth | Specify the maximum downlolad bandwidth in Mbps or Kbps. |
Description | Specify a description for the PPSK |
Add PPSK
Radio
Under AP Managements → Radio, the user will be able to set the general wireless settings for all the Wi-Fi SSIDs created by the router. These settings will take effect on the level of the access points which are paired with the router.
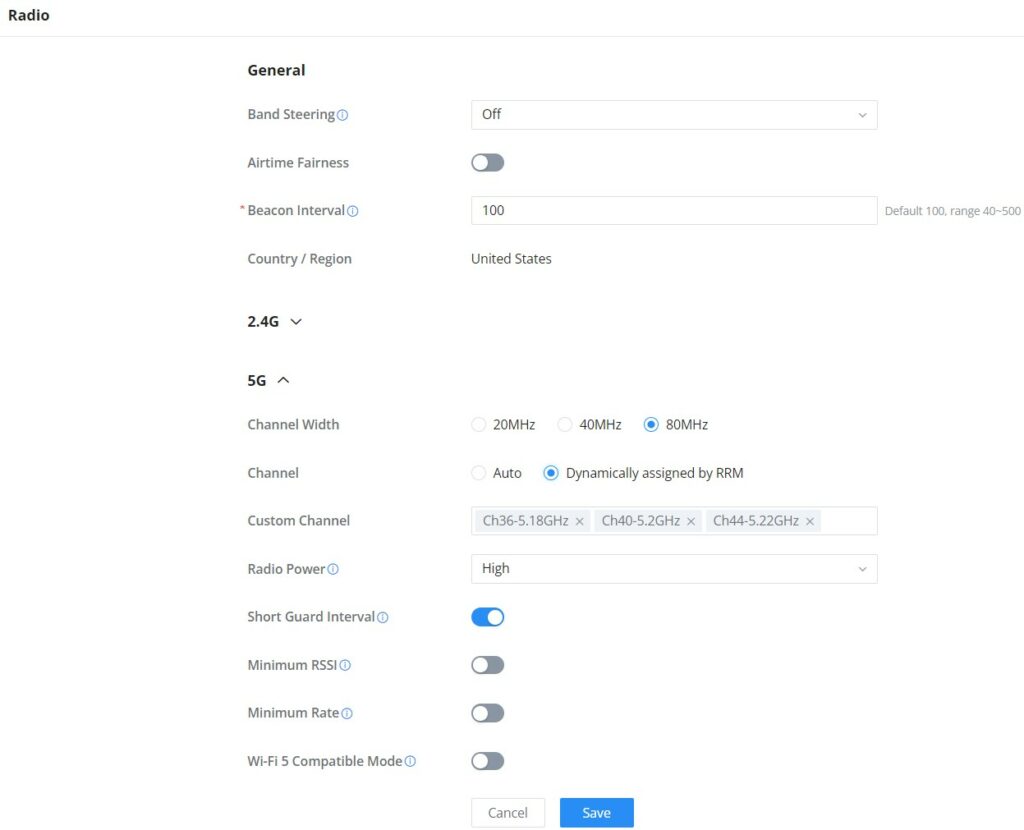
General | |
Band Steering | Band steering functions are divided into four items: 1) 2.4G in priority, lead the dual client to the 2.4G band; 2) 5G in priority, the dual client will be led to the 5G band with more abundant spectrum resources as far as possible; 3) Balance,access to the balance between these 2 bands according to the spectrum utilization rate of 2.4G and 5G. In order to better use this function, proposed to enable voice enterprise via SSIDs → Advanced → Enable Voice Enterprise. |
Airtime Fairness | Enabling Airtime Fairness will make the transmission between the access point and the clients more efficient. This is achieved by offering equal airtime to all the devices connected to the access point. |
Beacon Interval | Configures the beacon period, which decides the frequency the 802.11 beacon management frames router transmits. Please input an integer, from 40 to 500.1. When router enables several SSIDs with different interval values, the max value will take effect;2. When router enables less than 3 SSIDs, the interval value will be effective are the values from 40 to 500;3. When router enables more than 2 but less than 9 SSIDs, the interval value will be effective are the values from 100 to 500;4. When router enables more than 8 SSIDs, the interval value will be effective are the values from 200 to 500.Note: mesh feature will take up a share when it is enabled. |
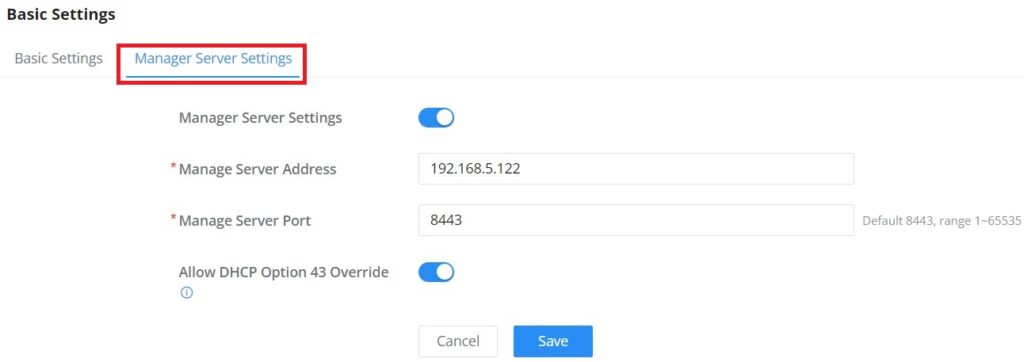
Country / Region | This option shows the country/region which has been selected. To edit the region, please navigate to System Settings → Basic Settings. |
2.4G & 5G | |
Channel Width | Select the channel width.
|
Channel | Pick how the access points will be able to choose a specific channel.
|
Custom Channel | Select a custom channel(s) from the drop-down list, there are two categories:
|
Radio Power | Please select the radio power according to the actual situation, too high radio power will increase the disturbance between devices.
|
Short Guard Interval | This can improve the wireless connection rate if enabled under non multipath environment. |
Allow Legacy Devices (802.11b) (2.4Ghz Only) | When the signal strength is lower than the minimum RSSI, the client will be disconnected (unless it's an Apple device). |
Minimum RSSI | When the signal strength is lower than the minimum RSSI, the client will be disconnected (unless it's an Apple device). |
Minimum Rate | Specify whether to limit the minimum access rate for clients. This function may guarantee the connection quality. |
Wi-Fi 5 Compatible Mode | Some old devices do not support Wi-Fi6 well, and may not be able to scan the signal or connect poorly. After enabled, it will switch to Wi-Fi5 mode to solve the compatibility problem. At the same time, it will turn off Wi-Fi6 related functions. |
Radio
Mesh
Through the controller embedded in the GWN70x2 routers, the user can configure a Wi-Fi Mesh using the GWN access points. The configuration is centralized and the user can view the topology of the Mesh.
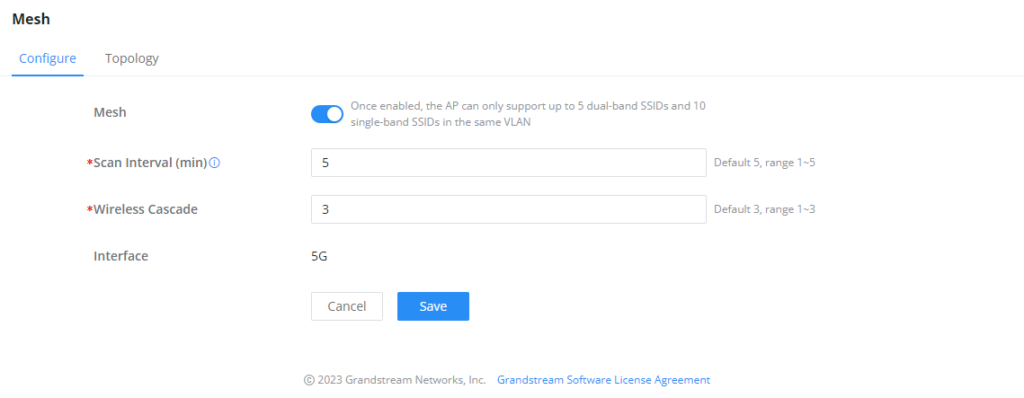
- Configuration:
To configure GWN access points in a Mesh network successfully, the user must pair the access points first with the GWN router, then configure the same SSID on the access points. Once that’s done, the user should navigate to AP Management → Mesh → Configure, then enable Mesh and configure the related information as shown in the figure below.
For more information about the parameters that need to be configured, please refer to the table below.
Mesh | Enable Mesh. Once enabled, the AP can only support up to 5 dual-band SSIDs and 10 single-band SSIDs in the same VLAN. |
Scan Interval (min) | Configures the interval for the APs to scan the mesh. The valid range is 1-5. The default value is 5. |
Wireless Cascade | Define the wireless cascade number. The valid range is 1-3. The default value is 3. |
Interface | Displays which interface is going to be used for mesh. |
Mesh Configuration
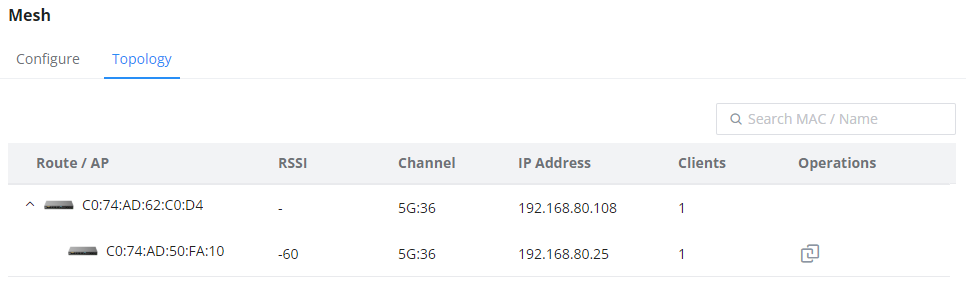
- Topology:
On this page, the user will be able to see the topology of the GWN access points when they are configured in a Mesh network. The page will display information related to the APs like the MAC address, RSSI, Channel, IP Address, and Clients. It will show as well the cascades in the Mesh.
ACCESS CONTROL
GWN70x2 has features that can enable the user to block clients and sites as well and also limit the bandwidth per client or SSID.
Blocklist
The Blocklist is a feature in GWN70x2 that enables the user to block wireless clients from the available ones or manually add the MAC Address.
To create a new Blocklist, Navigate under: “Web UI → Access Control → Blocklist“.
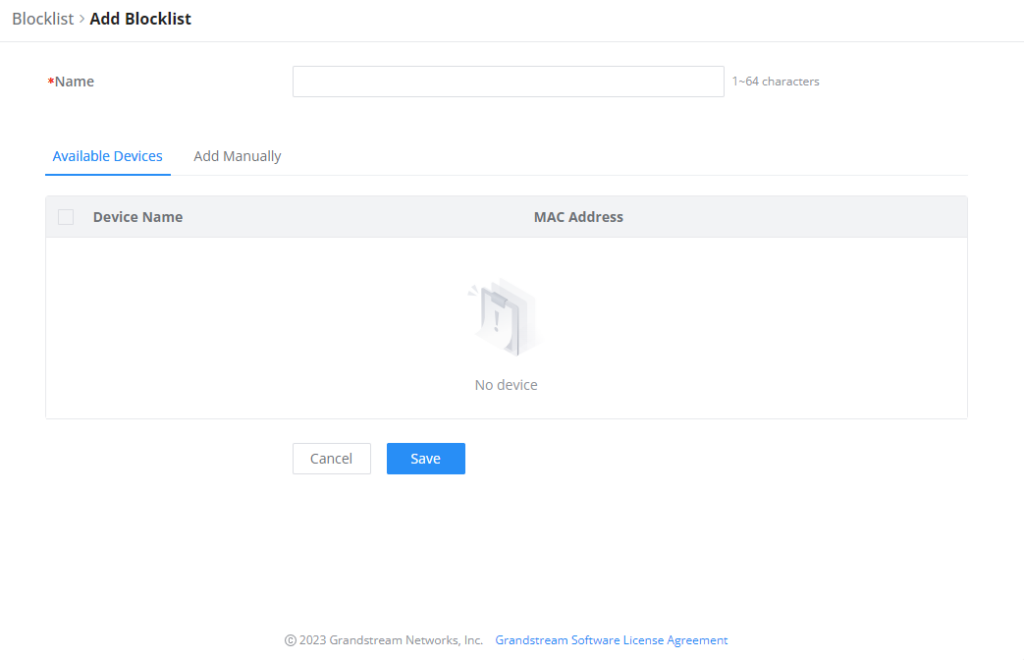
- Add devices from the list:
Enter the name of the blocklist, then add the devices from the list.
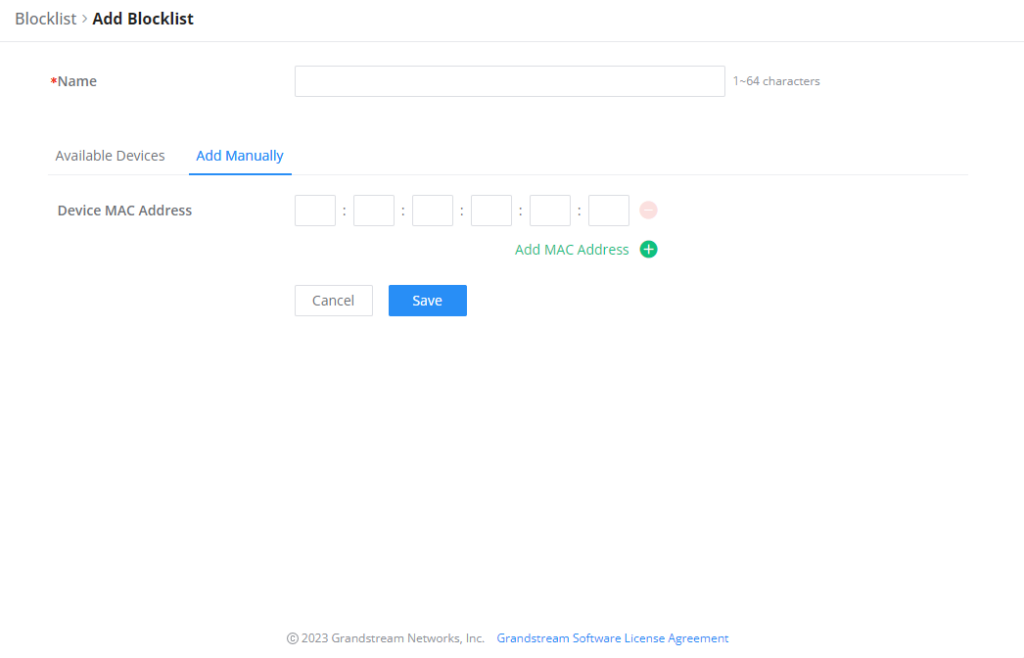
- Add Devices Manually:
Enter the name of the blocklist, then add the devices’ MAC addresses.
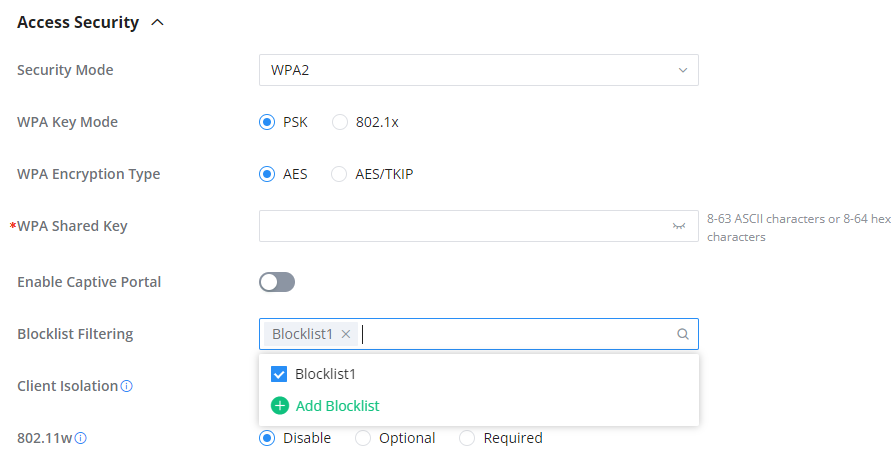
After the blocklist is created, to take effect the user needs to apply it on the desired SSID.
Navigate to ” Web UI → AP Management → SSIDs“, either click on the “Add” button to create a new SSID or click on the “Edit” icon to edit a previously created SSID, scroll down to “Access Security” section then look for “Blocklist Filtering” option and finally select from the list the previously created blocklists, the user can select one or more, or click on “Create Blocklist” at the bottom of the list to create new one.
Please refer to the figure below:
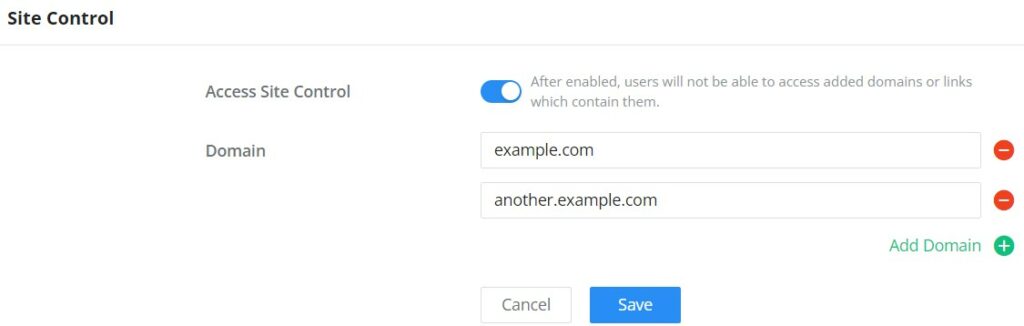
Site Control
Site Control is a feature that allows the system administrator to block DNS queries to some domains. This feature can be used to block adware sites and malware sites, and can be used to block popular social media websites (Facebook, YouTube…etc).
To configure the website blocking policy:
Navigate under: “Web UI → Access Control → Site Control“.
Click on the “Plus” or “Minus” icons to add or delete a domain.
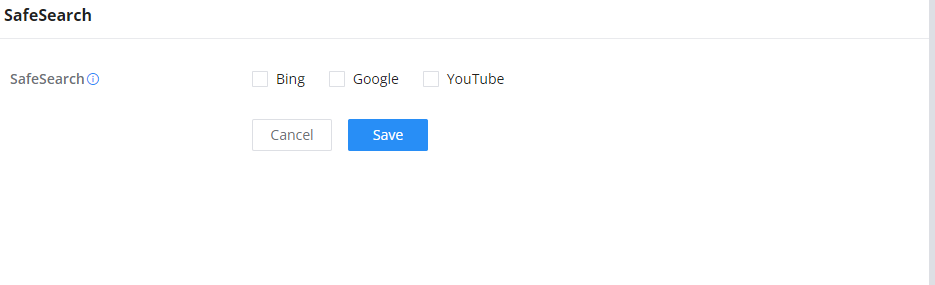
SafeSearch
The GWN70x2 routers offer SafeSearch features on Bing, Google, and YouTube. Enabling this option will hide any inappropriate or explicit search results from being displayed.
EXTERNAL ACCESS
By default, all the requests initiated from the WAN side are rejected by the router GWN70x2 external access features allow hosts located on the WAN side to access the services hosted on the LAN side of the GWN router.
DDNS
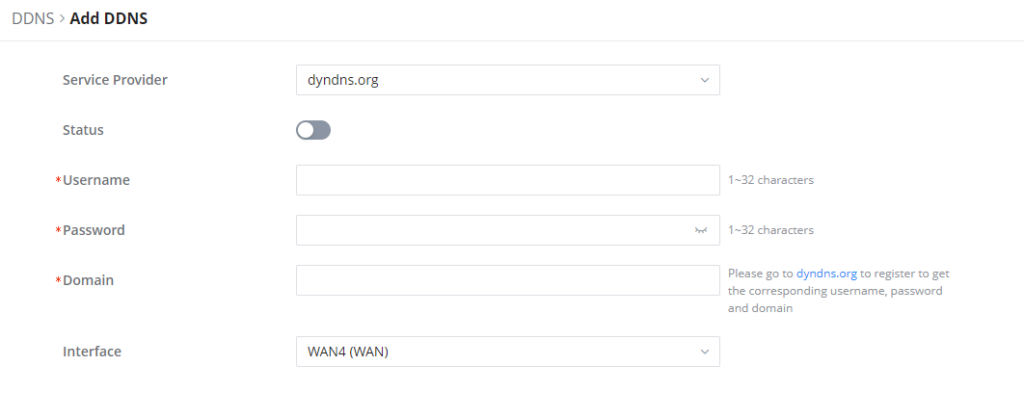
1. Access to GWN70x2 web GUI, navigate to External Access → DDNS, and click to Add Service.
2. Fill in the domain name created with the DDNS provider under the Service Provider field.
3. Enter your account username and password under the User Name and Password fields.
4. Specify the Domain to which the DDNS Account is applied under Domain.
Service Provider | Select the DDNS provider from the list |
Username | Enter the Username |
Password | Enter the Password |
Domain | Enter the Domain |
Interface | Select the Interface |
DDNS Page
Port Forward
Port forwarding allows forwarding requests initiated from the WAN side of the router to a LAN host. This is done by configuring either the port only or the port and the IP address in case we want to restrict access over that specific port to one IP address. Once the router receives the requested IP address, the router will verify the port on which the request has been initiated and will forward the request to the host IP address and the port of the host which is configured as the destination.
Port forwarding can be used in the case when a host on the WAN side wants to access a server on the LAN side.
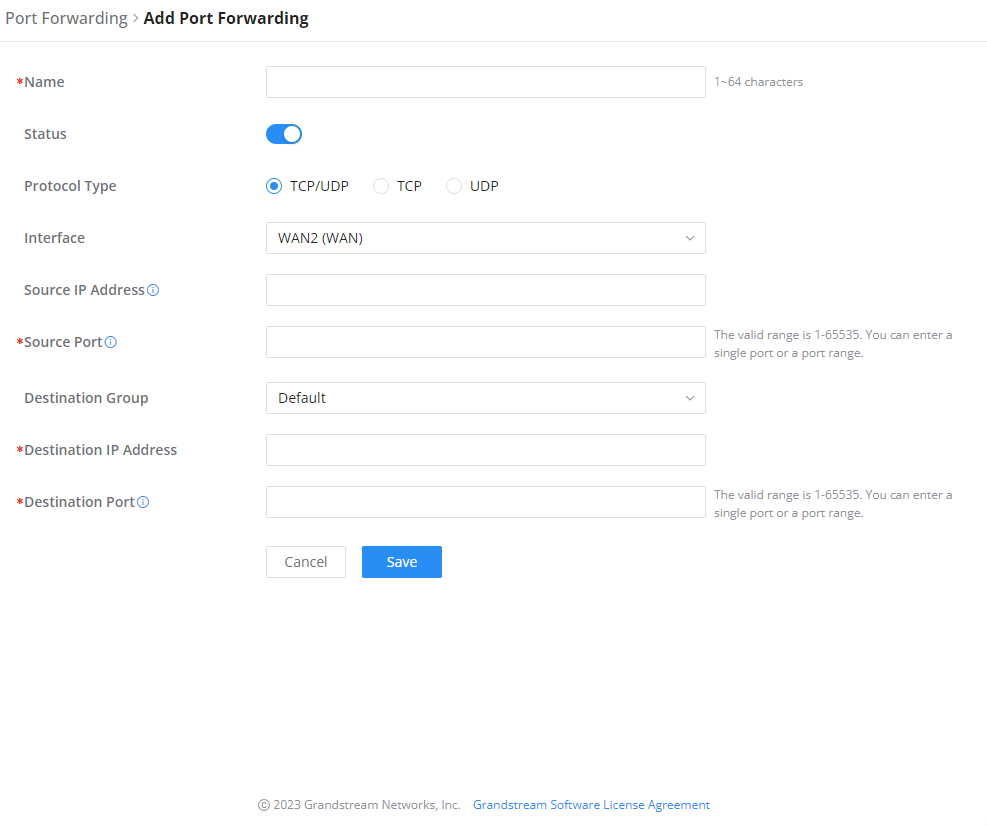
Navigate to GWN70x2 WEB UI → External Access → Port Forward:
Refer to the following table for the Port Forwarding option when editing or creating a port forwarding rule:
Name | Enter a name for the port forwarding rule. |
Status | Toggle on/off the rule status. |
Protocol Type | Select a protocol, users can select TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP. |
Interface | Select the WAN port |
Source IP Address | Sets the IP address that external users access to this device. If not set, any IP address on the corresponding WAN port can be used |
Source Port | Set a single or a range of Ports. |
Destination Group | Select VLAN group. |
Destination IP Address | Set the destination IP address. |
Destination Port | Set a single or a range of Ports. |
Port Forwarding page
DMZ
Configuring the DMZ, the router will allow all external access requests to the DMZ host. This is
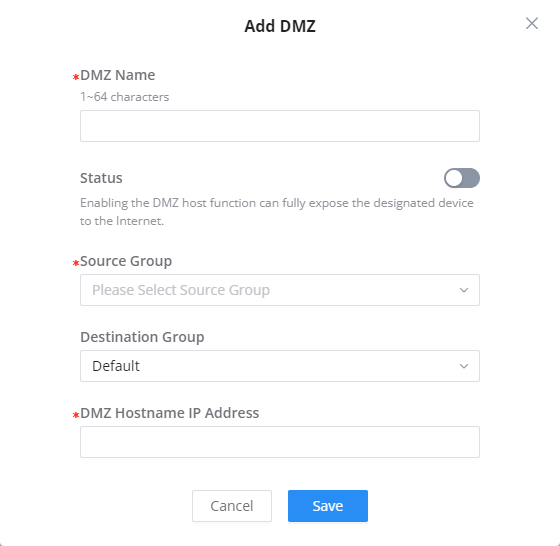
This section can be accessed from GWN70x2 Web GUI → External Access → DMZ.
GWN70x2 supports DMZ, where it is possible to specify a Hostname IP Address to be put on the DMZ.
Enabling the DMZ host function, the computer set as the DMZ host can be completely exposed to the Internet, realizing two-way unrestricted communication.
Refer to the below table for DMZ fields:
DMZ Name | Enter a name for the DMZ rule. |
Status | Toggle on/off the status of the DMZ rule. |
Source Group | Select the interface to allow access to the DMZ host. |
Destination Group | Select the VLAN on which the DMZ host belong. |
DMZ Hostname IP Address | Enter the DMZ host IP address. |
DMZ Page
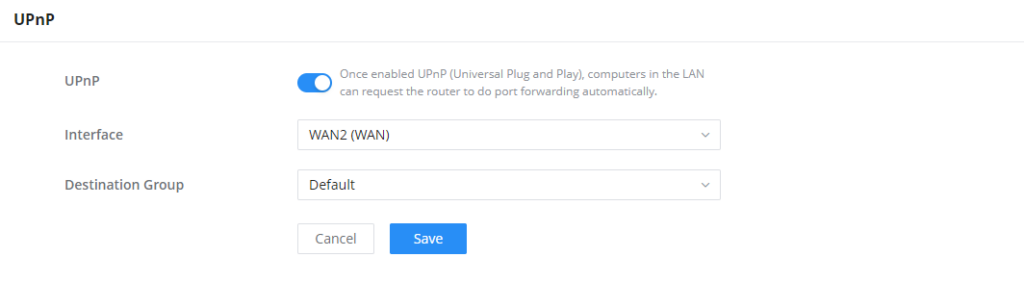
UPnP
GWN70x2 supports UPnP that enables programs running on a host to configure automatically port forwarding.
UPnP allows a program to make the GWN70x2 open necessary ports, without any intervention from the user, without making any check.
UPnP settings can be accessed from GWN70x2 Web GUI → External Access → UPnP.
UPnP | Click on "ON" to enable UPnP. Note: Once enabled UPnP (Universal Plug and Play), computers in the LAN can request the router to do port forwarding automatically |
Interface | Select the interface (WAN) |
Destination Group | Select the LAN Group |
UPnP Settings
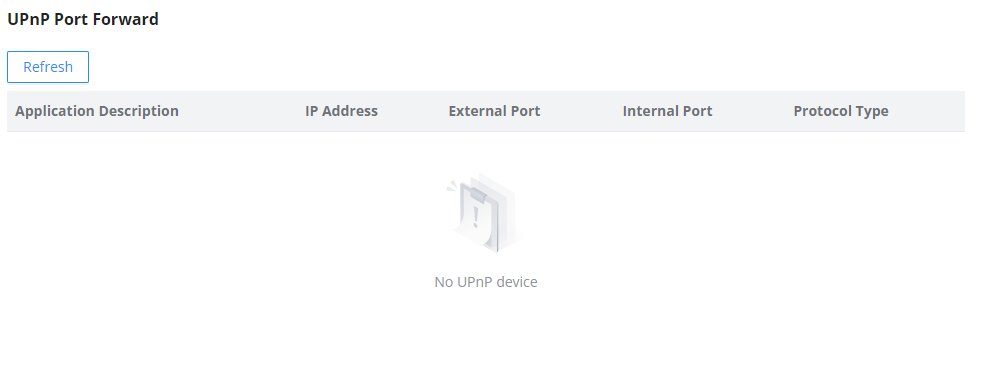
When UPnP is enabled, the ports will be shown in the section below. The information shown includes the application name, the IP address of the LAN host that has requested the opening of the port, the external port number, the internet port number, and the transport protocol used (UDP or TCP).
FIREWALL
The Firewall in GWN routers enables the user to secure the network by blocking the most common attacks and allowing for more control over the traffic.
The Firewall section provides the ability to set up input/output policies for each WAN interface and LAN group as well as setting configuration for Static and Dynamic NAT and ALG.
Firewall – Basic Settings
General Settings
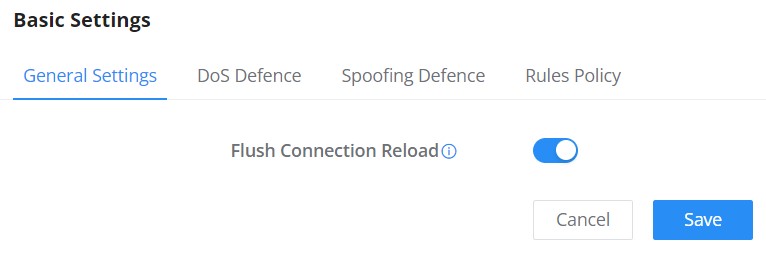
- Flush Connection Reload
When this option is enabled and the firewall configuration changes are made, existing connections that had been permitted by the previous firewall rules will be terminated.
If the new firewall rules do not permit a previously established connection, it will be terminated and will not be able to reconnect. With this option disabled, existing connections are allowed to continue until they timeout, even if the new rules would not allow this connection to be established.
DoS Defense
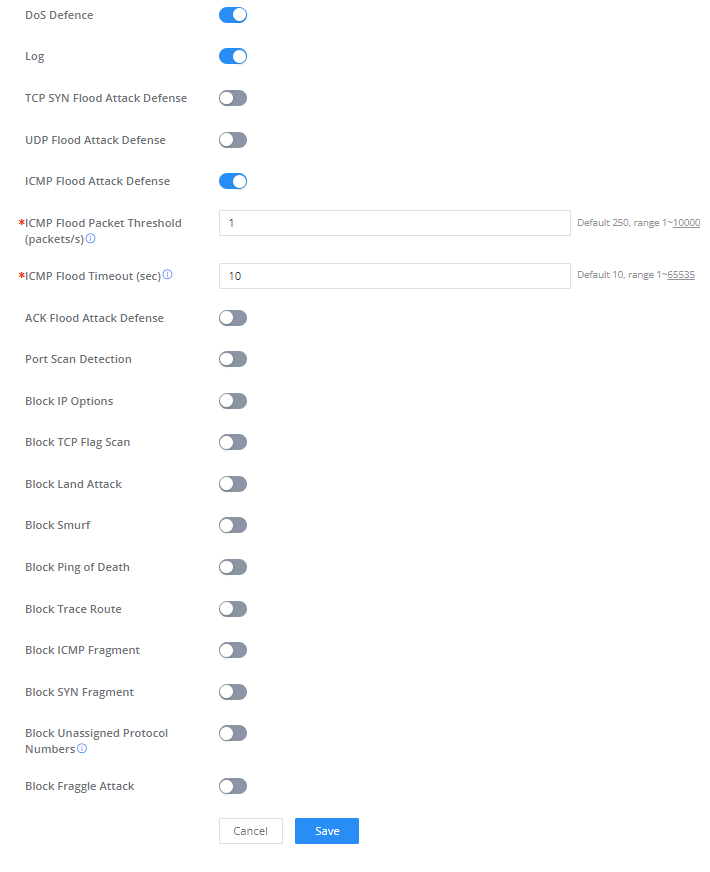
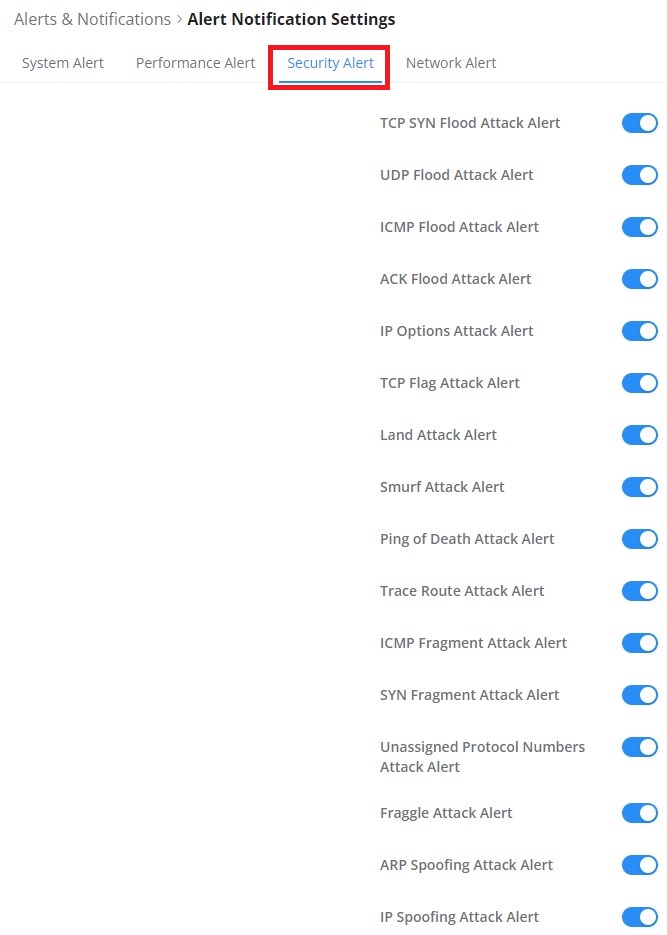
Denial-of-Service Attack is an attack aimed to make the network resources unavailable to legitimate users by flooding the target machine with so many requests causing the system to overload or even crash or shut down.
DoS Defence | Toggle on/off DoS Defence |
Log | When this option is enabled, all the attempts of the attacks below will be recorded in a log. |
TCP SYN Flood Attack Defense | When this option is enabled, the router will take counter measures to SYN Flood Attack.
|
UDP Flood Attack Defense | When this option is enabled, the router will take counter measures to the UDP Flood Attack.
|
ICMP Flood Attack Defense | When this option is enabled, the router will take counter measures to the ICMP Flood Attack.
|
ACK Flood Attack Defense | When this option is enabled the router will take counter measures to ACK Flood Attack.
|
Port Scan Detection | When this option is enabled, the router will take counter measure to the port scanning attempts
|
Block IP Options | When this option is enabled, the router will ignore any IP packets with Options field. |
Block TCP Flag Scan | When this option is enabled, the router will ignore any packets with unexpected information in the TCP flags. |
Block Land Attack | When this option is enabled, the router will block any SYN packets which may have been spoofed and modified to set the source and the destination address to the address of the router. If this option is disabled, it might cause the router to be stuck in a loop of responding to itself. |
Block Smurf | When this option is enabled, the router will drop any ICMP echo requests. |
Block Ping of Death | When this option is enabled, the router will drop any abnormal or corrupted ping packets. |
Block Traceroute | When this option is enabled, the router will not allow the traceroute requests initiated from the WAN side. |
Block ICMP Fragment | When this option is enabled, the router will drop the ICMP packets which are fragmented. |
Block SYN Fragment | When this option is enabled, the router will drop the SYN packets which are fragmented. |
Block Unassigned Protocol Numbers | If enabled, the device will reject IP packets receiving IP protocol number greater than 133. |
Block Fraggle Attack | If enabled, the router will drop any UDP broadcast packets initiate from the WAN side. |
DoS Defense
Spoofing Defense
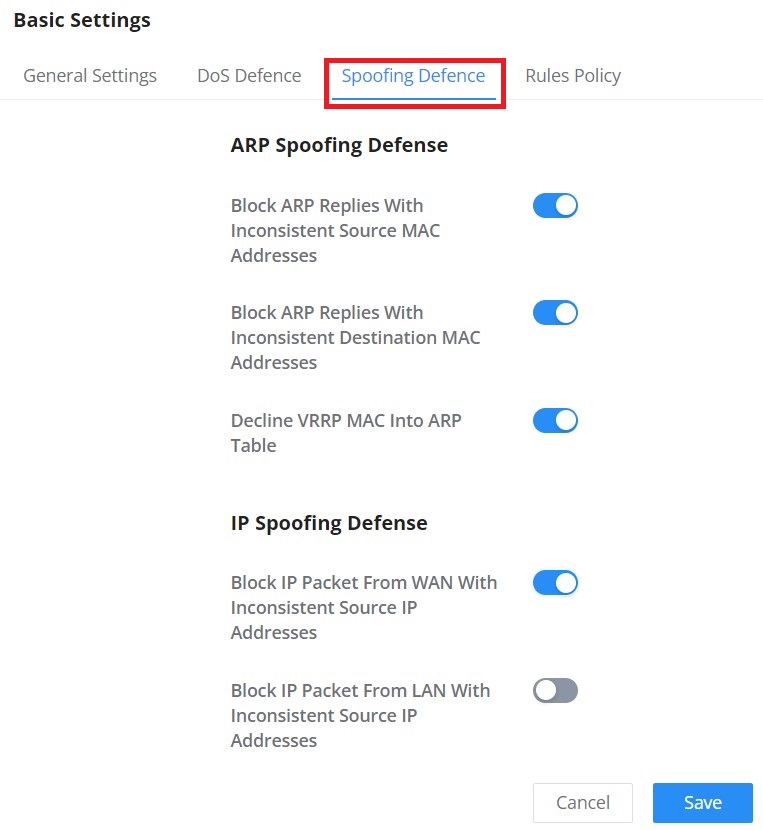
The Spoofing defense section offers several counter-measures to the various spoofing techniques. To protect your network against spoofing, please enable the following measures to eliminate the risk of having your traffic intercepted and spoofed. GWN routers offer measures to counter spoofing on ARP information, as well as on IP information.
ARP Spoofing Defense
- Block ARP Replies with Inconsistent Source MAC Addresses: The router will verify the destination MAC address of a specific packet, and when the response is received by the router, it will verify the source MAC address and it will make sure that they match. Otherwise, the router will not forward the packet.
- Block ARP Replies with Inconsistent Destination MAC Addresses: The router will verify the source MAC address when the response is received. The router will verify the destination MAC address and it will make sure that they match. Otherwise, the router will not forward the packet.
- Decline VRRP MAC Into ARP Table: The router will decline including any generated virtual MAC address in the ARP table.
IP Spoofing Defense
- Block IP Packet From WAN with Inconsistent Source IP Addresses: The router will verify the IP address of the inbound packets, the source IP address has to match the destination IP address to which the request was initially sent. If there is a mismatch between these two IP addresses, the router will drop the packet.
- Block IP Packet from LAN with Inconsistent Source IP Address: The router will verify the IP address of the packets forwarded. If the router discovers that there is a mismatch in the packet source IP address, the packet will not be forwarded.
Rules Policy
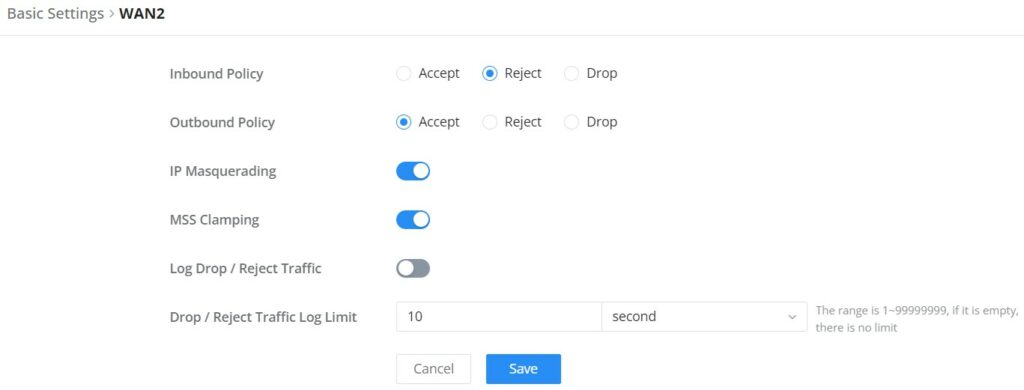
Rules policy allows to define how the router is going to handle the traffic based on whether it is inbound traffic or outbound traffic. This is done per the WAN port as well as the LAN ports of the router.
- Inbound Policy: Define the decision that the router will take for the traffic initiated from the WAN. The options available are Accept, Reject, and Drop.
- Outbound Traffic: Define the decision that the router will take for the traffic initiated from the LAN side. The options available are Accept, Reject, and Drop.
- IP Masquerading: Enable IP masquerading. This will masquerade the IP address of the internal hosts.
- MSS Clamping: Enabling this option will allow the MSS (Maximum Segment Size) to be negotiated during the TCP session negotiation
- Log Drop / Reject Traffic: Enabling this option will generate a log of all the traffic that has been dropped or rejected.
Traffic Rules
GWN70x2 offers the possibility to fully control incoming/outgoing traffic for different protocols in customized scheduled times and take actions for specified rules such as Accept, Reject, and Drop.
Traffic Rules settings can be accessed from GWN70x2 Web GUI → Firewall → Traffic Rules.
The following actions are available to configure Input, output, and forward rules for configured protocols
- To add new rule, Click on
- To edit a rule, click on
- To delete a rule, click on
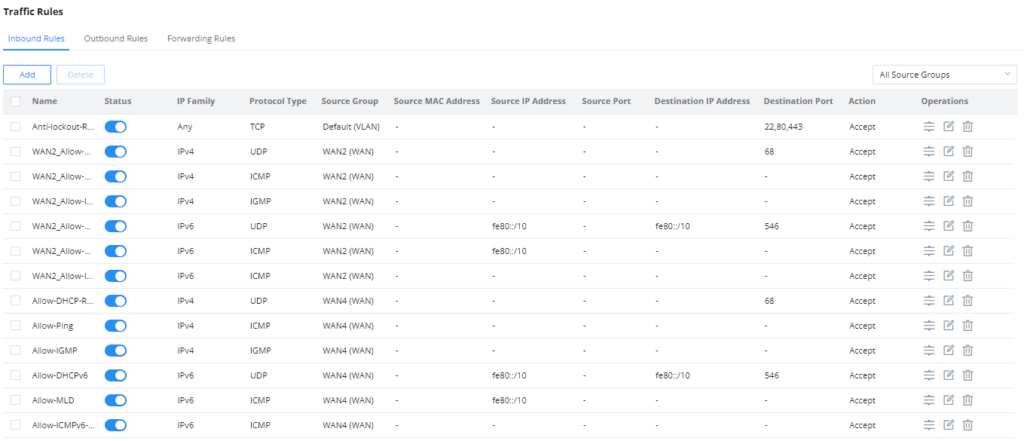
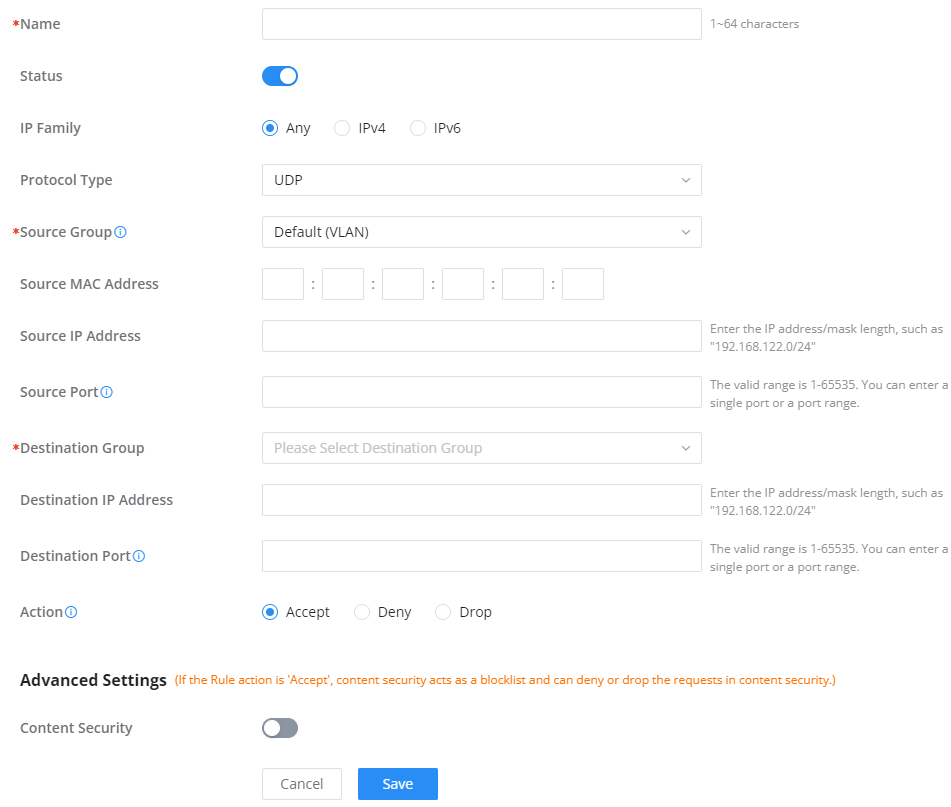
Inbound Rules
The GWN70x2 allows to filtering incoming traffic to networks group or port WAN and applies rules such as:
• Accept: To allow the traffic to go through.
• Deny: A reply will be sent to the remote side stating that the packet is rejected.
• Drop: The packet will be dropped without any notice to the remote side.
Name | Enter the name of the inbound rule. |
Status | Toggle on/off the status of the inbound rule. |
IP Family | Pick the IP family.
|
Protocol Type | Choose the protocol type.
|
Source Group | If set to "All", rules will be matched in preference to other specific ones. |
Source MAC Address | Specify the source MAC address. |
Source IP Address | Specify the source IP address. |
Source Port | To enter multiple port/port ranges, separate them using commas (,), for example:4,5-10. |
Destination IP Address | Specify the destination IP address. |
Destination Port | To enter multiple port/port ranges, separate them using commas (,), for example:4,5-10. |
Action | If set to "Accept", the external devices are allowed to access the router; if set to "Deny", the access of the external devices is denied and the result is returned; if set to "Drop", the access request of the external device will be directly droped. |
Traffic Rules – Inbound Rules
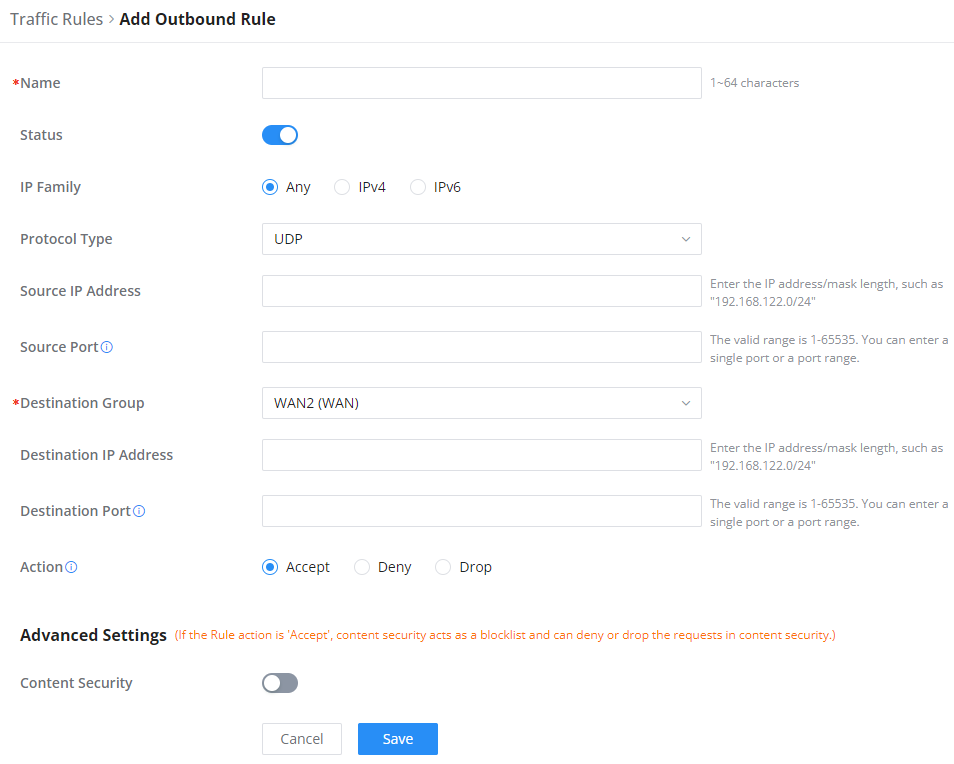
Outbound Rules
The GWN70x2 allows to filtering of outgoing traffic from the local LAN networks to outside networks and applies rules such as:
• Accept: To allow the traffic to go through.
• Deny: A reply will be sent to the remote side stating that the packet is rejected.
• Drop: The packet will be dropped without any notice to the remote side.
Name | Enter the name of the outbound rule. |
Status | Toggle on/off the status of the outbound rule. |
IP Family | Pick the IP family.
|
Protocol Type | Choose the protocol type.
|
Source IP Address | Specify the source IP address. |
Source Port | To enter multiple port/port ranges, separate them using commas (,), for example:4,5-10. |
Destination IP Address | Specify the destination IP address. |
Destination Port | To enter multiple port/port ranges, separate them using commas (,), for example:4,5-10. |
Action | If set to "Accept", the external devices are allowed to access the router; if set to "Deny", the access of the external devices is denied and the result is returned; if set to "Drop", the access request of the external device will be directly droped. |
Advanced Settings | |
Content Security | Enable content security, once enabled the user can customize security features which are described below. |
Content Security Action | If set to "Accept", the router is allowed to access the external network. |
DNS Filtering | Specify the DNS filtering rule. |
APP Filtering | Specify the app filtering rule. |
URL Filtering | Specify the URL filtering rule. |
Traffic Rules – Outbound Rules
Forwarding Rules
GWN70x2 offers the possibility to allow traffic between different groups and interfaces.
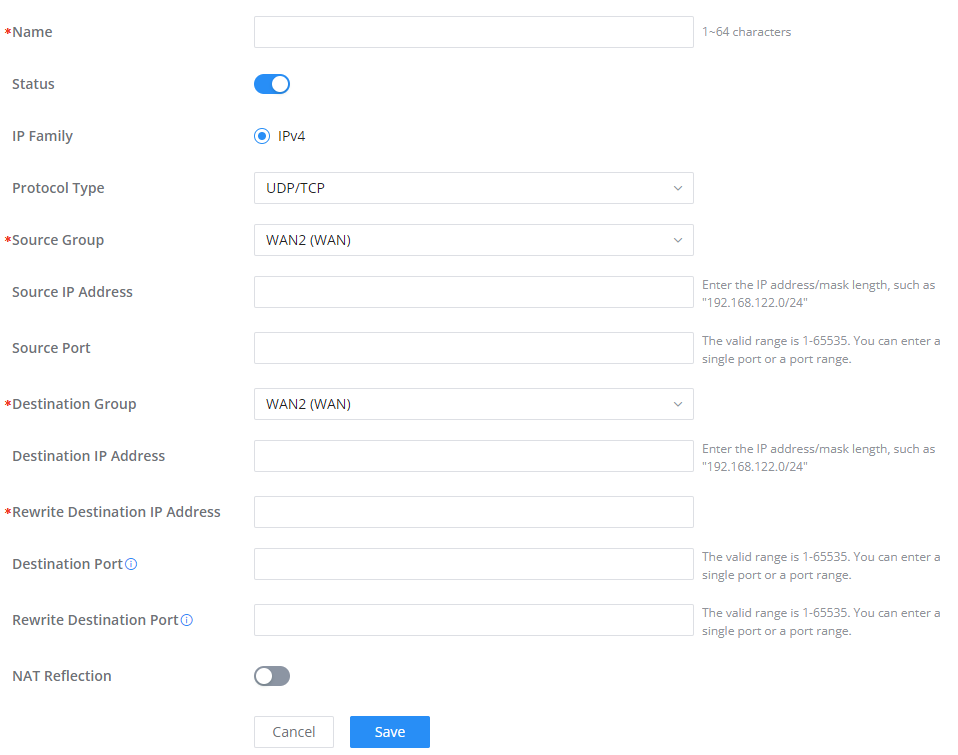
Advanced NAT
NAT or Network address translation as the name suggests it’s a translation or mapping private or internal addresses to public IP addresses or vice versa, and the GWN routers support both.
- SNAT: Source NAT refers to the mapping of clients’ IP addresses (Private or Internal Addresses) to a public one.
- DNAT: Destination NAT is the reverse process of SNAT where packets will be redirected to a specific internal address.
The Firewall Advanced NAT page provides the ability to set up the configuration for Static and Dynamic NAT.
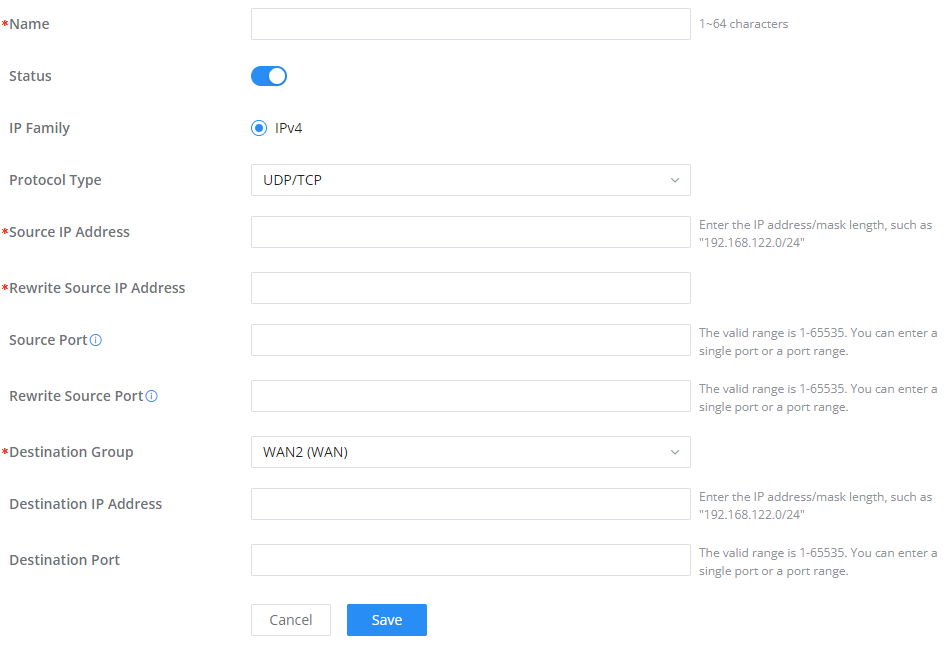
SNAT
The following actions are available for SNAT.
Click on to add the Port Forward rule.
Click on to edit a Port Forward rule.
Click on to delete a Port Forward rule.
Refer to the below table when creating or editing an SNAT entry:
Name | Specify a name for the SNAT entry |
IP Family | Select the IP version, two options are available: IPv4 or Any. |
Protocol Type | Select one of the protocols from dropdown list or All, available options are: UDP/TCP, UDP, TCP and All. |
Source IP Address | Set the Source IP address. |
Rewrite Source IP Address | Set the Rewrite IP. The source IP address of the data package from the source group will be updated to this configured IP. |
Source Port | Set the Source Port |
Rewrite Source Port | Set the Rewrite source port. |
Destination Group | Select a WAN interface or a VLAN for Destination Group. |
Destination IP Address | Set the Destination IP address. |
Destination Port | Set the Destination Port |
SNAT page
DNAT
The following actions are available for DNAT:
Click on to add the Port Forward rule.
Click on toedit a Port Forward rule.
Click on todelete a Port Forward rule.
Refer to the below table when creating or editing a DNAT entry:
Name | Specify a name for the DNAT entry |
IP Family | Select the IP version, three options are available: IPv4, IPv6 or Any. |
Protocol Type | Select one of the protocols from dropdown list or All, available options are: UDP, TCP, TCP/UCP and All. |
Source Group | Select a WAN interface or a LAN group for Source Group, or select All. |
Source IP Address | Set the Source IP address. |
Source Port | Set the Source Port. |
Destination Group | Select a WAN interface or a LAN group for Destination Group, or select All. Make sure that destination and source groups are different to avoid conflict. |
Destination IP Address | Set the Destination IP address. |
Rewrite Destination IP Address | Set the Rewrite Destination IP Address. |
Destination Port | Set the Destination Port. |
Rewrite Destination Port | Set the Rewrite Destination Port |
NAT Reflection | Click on "ON" to enable NAT Reflection |
NAT Reflection Source | Select NAT Reflection either Internal or External. |
Advanced NAT – DNAT
ALG
ALG stands for Application Layer Gateway. Its purpose is to prevent some of the problems caused by router firewalls by inspecting VoIP traffic (packets) and if necessary modifying it.
Navigate to Web GUI → Firewall → ALG to activate ALG.
CAPTIVE PORTAL
Captive Portal feature on GWN70x2 helps to define a Landing Page (Web page) that will be displayed on Wi-Fi clients’ browsers when attempting to access the Internet. Once connected Wi-Fi clients will be forced to view and interact with that landing page before Internet access is granted.
The Captive Portal feature can be configured from the GWN70x2 Web page under “Captive Portal”.
Policy
Users can customize a portal policy on this page. Click on the “Add” button to add a new policy or click on “Edit” to edit a previously added one.
The policy configuration page allows for adding multiple captive portal policies which will be applied to SSIDs and contain options for different authentication types.
Policy Name | Enter a policy name. |
Splash Page |
|
Client Expiration | Specify the expiration time for client network connection. Once timed out, client should re-authenticate for further network use. |
Client Idle Timeout (min) | Specify the idle timeout value for guest network connection. Once timed out, guest should re-authenticate for further network use. |
Daily Limit | When enable, the client is only allowed to access once a day. |
Splash Page Customization | Select the customized splash page. |
Login Page | Set portal authentication through the page to automatically jump to the target page. |
HTTPS Redirection | If enabled, both HTTP and HTTPS requests sent from stations will be redirected by using HTTPS protocol. And station may receive an invalid certification error while doing HTTPS browsing before authentication. If disabled, only the http request will be redirected. |
Secure Portal | If enabled, HTTPS protocol will be used in the communication between STA and router. Otherwise, the HTTP protocol will be used. |
Pre Authentication Rule (sec) | Set pre authentication rules, allowing clients access some URLs before authenticated successfully. |
Post Authentication Rule (sec) | Set post authentications to restrict users from accessing the following addresses after authenticating successfully. |
Policy page
Splash Page
The splash page allows users with an easy-to-configure menu to generate a customized splash page that will be displayed to the users when trying to connect to the Wi-Fi.
On this menu, users can create multiple splash pages and assign each one of them to a separate captive portal policy to enforce the select authentication type.
The generation tool provides an intuitive “WYSIWYG” method to customize a captive portal with a very rich manipulation tool.
To add a splash page, click on the “Add” button or click on the “Edit” icon to edit a previously added one.
Users can set the following:
- Authentication type: Add one or more ways from the supported authentication methods (Simple Password, Radius Server, For Free, Facebook, Twitter, Google, and Voucher).
- Set up a picture (company logo) to be displayed on the splash page.
- Customize the layout of the page and background colors.
- Customize the Terms of Use text.
- Visualize a preview for both mobile devices and laptops.
Guests
This page displays information about the clients connected via the Captive portal including the MAC address, Hostname, Authentication Type, etc.
To export the list of all guests, please click on the “Export Guest List” button, and then an EXCEL file will be downloaded.
Vouchers
The Voucher feature will allow clients to have internet access for a limited duration using a code that is randomly generated from the platform controller.
As an example, a coffee shop could offer internet access to customers via Wi-Fi using voucher codes that can be delivered on each command. Once the voucher expires the client can no longer connect to the internet.
Note that multiple users can use a single voucher for connection with the expiration duration of the voucher that starts counting after the first successful connection from one of the users that are allowed.
Another interesting feature is that the admin can set data bandwidth limitations on each created voucher depending on the current load on the network, users’ profile (VIP customers get more speed than regular ones, etc.…), and the internet connection available (fiber, DSL or cable, etc.…) to avoid connection congestion and slowness of the service.
Click on the “Add” button to create a voucher group.
Please refer to the figure below when filling up the fields.
MAINTENANCE
GWN70x2 offers multiple tools and options for maintenance and debugging to help further troubleshoot and monitor the GWN70x2 resources.
TR-069
It is a protocol for communication between CPE (Customer Premise Equipment) and an ACS (Auto Configuration Server) that provides secure auto-configuration as well as other CPE management functions within a common framework.
TR-069 stands for a “Technical Report” defined by the Broadband Forum that specifies the CWMP “CPE WAN Management Protocol”. It commonly uses HTTP or HTTPS as transport for communication between CPE and the ACS. The message exchange uses SOAP (XML_RPC) for the configuration and management of the device.
TR-069 | Enable/disable TR-069 |
ACS URL | Enter the FQDN or the IP address of the ACS server. |
ACS Username | Enter the username. |
ACS Password | Enter the password. |
Periodic Inform | If enabled, the router will send connection inform packets to ACS regularly. |
Periodic Inform Interval (sec) | This configures the time duration between each inform sent by the device to the ACS server. |
Connection Request Username | When ACS server sends a connection request to the router, the username that the router authenticates ACS must be consistent with the configuration of ACS side. |
Connection Request Password | The password that the router authenticates ACS must be consistent with the configuration of ACS server. |
Connection Request Port | The port for ACS to send connection request to the router. This port cannot be occupied by other device features. |
CPE Cert File | Enter the certificate that the router needs to use when connecting to ACS through SSL. |
CPE Cert Key | Enter the certificate key that the router needs to use when connecting to ACS through SSL. |
TR-069 page
SNMP
GWN70x2 routers support SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) which is widely used in network management for network monitoring for collecting information about monitored devices.
To configure SNMP settings, go to GWN70x2 Web GUI → Maintenance → SNMP, in this page the user can either enable SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, or enable SNMPv3, and enter all the necessary parameters.
To configure SNMPv1 or SNMPv2, please refer to the table below:
SNMPv1, SNMPv2 | Enable/disable SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 |
Community String | Enter the shared password of the community. |
SNMP – SNMPv1 or SNMPv2
To configure SNMPv3, please refer to the table below:
SNMPv3 | Enable/disable SNMPv3. |
Username | Enter a username. |
Authentication Mode | Select the algorithm used for the authentication. |
Authentication Key | Select the authentication password. |
Encryption Mode | Select the encryption protocol used for the encryption of the data. |
Encryption Key | Enter the encryption key. |
SNMP – SNMPv3
Backup and Restore
The GWN70x2 configuration can be backed up (e.g. when performing a firmware update), and the configuration can be uploaded to the router by clicking on “Import” and selecting the backup file. This will load the backed-up configuration back into the router quickly.
If the user wish to modify the configuration file before importing, then a GWN Router Configuration Tool can be used to make the necessary modifications to the configuration file. The tool is supported on Windows® and Linux environments. To download the tool: GWN Router Configuration Tool, then download the Windows® or Linux version accordingly.
Please, visit this guide on how to use the GWN Router Configuration Tool User Guide.
If the user wants to reset the device to its initial configuration, he/she can click “Factory Reset”.
System Diagnostics
Many debugging tools are available on GWN70x2’s Web GUI to check the status and troubleshoot GWN70x2’s services and networks.
To access these tools navigate to “Web UI → System Settings → System Diagnosis“
Ping/Traceroute
Ping and Traceroute are useful debugging tools to verify reachability with other clients across the network (WAN or LAN). The GWN70x2 offers both Ping and Traceroute tools for IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
Core File
When a crash event happens on the unit, it will automatically generate a core dump file that can be used by the engineering team for debugging purposes.
Capture
This section is used to capture packet traces from the GWN70x2 interfaces (WAN ports and network groups) for troubleshooting purposes or monitoring. It’s even possible to capture based on MAC address or IP Address, once done the user can click on and the file (CAP) will start downloading right away.
External Syslog
GWN70x2 routers support dumping the Syslog information to a remote server under Web GUI → System Settings → System Diagnosis → External Syslog Tab
Enter the Syslog server Hostname or IP address and select the level for the Syslog information. Nine levels of Syslog are available: None, Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, Warning, Notice, Information, and Debug.
ARP Cache Table
GWN70x2 router keeps an ARP table record of all the devices that have been assigned an IP address from the router. The record will keep the device’s information when the device is offline. To access the ARP Cache Table, please navigate to System Diagnostics → ARP Cache Table
Link Tracing Table
The Link Tracing Table shows the flow of traffic by displaying the source IP address/Port (the green color) and the reply IP address/port (the blue color), also other information can be displayed like IP Family, Protocol Type, Life Time, Status, Packets/Bytes, etc.
Users/Administrators can also delete the flow of certain IP addresses/Ports (Source and Destination) or then click on the “Delete” button to clear the link tracing statistic.
Network Diagnostics
The network diagnostics feature allows the user to quickly diagnose the connection link on a specific WAN interface.
Cloud/Manager Connection Diagnostics
If the GWN70x2 router is added to the GWN.Cloud or GWN Manager will display a Cloud icon with a green check mark (as shown in the figure below) indicating it’s added to either GWN.Cloud or GWN Manager.
In case there is an issue with the connection, then the user can navigate to Maintenance → System Diagnosis → Cloud/Manager Connection Diagnostics and then click on “Detection” or “Redetect” button to see in what stage/step the connection has failed.
Upgrade
Under Maintenance → Upgrade. The user has the option to upgrade the GWN router via manual upload (a bin file) or network either HTTP/HTTPS or TFTP or even schedule to upgrade at a specific time.
Please refer to the figure below:
Alerts & Notifications
Alerts
The Alerts page displays alerts about the network, the user can specify to display only certain types like (System, Performance, Security, or Network) or the levels. To check the alerts that have been generated, please navigate to the Maintenance → Alerts & Notifications page → Alerts tab.
The alerts can be displayed either by type or level. However, that is not the only way to display them. The user can filter through the alert log using a date interval or search by MAC address or device name.
Alerts Types
The available types are System, Performance, Security, and Network, or the user can choose to display all the types.
Alerts Levels
The user can filter the alert level by the following levels: All Levels, Emergency, Warning or Notice.
Alert Notification Settings
To enable the notifications on the Alerts tab, please click on the “Alert Notification Settings” button as shown below:
The figures below show all the possible alert notifications that the user can enable on the Alerts tab, organized into 4 categories: System Alert, Performance Alert, Security Alert, and Network Alert.
Please refer to the figures below:
E-mail Notifications
On this tab, the user can set up the E-mails that will receive the notifications, once the feature is enabled, then the user can fill up the fields according to SMTP parameters. Refer to the figure below:
It’s possible to add more than one receiver E-mail address as shown in the figure above.
- Click on the “Minus” icon to delete the receiver’s E-mail address.
- Click on the “Plus” icon to add the receiver’s E-mail address.
E-mail Notification Settings
To select what notifications will be sent to the receiver’s E-mail addresses, please click on the “E-mail Notification Settings” button as shown below:
The figures below show all the possible E-mail notifications that the user can send to the pre-configured receiver E-mail Addresses, organized into 4 categories: System Alert, Performance Alert, Security Alert, and Network Alert.
SYSTEM SETTINGS
Basic Settings
On this page, the user can specify a name for the GWN70x2 router, and configure basic settings: country/region, time zone, NTP server, Reboot plan, and LED Indicator either Always On, Always Off, or even based on a schedule.
Manager Server Settings
In the case of GWN manager (on-premise GWN management solution), the user can specify the manager server address and port, there is also the option to allow DHCP option 43 override.
Security Management
Under “Web UI → System Settings → Security Management“ the user can change the login password and activate the web service for example web WAN port access for HTTPS port 443 as well as enabling SSH remote access.
Login Password
On this page, the user can change the password by entering the old password and then confirming the new password.
Web Service
Web Service feature allows the user to access the router’s web GUI from the WAN side. The connection is established over HTTPS for enhanced security. It’s also possible to specify a hostname for the GWN70x2 router as shown in the figure below:
SSH Service
This feature allows the user to access the device using SSH remotely. Enable this option by clicking on the “SSH Remote Access” button and then entering the SSH remote access password (login password). Once that’s done, SSH access will be provided to remote users when they enter the correct password.
Please, refer to the figures below:
Passwordless Remote Access
Enabling the Passwordless Remote Access feature, accessing the device using GWN.Cloud will not require entering the password to be able to access the web GUI of the router.
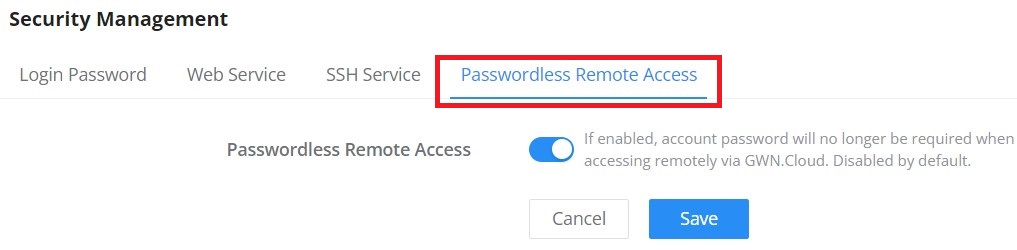
Operation Mode (Beta)
The operation mode feature allows the user to turn GWN70x2 wireless routers into an access point, and when paired with GWN routers/access points as a slave, the router will act as an AP for wireless Mesh networking with the uplink device.
Schedule
GWN routers allow the user to create a schedule, either weekly based or an absolute date/time (specific date and an interval), then these schedules can be assigned to various services on GWN routers: Upgrade, SSID, Bandwidth limit, Policy route, and reboot.
To create a schedule, navigate to System Settings → Schedule, then click on the “Create Schedule” button as shown below:
Certificates
CA Certificates
In this section, the user can create a CA certificate. This certificate will authenticate the user when connected to the VPN server created on the router. This authentication will ensure that no identity is being usurped and that the data exchanged remains confidential. To create a certificate, please access the web GUI of the router and access System Settings → Certificates → CA Certificates then click “Add” and fill in the necessary information.
Cert. Name | Enter the Certificate name for the CA. Note: It could be any name to identify this certificate. Example: “CATest”. |
Key Length | Choose the key length for generating the CA certificate. The following values are available:
|
Digest Algorithm | Choose the digest algorithm:
Note: Hash is a one-way function, it cannot be decrypted back. |
Expiration (D) | Enter the validity date for the CA certificate in days. The valid range is 1~999999.. |
Country / Region | Select a country code from the dropdown list. Example: “United Stated of America”. |
State / Province | Enter a state name or province. Example: “Casablanca”. |
City | Enter a city name. Example: “SanBern”. |
Organization | Enter the organization’s name. Example: “GS”. |
Organizational Unit | This field is the name of the department or organization unit making the request. Example: “GS Sales”. |
Enter an email address. Example: “EMEAregion@grandstream.com” |
Add CA Certificate
Certificate
In this section, the user can create a server or a client certificate. To create a certificate please access the web UI of the router, then navigate to System Settings → Certificates → Add Certificate, click “Add”, then enter the necessary information regarding the certificate.
Cert. Name | Enter the certificate's name. |
Key Length | Choose the key length for generating the CA certificate.The following values are available:
|
Digest Algorithm | Select the digest algorithm.
Note: Hash is a one-way function, it cannot be decrypted back. |
Expiration (D) | Select the duration of validity of the certificate. The number entered represents the days that have to elapse before the certificate is considered as expired. The valid range is 1 - 999999. |
SAN | Enter the address IP or the domain name of the SAN (Subject Alternate Name). |
Country / Region | Select a country from the dropdown list of countries. Example: "United States of America". |
State / Province | Enter a state name or a province. Example: California |
City | Enter a city name. Example: "San Diego" |
Organization | Enter the organization’s name. Example: “GS”. |
Organization Unit | This field is the name of the department or organization unit making the request. Example: “GS Sales”. |
Enter an email address. Example: “EMEAregion@grandstream.com” |
Add Certificate
Certificates Backup and Restore
To back up the created certificates, first select all the desired certificates, then click on the “Backup” button and enter a password to protect it as shown below:
To restore a certificate, click on the “Restore” button, then upload the file and enter the password.
File Sharing
The GWN routers have a USB port that can be used for file sharing, either using a USB flash drive or a Hard Drive, enabling clients with Windows, Mac, or Linux to access files easily on the local network. There is also an option to enable a password for security reasons.
Navigate to System Settings → File Sharing.
CHANGE LOG
This section documents significant changes from previous versions of the GWN70xx routers’ user manuals. Only major new features or major document updates are listed here. Minor updates for corrections or editing are not documented here.
Firmware Version 1.0.9.42
- No major changes.
Firmware Version 1.0.9.37
- No major changes
Firmware Version 1.0.9.34
- Added the new feature of Speed test [WAN].
Firmware Version 1.0.9.15
- No major changes
Firmware Version 1.0.9.10 (1.0.9.9)
- Changed to new GWN router UI [Web UI]
- Added support for USB 4G Dongle (GWN7062 only) [WAN]
- Added new feature of Triple Play (Bridge Mode) [WAN]
- Added new feature of disabling the router ports [Port Configuration]
- Added new feature of DHCP Option Optimization & Option 43 Service List [LAN]
- Added IGMP proxy and IGMP snooping [IGMP]
- Added new feature of IP Routed Subnet [LAN]
- Added Bonjour Gateway [Bonjour Gateway]
- Added Binding Mode and Device Name under Static IP Binding [Static IP Binding]
- Added new feature of transferring GWN APs taken over by GWN router to GWN Cloud/Manager [AP Management]
- Added Client list under Access Point for clients connected currently to the AP [Access Points]
- Added SSID Bandwidth limit feature with schedule support [SSIDs]
- Added WireGuard® VPN [WireGuard®]
- Added new feature of exporting clients list [Clients]
- Added clients bandwidth limit feature with schedule support [Clients]
- Added Bandwidth limit feature for both wireless and wired clients [Bandwidth Limit]
- Added more social authentication (Facebook, Twitter, and Google) under the Captive portal [Splash Page]
- Added Vouchers feature under Captive Portal [Vouchers]
- Added new feature of exporting Guestlist [Guests]
- Added support for more alerts [Alerts]
- Added new feature of naming the GWN router [Basic Settings]
- Added new feature of customizing the Hostname [Web Service]
- Added GWN.Cloud/Manager connection status detection [System Diagnostics]
- Added new feature of AP Mode [Operation Mode]
- Added new feature of DoS Defense [DoS Defense]
- Added new feature of Spoofing Defense [Spoofing Defense]
- Added new feature of Policy Routing: ICMP and Schedule [Policy Route]
- Added new feature of TR069 [TR-069]
- Added new feature of PPSK [PPSK]
- Added support of 2.4G & 5G custom channel [Radio]
- Added support for discovering APs across VLANs [Access Points]
- Added support of GWN Menu when using SSH [SSH Service]
- Added support of more GWN Cloud/Manager Features: Portal, VPN, Policy Routing, Modifying web Password, Certification management, WAN Health, WAN VLAN Priority, Event: Client Authentication Information, Global Blacklist
Firmware Version 1.0.7.2
- No major changes
Firmware Version 1.0.7.1
- Added a new feature of importing configuration files across different devices of the same model [Backup and Restore]
- Added support of Cloud/Manager connection detection [Cloud/Manager Connection Diagnostics]
Firmware Version 1.0.5.44
- Added support of Mesh as a CAP feature when managed by GWN.Cloud/GWN.Manager [Mesh Network]
Firmware Version 1.0.5.34
- Added support for the GWN Cloud 1.1.23.28 and GWN Manager 1.1.23.28
- Added support third layer discovery for GWN Manager [Manager Server Settings]
- Optimized the alert system [Alerts & Notifications]
Firmware Version 1.0.5.12
Product Name: GWN7052 / GWN7062
- No major changes
Firmware Version 1.0.5.9
Product Name: GWN7052 / GWN7062
- No major changes
Firmware Version 1.0.5.6
Product Name: GWN7062
- This is the initial version
Firmware Version 1.0.5.5
Product Name: GWN7052
- This is the initial version