Overview
Priority Mapping is a configuration feature in the Quality of Service (QoS) functionality of the GWN78xx network switches. It allows you to map incoming traffic to specific priority levels for effective QoS treatment.
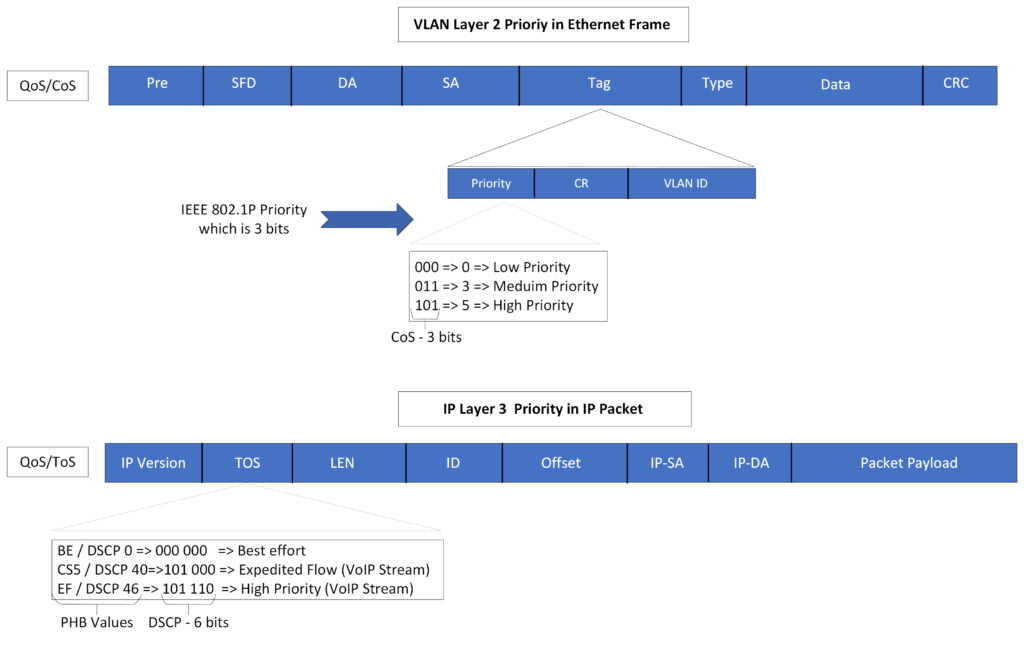
Priority mapping is used to map the QoS information found in the packet (whether it is an Ethernet frame or IP Packet) to the switch’s internal class of service.
- In the layer 2 frame, the priority information is stored in the priority section of the Ethernet frame tag, the parameter responsible for this value is called Class of service, and it is a 3-bit binary value.
- In a layer 3 packet, the priority information is stored in the Type of service section of the packet, the parameter responsible for the value is called Differentiated services code point (DSCP) and it is a 6 bits binary number, usually mapped with a Per behavior value (PHB).
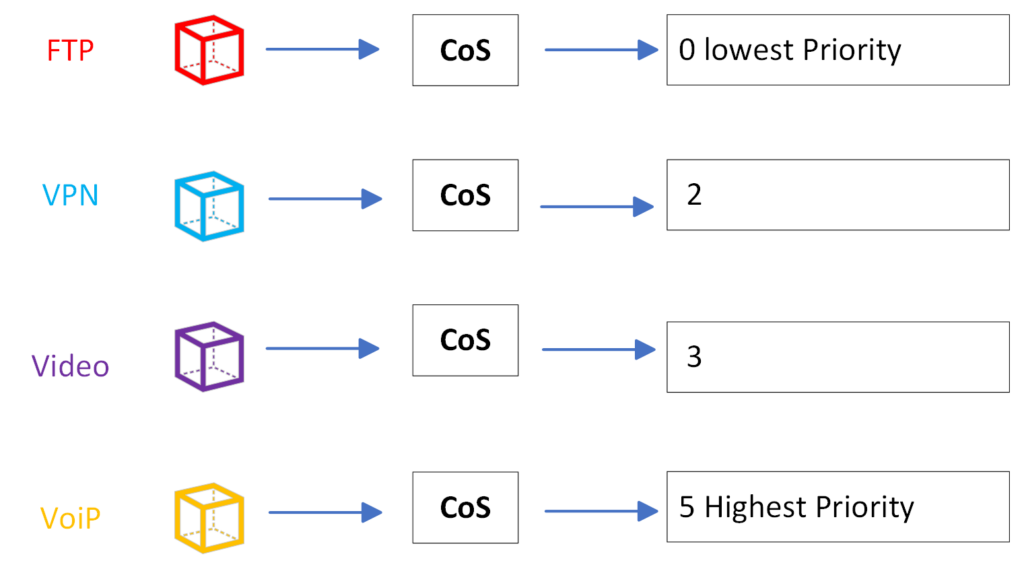
By configuring Priority Mapping, you can assign different priority levels to various types of traffic based on specific criteria. This ensures that critical data, that are meant to be delivered to critical devices or applications, receive higher priority, while less time-sensitive traffic is assigned lower priority.
Priority Mapping Types
802.1p Mapping
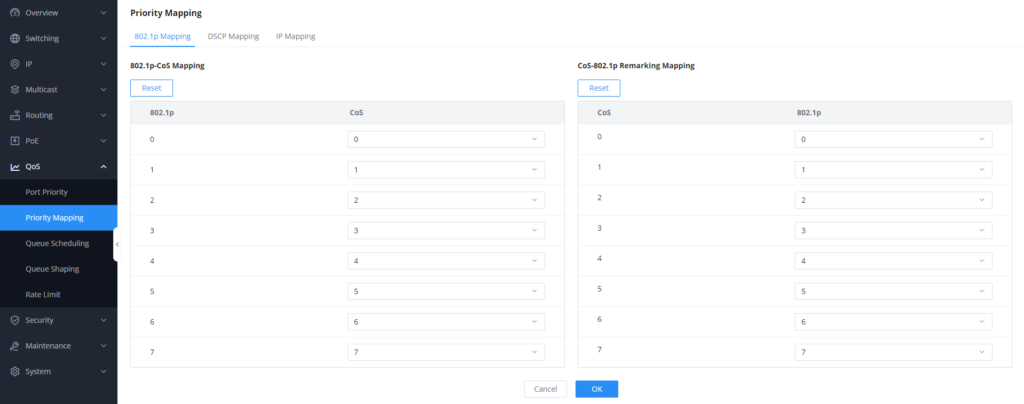
The 802.1p Mapping in Priority Mapping configures the association between the 802.1p priority tag and Class of Service (CoS) levels. It includes two types:
802.1p-CoS Mapping: maps the 802.1p tag to internal switch values of CoS levels.
CoS-802.1p Remarking Mapping: allows modifying the CoS level and assigning a new 802.1p tag. These mappings ensure consistent and flexible prioritization of traffic.
DSCP Mapping
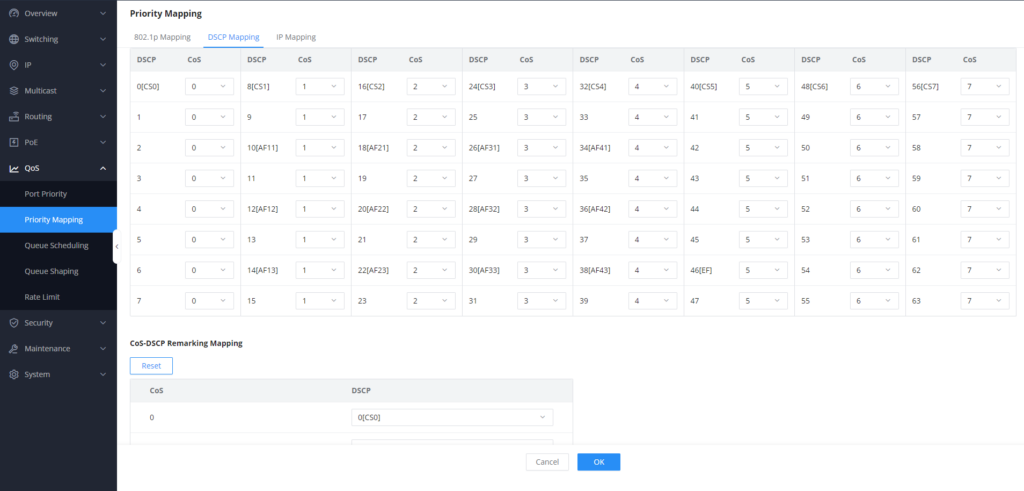
The DSCP Mapping in Priority Mapping allows you to assign priority levels to Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) values for effective Quality of Service (QoS) treatment.
DSCP-CoS Mapping: This associates DSCP values with Class of Service (CoS) priority levels.
CoS-DSCP Remarking Mapping: This modifies the CoS priority level and assigns a new DSCP value. These mappings ensure proper prioritization and flexibility in QoS handling for different types of traffic.
IP Mapping
The IP Mapping in Priority Mapping assigns Class of Service (CoS) priority levels to IP addresses for Quality of Service (QoS) treatment. It includes two types:
IP-CoS Mapping: Associates IP addresses or ranges with CoS priorities based on a 3-bit value in an IP packet called IP precedence.
CoS-IP Remarking Mapping: Modifies the CoS priority level and assigns a new IP precedence value. These mappings enable customized QoS treatment based on specific sources or destinations of traffic.
Mapping vs Remarking Mapping
Mapping in Quality of Service (QoS) involves assigning priority levels or QoS values to packets based on specific criteria like the criticality of the application or device connected. It associates packets incoming packets with predefined classes or priorities based on a Class of service model or a differentiated services model.
On the other hand, remarking in QoS refers to modifying or changing the existing priority or QoS markings of packets as they travel through the network and as they go on the outbound traffic. It can be used to align markings with internal policies or adjust priorities dynamically based on network conditions like congestion.
So in summary, Mapping assigns initial priorities, while remarking adjusts or changes existing priorities when going on outbound traffic.
Priority Mapping Configuration
To configure Priority Mapping, you can choose from three methods: 802.1p Mapping, DSCP Mapping, or IP Mapping. All of them follow the same logic; assign higher priority to DSCP values that will be mapped to specific packets.
Refer to the below table for Layer3 and Layer2 classifications regarding the used applications/services, this represents the specific Class of Service and DCSP values related to each specific traffic type:
Application/Service | L3 Classification | L2 Classification | |
Per-Hop-Behavior (PHB) | DSCP | CoS | |
Routing | CS6 | 48 | 6 |
Voice | EF | 46 | 5 |
Multimedia Conferencing | AF41 | 34 | 4 |
Multimedia Streaming | CS4 | 32 | 4 |
Mission-Critical Data | 25 | 3 | |
Call Signaling | [AF31 CS3] | [26 24] | 3 |
Transactional Data | AF21 | 18 | 2 |
Network Management | CS2 | 16 | 2 |
Bulk Data | AF11 | 10 | 1 |
Scavenger | CS1 | 8 | 1 |
Best Effort (Default) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
- Configuration Example
Let’s say you have a company with a Voice over IP (VoIP) system in place, where employees rely on voice calls for their day-to-day communication. Additionally, the company’s network is also used for regular data traffic, such as file transfers, web browsing, and email.
To ensure that voice traffic receives the necessary quality and priority, you can implement QoS mechanisms with different queues and DSCP values. in this example, we will be using the DSCP mapping, the same concept applies to 802.1p Mapping and the legacy IP Mapping.
Here’s how it could be configured:
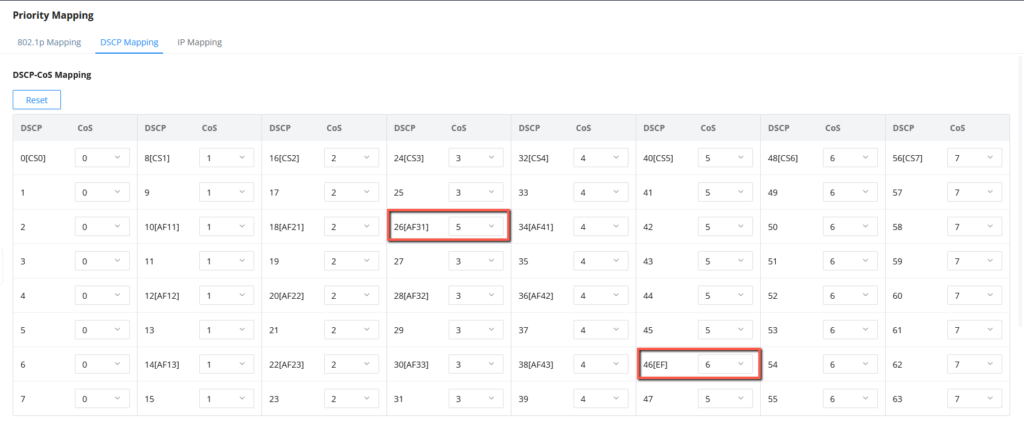
- Go to QoS => Priority Mapping => DSCP Mapping.
- Assign a specific priority for the DSCP value based on the table above, we will set DSCP 46 to a higher priority 6, and DSCP 26 to 5, this is to prioritize call signaling going through IP phones, and voice traffic.
- There will be no need to configure the CoS-DSCP Remarking mapping since we will not need the priority to change on outbound traffic.
By implementing this configuration, the GWN78xx switch will prioritize voice packets over other data traffic based on their DSCP values. Voice packets with DSCP 46 will be placed in the high-priority queue, while data packets will be placed in their respective queues based on their assigned DSCP values.
Supported Devices
Device Name | Supported | Firmware Required |
GWN7801 | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7801P | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7802 | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7802P | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7803 | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7803P | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7811 | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7811P | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7812P | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7813 | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7813P | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7806 | Yes | 1.0.1.14 or higher |
GWN7806P | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
GWN7830 | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
GWN7831 | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
GWN7832 | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
List of Supported Devices