Overview
Queue Scheduling is a configuration parameter in the Quality of Service (QoS) feature of the GWN78xx network switches. It determines the order in which packets are transmitted from various queues.
By assigning priorities and scheduling algorithms to different queues, it helps optimize network performance and ensure that higher-priority traffic is given precedence. This configuration parameter ensures efficient resource allocation, minimizes latency, and enhances overall QoS in the network switch.
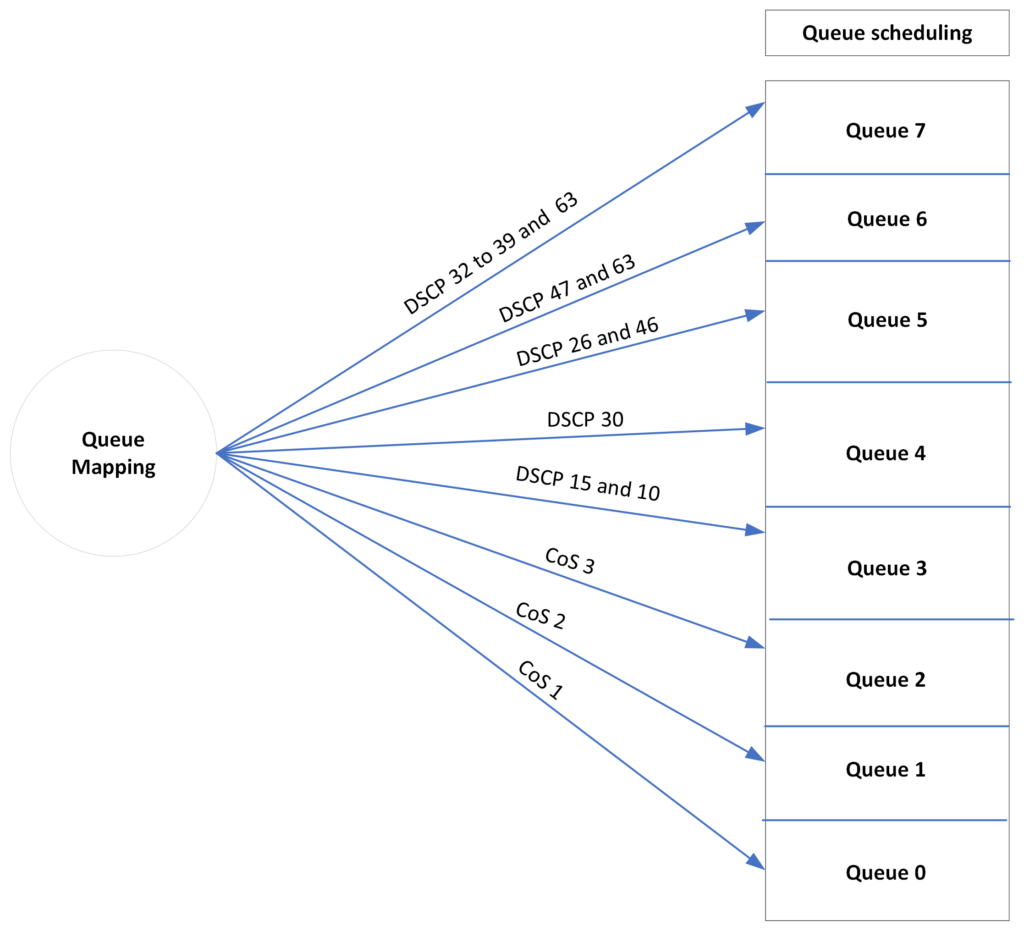
GWN78xx switches support 8 queues (0-7) for each port, Queue 7 has the highest priority.
Queue Scheduling Parameters
- Queuing Algorithm: The Queuing Algorithm determines how packets are prioritized and scheduled in the GWN78xx network switch. based on different algorithms :
- Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ): WFQ assigns weights to different queues based on priority or fairness criteria. Each queue gets a fair share of the port’s bandwidth based on its weight. It ensures that low-traffic flows are not starved and high-traffic flows do not monopolize the bandwidth.
- Weighted Round Robin (WRR): WRR assigns weights to different queues. Each queue gets a share of the link’s bandwidth based on its weight. Queues are served in a round-robin fashion, and the weight determines the amount of data each queue can transmit in each round.
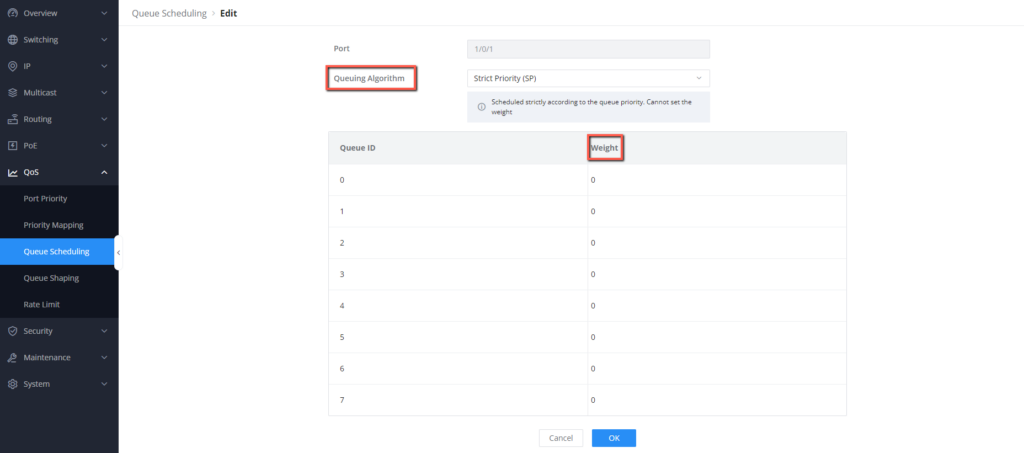
- Strict Priority(SP): SP assigns priorities to different queues, and packets from high-priority queues are served before lower-priority queues. This ensures that high-priority traffic is processed with minimal delay, but it can lead to lower-priority queues being starved if there is constant high-priority traffic.
- SP-WFQ: SP-WFQ combines strict priority and WFQ. It divides traffic into multiple classes, each with its own priority and WFQ characteristics. High-priority queues are served before lower-priority queues, and within each priority class, WFQ is applied for fairness.
- SP-WRR: SP-WRR combines strict priority and WRR. It assigns priorities to different queues, and high-priority queues are served before lower-priority queues. Each queue, regardless of priority, follows a weighted round-robin scheduling algorithm to determine the order in which packets are transmitted.it is better to use this method when assigning higher weights to lower queues and keeping higher queues with strict priority.
- Weight: The “Weight” determines the priority and percentage of available bandwidth assigned to a specific queue. Higher weight values indicate higher priority and a larger share of bandwidth, while lower weight values indicate lower priority and a smaller share.
Queue Scheduling Configuration
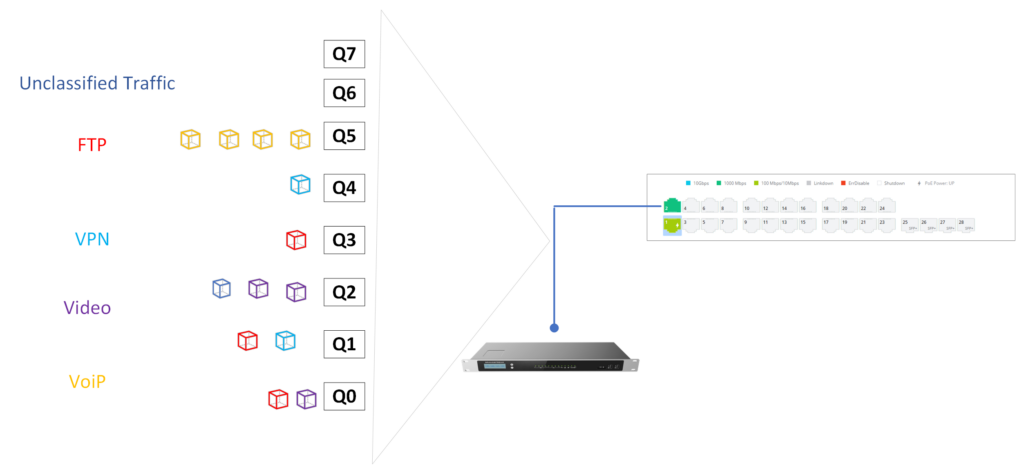
Let’s consider we have a a IP PBX system such as UCM63xx connected to the GWN78xx network switch on port 1/0/2, we want to make sure that all traffic on this port is prioritized on queue 5 which is the queue defined for Voice Traffic in internal class of service value of the switch for port 1/0/2 ,
To configure Queue Scheduling on the GWN78xx switch for that specified ports, follow these steps:
- Access the switch’s management interface.
- Navigate to the Quality of Service (QoS) => Queue Scheduling.
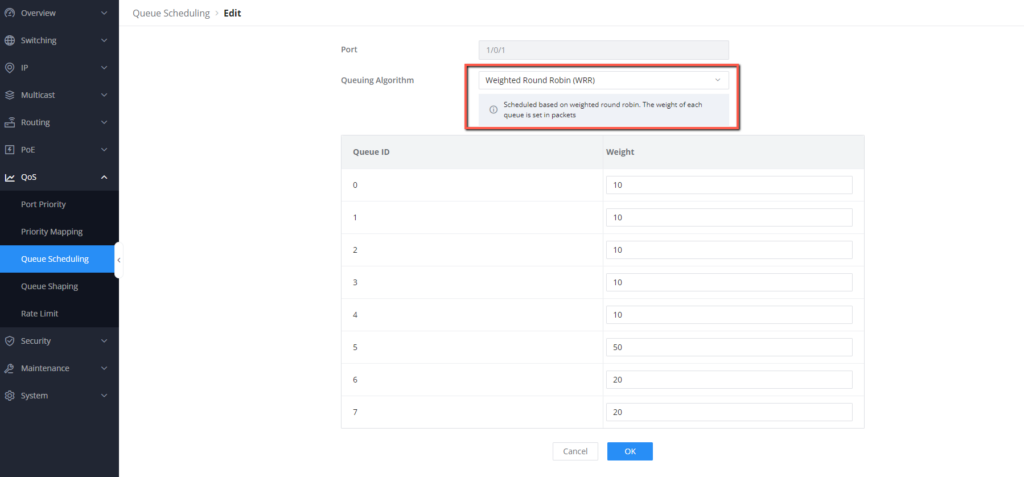
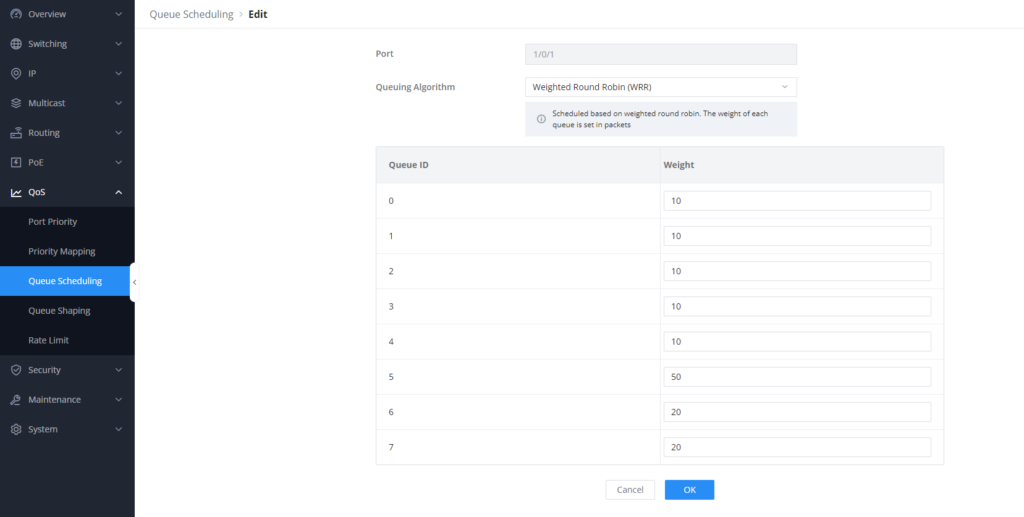
- Select the port 1/0/2, set the Queue Scheduling algorithm to Weighted Round Robin (WRR). this is our choice of algorithm because we want to allocate higher share of bandwidth only for the queue that will be primarly be used for voice traffic, the other quesus will get their share o bandwith in a round robin form.
- Define the weights for each priority queue, we will set queues 7 and 6 to 20, queue 5 to 50, and the rest of the queues to 10.
After saving this configuration, the switch will give the higher percentage of bandwidth coming through port 1/0/2 to queue 5 while making sure that the other queues are not starved and are allocated in round-robin manner.
Supported Devices
Device Name | Supported | Firmware Required |
GWN7801 | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7801P | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7802 | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7802P | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7803 | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7803P | Yes | 1.0.1.20 or higher |
GWN7811 | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7811P | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7812P | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7813 | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7813P | Yes | 1.0.1.8 or higher |
GWN7806 | Yes | 1.0.1.14 or higher |
GWN7806P | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
GWN7830 | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
GWN7831 | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
GWN7832 | Yes | 1.0.3.3 or higher |
List of supported Devices