WIFI PERFORMANCE
Signal Strength issue
Symptoms:
- I can connect to my WiFi, but my WiFi speed is much slower than supposed to be!
- Signal level indicator shows a weak reception
. WiFi scan tools can help measuring signal strength (Ex: WiFi Analyzer for AndroidTM).
Troubleshooting
For diagnosis, users need to verify the signal strength on both directions (AP to Client, and Client to AP).
- Check the AP signal strength detected at the client station.
- You can run a protocol analyzer, Ex: Acrylic, for PC.

*RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is a term used to measure the relative quality of a received signal at a wireless device. Below are some reference values:
| Level (dBm) | Description |
| -30 | Excellent |
| -67 | Good |
| Between -80 and -70 | Acceptable |
- Check the client’s signal strength detected at the AP.
- View client’s signal strength detected by the AP on GWN web GUI under Access Point -> Edit -> User, and check user RSSI level. For GWN, it’s 0-60, and the larger the better.
Solution
- In case of multiple AP deployment, we recommend adding more APs for more coverage.
- In case of single AP deployment, make sure to verify that TX power is set to High which is the default.
GWN Settings
Under the menu Access Point -> Edit -> Configuration, users can:
- Increase the Radio Power to have more coverage around the area.
- Set the Channel Width (Lower channel width usually lead to better coverage, but usually device with auto-negotiate to lower width when signal is weak).
Interference Issue
Because WiFi is using unlicensed bands, Interference can be a serious issue which affects the signal transmission quality and performance. we can distinguish two sources of interference:
Non-WiFi Transmitters
For example, some HDMI wireless transmitters utilize almost 100% of the 2.4G channel, which makes it unusable.
Troubleshooting
User detects low performance and can confirm the existence of a neighboring interference source using spectrum analyzer.
Solution
- Check if possible to remove the offending device or change its location.
- Try to change your AP operating channel(s) (5Ghz band is cleaner and less vulnerable to interference).
Other WiFi Networks
WiFi operates on two standard bands (2.4Ghz and 5Ghz), APs using the 2.4Ghs band are more prone to co-channel interference when multiple access points are using the same channel at the same time.
Troubleshooting
Run a WiFi Analyzer (Ex: Acrylic), on PC at the problem location to find the list of APs using same channels.

Solution
- Rearrange WiFi channels to use less crowded channels (better use 5Ghz band if supported).
- Reduce the transmission power of each AP in high density deployment.
GWN Settings
From the web GUI menu Access Point -> Edit -> Configuration. Users can:
- Reduce the Radio Power.
- Reduce channel width (because large channels have more chance of interference.)
- Set Channel selection to auto. This way, the AP will choose the least crowded channel when wireless interface boots up.
- Disable Short Guard Interval. SGI should be used only in good and clean RF (Radio) environment.
Congestion Issue
WiFi has no congestion detection, and its mechanism is designed for avoiding collisions. That is when a unit hears a packet exceeding its strength threshold on same transmission channel, even if it doesn’t belong to its connecting SSID, this client will always wait until it detects a clear air interface to transmit data. And if the wireless network is crowded then this waiting time can become long.
Troubleshooting
Users could compare ping results between wired and wireless parts of a network. And if the ping on the wired network is good then frequent ping loss or long response time could indicate that the wireless part of the network is suffering from congestion and some adjustments are required to alleviate the problem.
Solution
Users can reduce the density of the devices on one single transmission channel with few ways:
- Enable band steering, this way the access point will send dual-band clients (WiFi clients that support both 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz frequencies) to connect via 5Gh channels which are less congested.

- Increase the number of APs in the area and set them to none overlapping (i.e. channels 1, 6 & 11).
- Limit the number of clients that are allowed to connect to one access point (if supported on the AP).
GWN Settings
The above suggestions can be activated from GWN as follow:
- Enable band steering under Access Point -> Edit -> Configuration -> Band steering.
- Users can limit the number of stations that can connect to one AP under SSIDs -> Edit -> WiFi -> Wireless Client Limit.
Low Data Rates Issue
Since its beginning, the WiFi standard was developed over the years to support more speed with the following amendments:
| WiFi Standard | Average data rate |
| 802.11 (legacy) | 1 Mbps |
| 802.11b | 11 Mbps |
| 802.11g | 54 Mbps |
| 802.11n | 600 Mbps |
| 802.11ac | 1300 Mbps |
Legacy protocol devices, or low data rate devices take longer time when transmitting same amount of data. Also, when the access point supports legacy clients, it will need to broadcast signaling beacon frames on low speed protocol (ex: 802.11b) and lower the whole network performance.
Troubleshooting
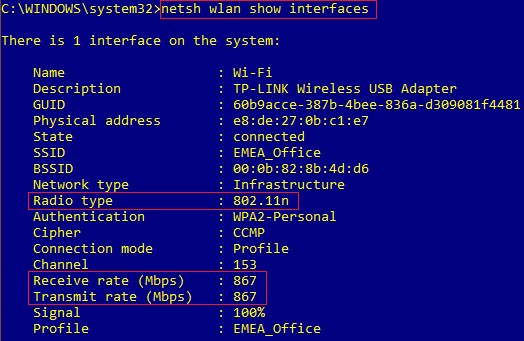
To avoid this problem is more like to optimize your network environment other than Troubleshooting the problem.
You can probably use a packet sniffer to check negotiated data rates or you can use the following commands:
Windows command: netsh wlan show interfaces
Linux command: iwconfig
Solution
- Disable legacy protocols like 802.11b (disabled by default on GWN).
- Disable low data rates and select higher standards.
GWN Settings
User can select which norm to enable on the GWN as follow:
- Make sure the option Radio -> Allow Legacy devices (802.11b) is disabled (default setting).
- Users can manage Upstream and Downstream bandwidth:
- Per SSID under Access Control -> Bandwidth rules -> Add -> Upload Limit/Download Limit
- Per client under Client -> Edit -> Bandwidth Rules.
WIFI CONNECTION PROBLEM
Phenomenon:
I cannot connect to WiFi, there is an exclamation mark on my WiFi icon , or I am connected to my WiFi, but cannot get onto the internet or a local network resource such as a local mail server.
Cannot Connect to WiFi
This issue is usually a less common in connection problem but it can be due to one of the following problems.
- Interference / signal strength. -> check sections [Interference Issue] and [Signal Strength issue]
- Misconfiguration.
- Security settings / wrong credential. -> double check the authentication credentials.
- Firmware problem. -> make sure to always upgrade to latest firmware version.
Cannot Connect to Network Resources
This issue usually happens with your wired network simultaneously, and is not related with your WiFi network. We recommend that you troubleshoot your wired network first!
- Confirm that there are no client IP issues (DHCP problem, IP pool depletion) (most common)
- DNS issues (DNS server not reachable or not responding).
- Routing problem (Gateway is down).
ANALYSIS TOOLS
Syslog
If the AP is a Master, the syslog Web page provides configuration settings for syslog.
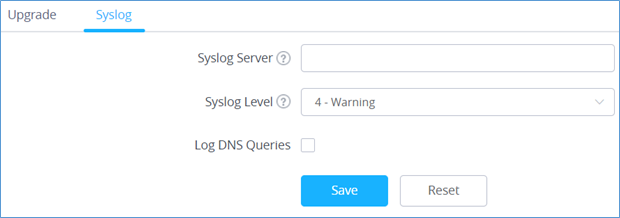
|
Field |
Description |
|
Syslog Server |
Enter the IP address or URL of Syslog server. |
|
Syslog Level |
Select the level of Syslog, 8 levels are available: Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, Warning, Notice, Information and Debug |
|
Log DNS Queries |
Check to log DNS Queries. |
Table 3: Syslog Parameters
Debug
In a slave mode the GWN76XX web interface provides access to
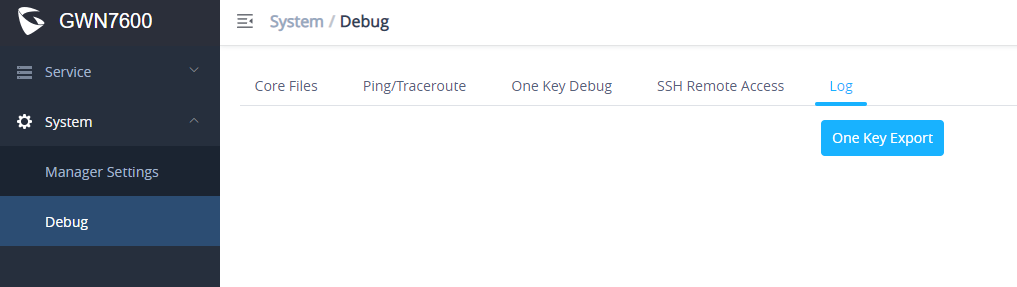
Core Files
when a crash event happens on the unit, it will automatically generate a core dump file that can used by engineering team for debugging purposes.
Ping/Traceroute
Allows the users to Ping and traceroute. Input the target’s IP address or URL and click on run.
One key Debug
Allows to capture Wireless, Portal or Mesh traffic and logs will be found in Core Files.
SSH Remote Access
Enables the SSH remote access on the slave AP.
Log
Allows the users to retrieve the logs generated for troubleshoot purpose.
Protocol Analyzers
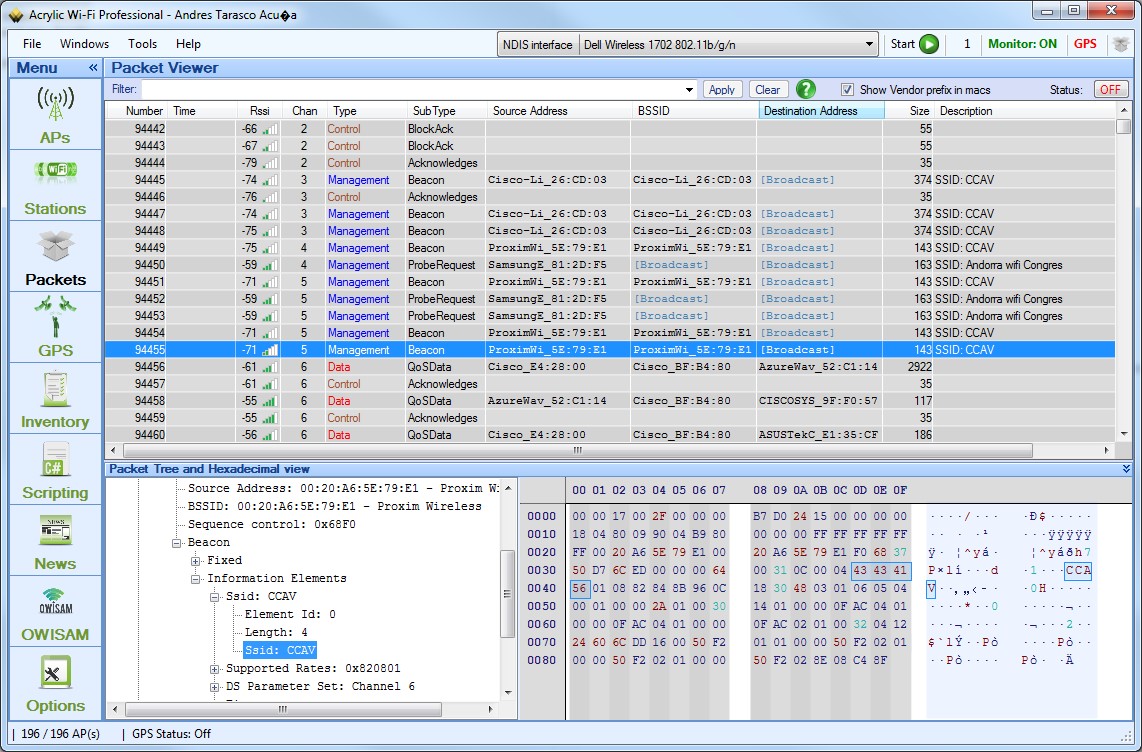
Acrylic WiFi Pro
This tool will help you to capture and analysis your network environment.
Make sure you enable the channel hooping for both 2.4G and 5G and capture long enough for your environment analysis. You can also set it to capture on designated channel to only capture continues packet on that channel.
Saved pcap file can be imported by acrylic pro. If you need help with Troubleshooting, make sure you saved the pcap file, so you can pass to others to review.
Below is a reference guide for Acrylic WiFi sniffer:
https://www.acrylicwifi.com/en/wlan-software/wifi-analyzer-acrylic-professional/wifi-network-scannerwindows/
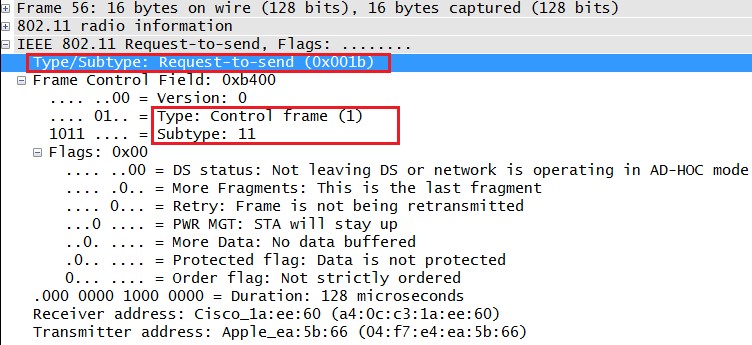
Wireshark
Wireshark is the well know packet sniffer which helps troubleshoot network issues in depth, by checking in details the traffic between the network components, below is a list of useful filters that can be used for WiFi:
| Frame type | Filter |
| Management frames | wlan.fc.type eq 0 |
| Control frames | wlan.fc.type eq 1 |
| Data frames | wlan.fc.type eq 2 |
| Frame subtype | Filter |
| Association request | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 0 |
| Association response | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 1 |
| Probe request | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 4 |
| Probe response | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 5 |
| Beacon | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 8 |
| Authentication | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 11 |
| De-authentication | wlan.fc.type_subtype eq 12 |
RF Analyzers
Suggested Device: http://nutsaboutnets.com/models/ WiFi Combo for $270 USD
Reference
WLAN channels: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_WLAN_channels
Wireshark 802.11 filters: wireshark_802.11_filters_-_reference_sheet