Overview
Quality of Service (QoS) is a crucial aspect of network management that ensures the efficient allocation of network resources and prioritization of traffic flows. In this guide, we will explore the configuration of QoS settings in GWN78xx network switches. By implementing QoS, you can improve network performance, minimize latency, and optimize the delivery of critical applications. Let’s dive into the different sections of QoS configuration in a GWN78xx network switch.
Understanding QoS
QoS refers to techniques that prioritize and manage network traffic based on parameters like bandwidth and latency. It ensures critical applications receive necessary resources and function well under congestion.
Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms, such as Class of Service (CoS) and Differentiated Services (DiffServ), are implemented to prioritize and manage network traffic, ensuring that critical applications receive better treatment than less time-sensitive traffic.
The below table shows some key differences when it comes to configuring a Quality of service model based on the Class of Service approach or based on the Differentiated Services approach:
Class of Service Model (CoS) | Differentiated Services Model (Diffserv) | |
OSI Layer | Operates at Layer 2 (Ethernet Frame) | Operates at Layer 3 (IP Packet) |
Tagged or Untagged VLAN | Applies to VLAN-tagged traffic only | Does not require a VLAN Tag |
Frame Tagging | CoS assigns priority levels to Ethernet frames. These priority levels indicate the relative importance or urgency of the frames. The values range from 0 to 7, 0 being the lowest priority and 7 being the highest | DiffServ operates at the network layer (Layer 3) and involves marking packets with Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) values in the IP header. The values range from 0 to 63, with 0 being the lowst value also reffered to as best effort , and 63 being the highest. |
Priority Levels | CoS uses priority levels assigned to Ethernet frames, indicating their relative importance or urgency within a VLAN. | DiffServ uses the DSCP field in the IP header to mark packets with different priority levels, typically defining a small number of traffic classes. |
Queue Management | CoS is associated with queue management in switches. Different priority levels are used to enqueue and dequeue frames in different queues, allowing for differentiated treatment. | DiffServ defines a set of Per-Hop Behaviors (PHBs) that routers use to treat packets differently based on their DSCP markings. |
Traffic Differentiation | CoS provides a fine granularity of service differentiation within a VLAN. It is effective in local network environments. | DiffServ provides a more scalable and flexible approach for traffic differentiation, suitable for larger networks and the Internet. |
Deployement scenarios | CoS is effective within a local network (e.g., a LAN) and is commonly used for QoS in LAN environments. | DiffServ is designed for end-to-end QoS across larger networks. It is commonly used in the Internet to provide QoS for various applications and services. |
CoS vs Diffserv
QoS Mechanisms: Classification, Marking, Queuing, and Policing
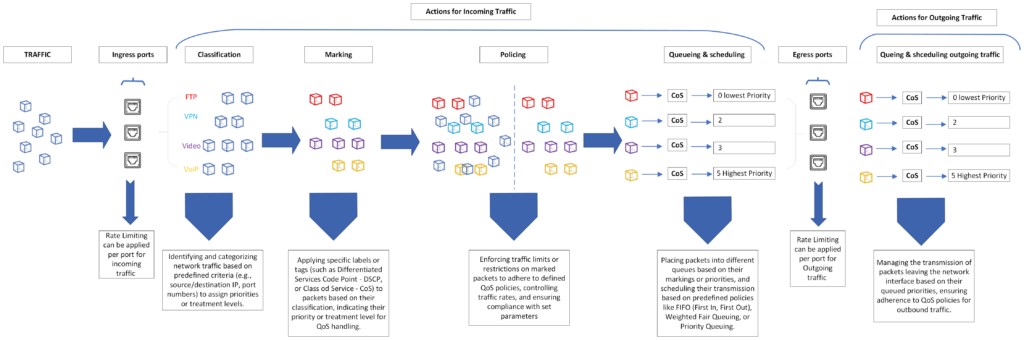
QoS mechanisms consist of several components that work together to manage network traffic effectively. the following diagram will represent a simple QoS model it shows how the Incoming (ingress) and outgoing (Egress) traffic is treated within the GWN78xx network switch:
- Classification: Identifying and categorizing network traffic based on predefined criteria (e.g., source/destination IP, port numbers) to assign priorities or treatment levels.
- Marking: Applying specific labels or tags (such as Differentiated Services Code Point – DSCP) to packets based on their classification, indicating their priority or treatment level for QoS handling.
- Policing: Enforcing traffic limits or restrictions on marked packets to adhere to defined QoS policies, controlling traffic rates, and ensuring compliance with set parameters.
- Queuing and Scheduling: Placing packets into different queues based on their markings or priorities, and scheduling their transmission based on a predefined queueing algorithm, like Weighted Fair Queuing, Weighted Round Robin, or a simple strict priority.
- Queuing and Scheduling Outgoing Traffic: Managing the transmission of packets leaving the network interface based on their queued priorities, ensuring adherence to QoS policies for outbound traffic.
Understanding these QoS mechanisms is crucial for effective configuration and management of QoS in a layer 2 and layer 3 network switch. It allows network administrators to control the flow of traffic, allocate resources appropriately, and prioritize critical applications, resulting in improved network performance and user experience.
Pre-Configuration Steps
Network Traffic Analysis
Before configuring QoS in a network switch, it is important to conduct a thorough analysis of network traffic. This involves examining the types of applications and services running on the network, identifying traffic patterns, and understanding their requirements. By analyzing traffic, you can determine which applications require prioritization and allocate appropriate resources.
Identifying Critical Applications and Traffic Flows
During the traffic analysis phase, it is crucial to identify critical applications and traffic flows that require special treatment. These can include real-time applications like VoIP or video conferencing, which are sensitive to delay or packet loss. By identifying these devices or applications, you can prioritize their traffic and allocate sufficient bandwidth and resources to ensure their smooth operation.
- Example:
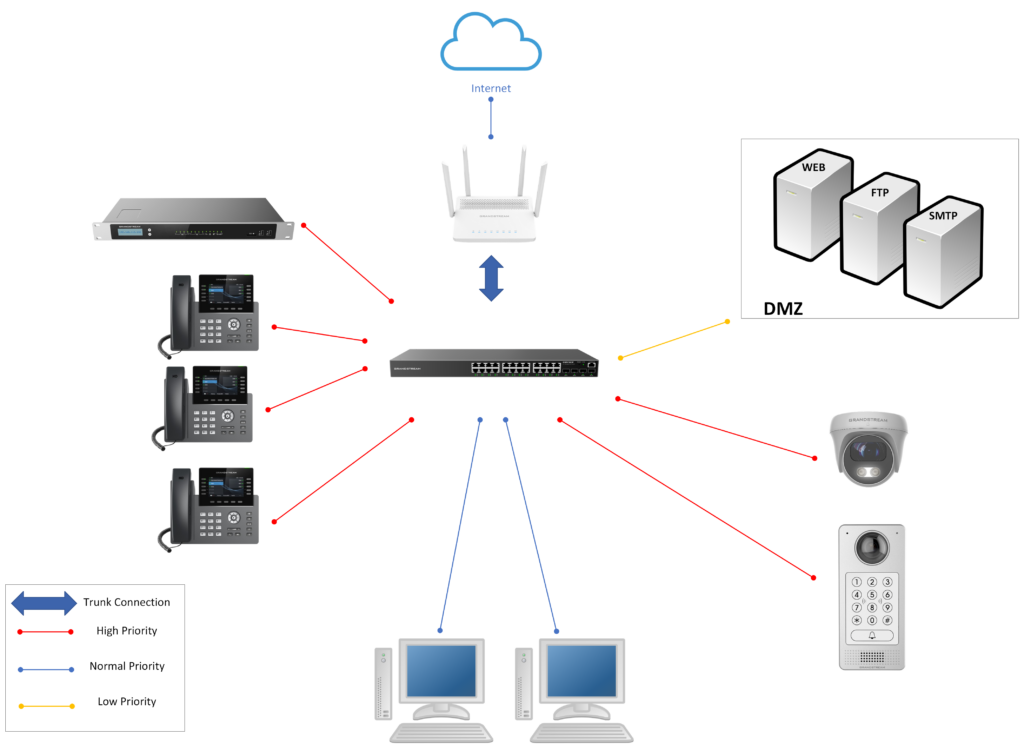
The following illustration is an example of how identifying critical applications for a network environment can help manage the bandwidth better and keep all the bandwidth well distributed, in our scenario we are deploying our GWN78xx network switch in a call center, so automatically, we should be able to configure higher priority levels for Voice Traffic, we will set the facility access devices to a higher priority as well:
Configuration Parameters
The GWN78xx Network switch offers a range of configuration options for its Quality of Service (QoS) feature. Each configuration serves a specific purpose, such as limiting throughput on a specific port, classifying inbound and outbound traffic, or prioritizing bandwidth for specific types of data.
Please refer to the below guides for each configuration: