OVERVIEW
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is used to create an encrypted connection enabling users to exchange data across shared or public networks acting as clients connected to a private network. The benefit of using a VPN is to ensure the appropriate level of security for connected systems when the underlying network infrastructure alone cannot provide it. The most common types of VPNs are remote-access VPNs and site-to-site VPNs.
VPNs can be defined between specific endpoints such as IP-Phones and computers, and servers in separate data centers when security requirements for their exchanges exceed what the enterprise network can deliver. Increasingly, enterprises use VPNs to secure data and voice exchange.
The VPN security model provides:
- Client authentication to forbid any unauthorized user from accessing the VPN network.
- Encryption and confidentiality will prevent man-in-middle attacks and eavesdropping on the network traffic.
- Data integrity to maintain the consistency, and trustworthiness of the messages exchanged.
Users must be authenticated before establishing secure VPN tunnels. Client/server tunnels use passwords or digital certificates. It is possible to permanently store the key to allow the tunnel to be established automatically.
GWN70XX VPN TYPES
Grandstream GWN70xx routers support the VPN feature giving the ability to create encrypted and tunneled connections across shared or public networks allowing users to exchange data securely. GWN70xx routers support 4 VPN technologies:
- OpenVPN®: Client/Server
- IPSec: Client/Server
- L2TP: Client
- PPTP: Client
OpenVPN®
OpenVPN® is Virtual Private Network (VPN) system, it offers also an open-source Community Edition (CE). It supports both implementations site-to-site or point-to-point connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities. It implements both client and server applications.
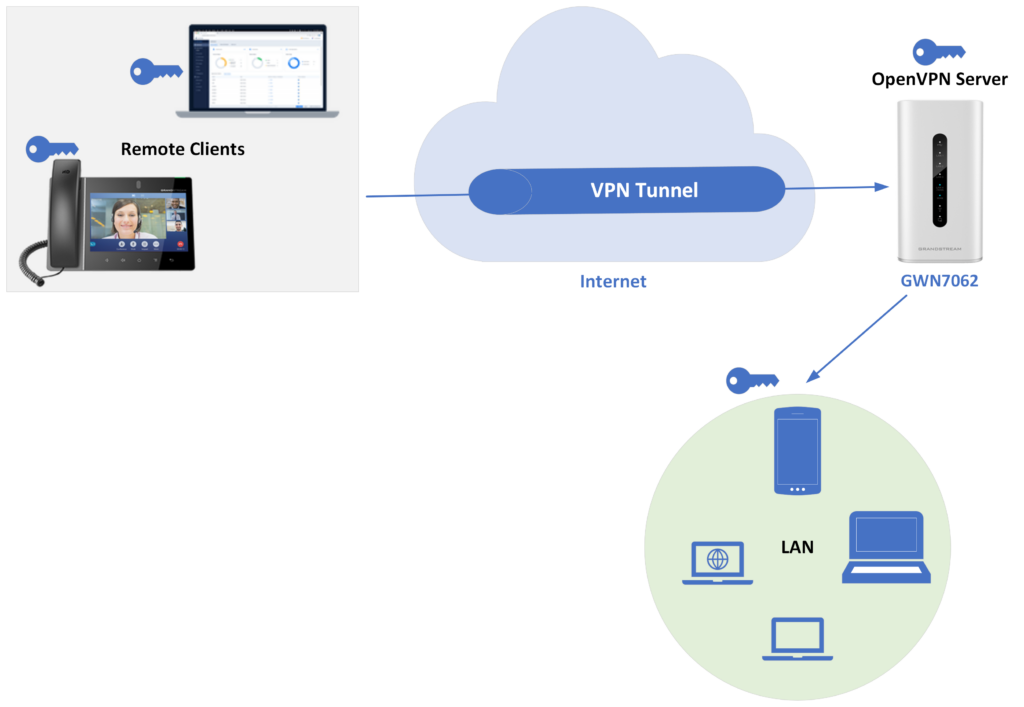
The following figure illustrates GWN70xx acting as an OpenVPN® server with remote clients connected via a VPN tunnel.
L2TP Client
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs. It does not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself. Rather, it relies on an encryption protocol that it passes within the tunnel to provide privacy.
PPTP
PPTP is A data-link layer protocol for wide area networks (WANs) based on the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and developed by Microsoft that enables network traffic to be encapsulated and routed over an unsecured public network such as the Internet. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) allows the creation of virtual private networks (VPNs), which tunnel TCP/IP traffic through the Internet.
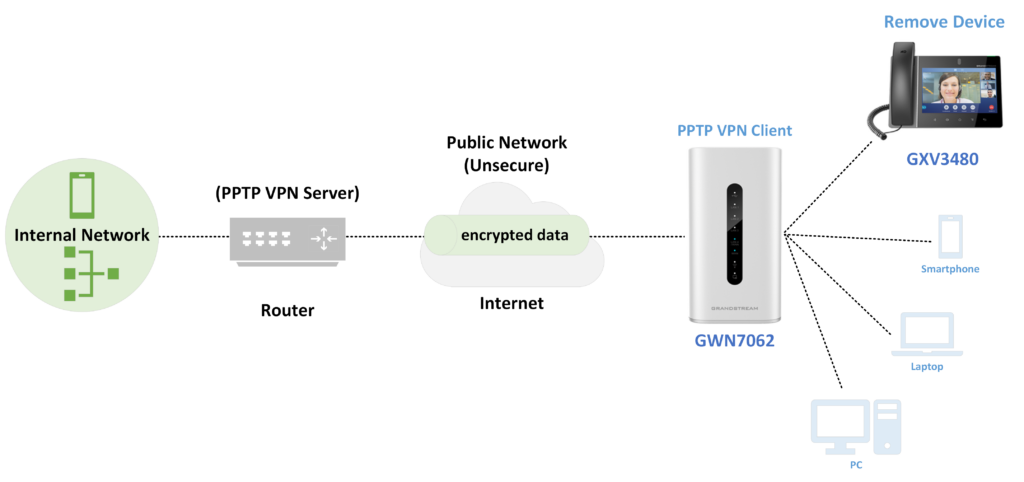
The following figure illustrates Grandstream GXV3480 (Remote Device) acting as a PPTP Client remotely connected to a PPTP VPN Server (Router).
© 2002-2023 OpenVPN Inc. OpenVPN is a registered trademark of OpenVPN Inc.